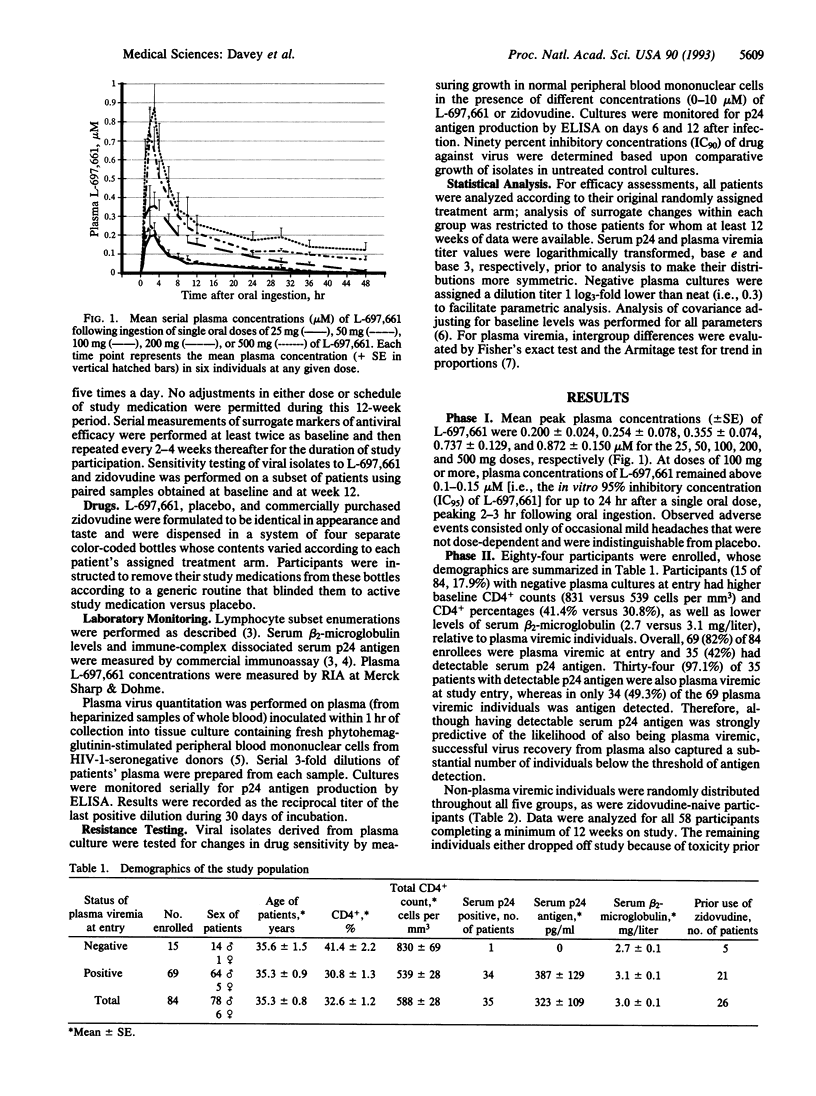
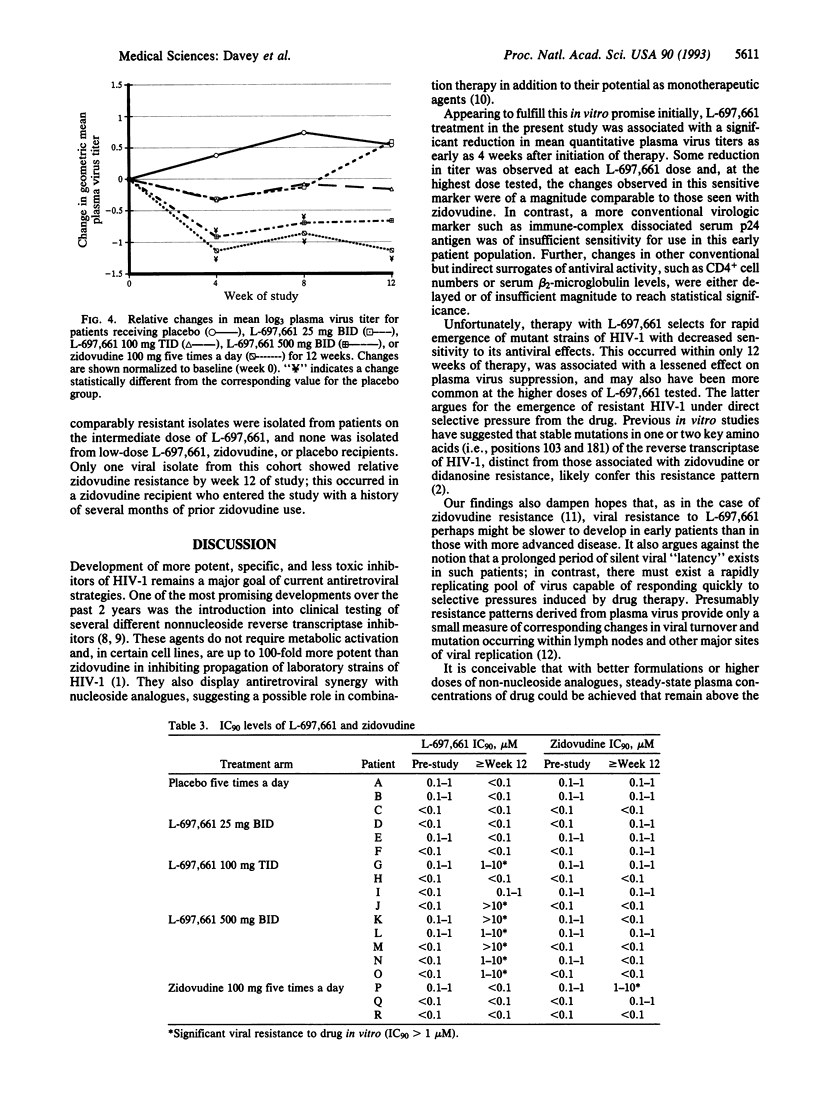
Abstract
L-697,661 is a non-nucleoside analogue with potent, selective inhibitory activity against the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). The present study evaluated the potential role of this compound in the treatment of HIV-1-infected patients in a double-blinded, placebo- and zidovudine-controlled trial using plasma viremia as a marker of antiviral activity and real-time phenotypic evaluation of viral isolates for the emergence of resistance. Participants received 12 weeks of either placebo, 25 mg twice a day, 100 mg three times a day, or 500 mg twice a day of L-697,661, or zidovudine, 100 mg five times a day. Mean logarithmic reciprocal titers of plasma virus in patients taking either L-697,661 or zidovudine decreased by week 4 of therapy; for L-697,661 recipients these changes were dose-dependent and, at the highest dose tested, were comparable in magnitude to those seen with zidovudine. Viral suppression induced by L-697,661 persisted through 8 weeks of treatment but decreased by week 12. This rebound paralleled emergence of viral isolates showing resistance to L-697,661. We conclude that although L-697,661 has potent antiretroviral activity in vivo, its utility may be compromised by rapid emergence of L-697,661-resistant virus. Plasma viremia is a highly sensitive technique affording considerable utility in the early testing of such agents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davey R. T., Jr, Lane H. C. Laboratory methods in the diagnosis and prognostic staging of infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Sep-Oct;12(5):912–930. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.5.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewar R. L., Sarmiento M. D., Lawton E. S., Clark H. M., Kennedy P. E., Shah A., Baseler M., Metcalf J. A., Lane H. C., Salzman N. P. Isolation of HIV-1 from plasma of infected individuals: an analysis of experimental conditions affecting successful virus propagation. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(8):822–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. E., Nunberg J. H., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Schleif W. A., Freund K. F., Gaul S. L., Saari W. S., Wai J. S., Hoffman J. M. Pyridinone derivatives: specific human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors with antiviral activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6863–6867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestens L., Hoofd G., Gigase P. L., Deleys R., van der Groen G. HIV antigen detection in circulating immune complexes. J Virol Methods. 1991 Jan;31(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90145-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J., Hargrave K. D., Labadia M., Grozinger K., Skoog M., Wu J. C., Shih C. K., Eckner K., Hattox S., Adams J. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.1701568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Boots E. J., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Hoffman J. M., Emini E. A., Goldman M. E. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4887–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4887-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Fauci A. S. New concepts in the immunopathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 4;328(5):327–335. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302043280508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Andries K., Desmyter J., Schols D., Kukla M. J., Breslin H. J., Raeymaeckers A., Van Gelder J., Woestenborghs R., Heykants J. Potent and selective inhibition of HIV-1 replication in vitro by a novel series of TIBO derivatives. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):470–474. doi: 10.1038/343470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Grimes J. M., Lagakos S. W. Effect of stage of disease and drug dose on zidovudine susceptibilities of isolates of human immunodeficiency virus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(8):743–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Rosenthal A. S., Skoog M., Eckner R. J., Chou T. C., Sabo J. P., Merluzzi V. J. BI-RG-587 is active against zidovudine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and synergistic with zidovudine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):305–308. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


