Abstract
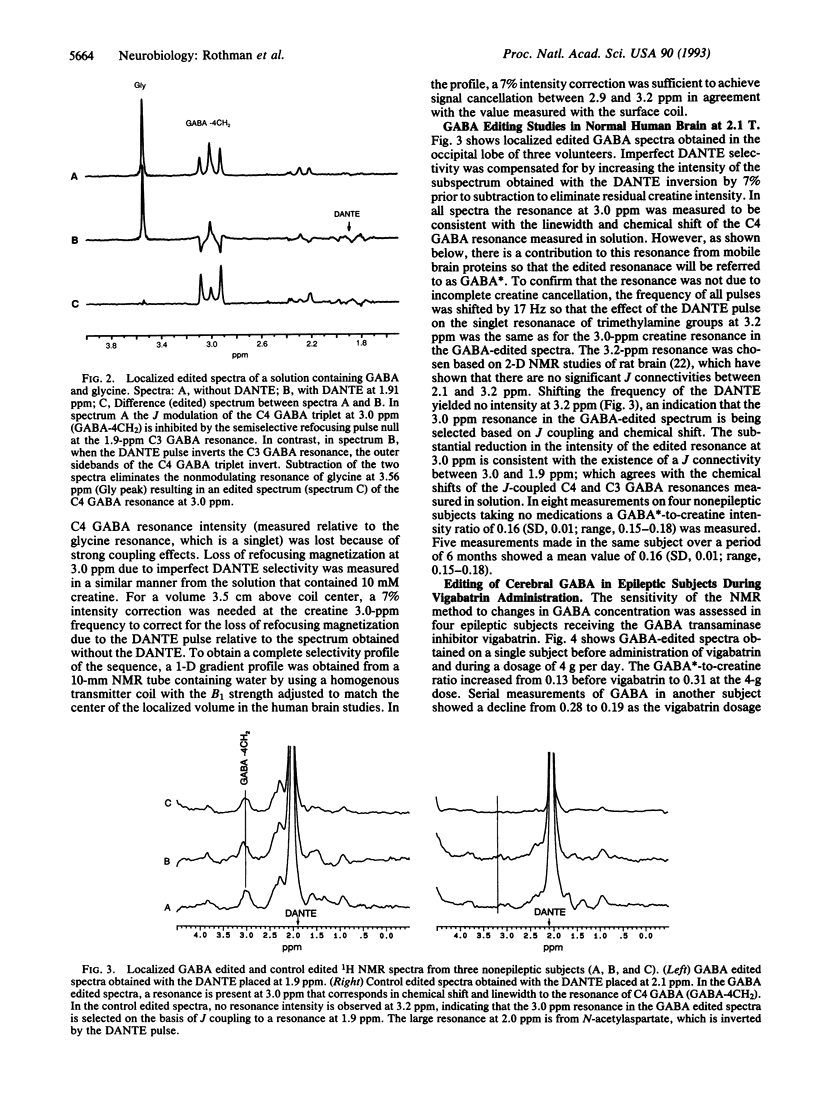
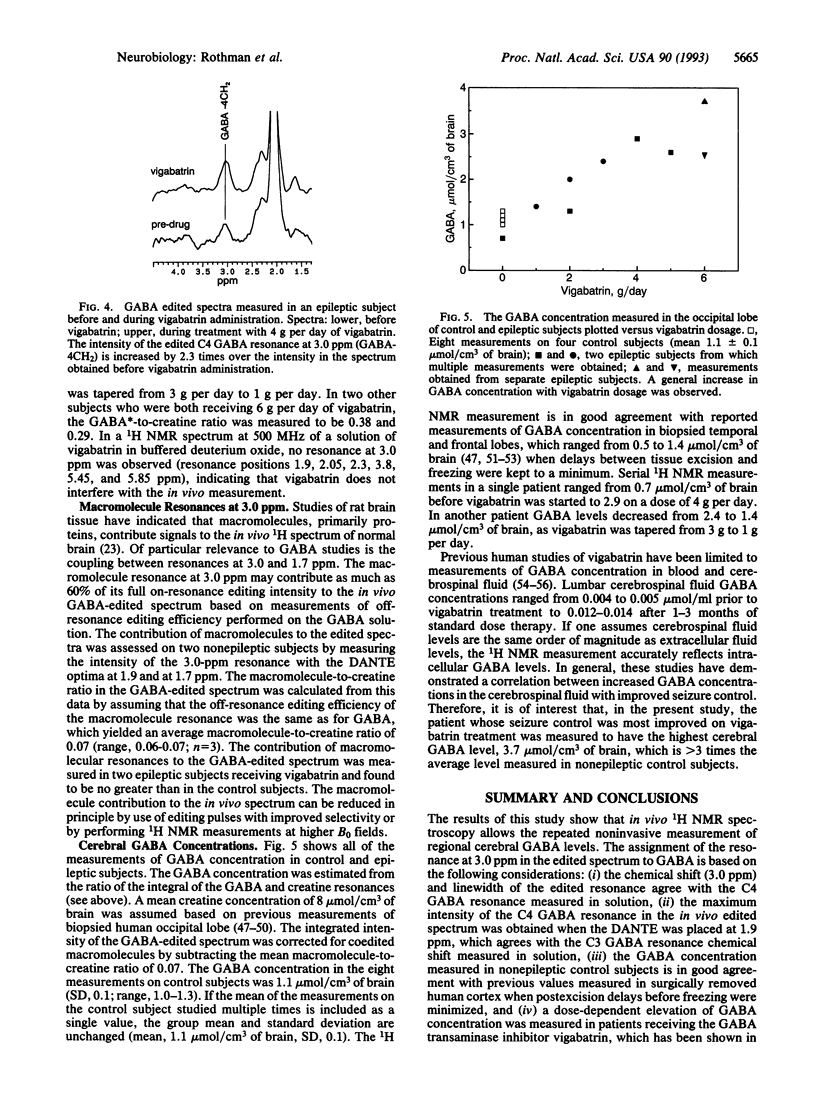
Localized 1H NMR spectroscopy in conjunction with J editing was used to measure the concentration of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the occipital lobe of four control human volunteers and four epileptic volunteers who were receiving the drug vigabatrin. The GABA concentration measured in four nonepileptic subjects was 1.1 +/- 0.1 mumol/cm3 of brain, which is in good agreement with previous values measured in surgically removed human cortex. A dose-dependent elevation of GABA concentration was measured in patients receiving the GABA transaminase inhibitor vigabatrin, with the maximum measured level of 3.7 mumol/cm3 of brain measured at the highest dose (6 g per day) studied. 1H NMR measurements of GABA in those patients receiving GABA-elevating agents such as vigabatrin will be of importance in establishing the relationship between seizure suppression and the concentration of brain GABA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behar K. L., Ogino T. Assignment of resonance in the 1H spectrum of rat brain by two-dimensional shift correlated and J-resolved NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Feb;17(2):285–303. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar K. L., den Hollander J. A., Stromski M. E., Ogino T., Shulman R. G., Petroff O. A., Prichard J. W. High-resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of cerebral hypoxia in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4945–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Menachem E. Pharmacokinetic effects of vigabatrin on cerebrospinal fluid amino acids in humans. Epilepsia. 1989;30 (Suppl 3):S12–S14. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1989.tb05826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton J. B., Rimmer E., Williams J., Richens A. The effect of vigabatrin on brain and platelet GABA-transaminase activities. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):35S–42S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Edelstein W. A., Foster T. H., Adams W. A. In vivo solvent-suppressed localized hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a window to metabolism? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne T. R., Mattson R. H., Penry J. K., Smith D. B., Treiman D. M., Wilder B. J., Ben-Menachem E., McBride R. G., Sherry K. M. Multicenter long-term safety and efficacy study of vigabatrin for refractory complex partial seizures: an update. Neurology. 1991 Mar;41(3):363–364. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne T. R., Mattson R. H., Penry J. K., Smith D. B., Treiman D. M., Wilder B. J., Ben-Menachem E., Miketta R. M., Sherry K. M., Szabo G. K. A multicentre study of vigabatrin for drug-resistant epilepsy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):95S–100S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne T. R., Mattson R. H., Penry J. K., Smith D. B., Treiman D. M., Wilder B. J., Ben-Menachem E., Napoliello M. J., Sherry K. M., Szabo G. K. Vigabatrin for refractory complex partial seizures: multicenter single-blind study with long-term follow-up. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):184–189. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Ackerman J. J. Surface coil single-pulse localization in vivo via inhomogeneous surface spoiling magnetic gradient. NMR Biomed. 1989 Apr;1(4):205–207. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940010409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey H. H., Popp C., Löscher W. Influence of inhibitors of the high affinity GABA uptake on seizure thresholds in mice. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Jul;18(7):581–590. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk-Holmberg M., Kerth P., Meyer P. Effect of food on the absorption of vigabatrin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):23S–25S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. S., Thomas D. G., Van Bruggen N., Gadian D. G., Peden C. J., Bell J. D., Cox I. J., Menon D. K., Iles R. A., Bryant D. J. Proton MR spectroscopy of intracranial tumours: in vivo and in vitro studies. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):497–504. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199007000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram L., Larsson O. M., Johnsen A., Schousboe A. Experimental studies of the influence of vigabatrin on the GABA system. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):13S–17S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter R., Rothman D. L., Novotny E. J., Shulman G. I., Prichard J. W., Shulman R. G. Detection and assignment of the glucose signal in 1H NMR difference spectra of the human brain. Magn Reson Med. 1992 Sep;27(1):183–188. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910270118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanstock C. C., Rothman D. L., Prichard J. W., Jue T., Shulman R. G. Spatially localized 1H NMR spectra of metabolites in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1821–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetherington H. P., Avison M. J., Shulman R. G. 1H homonuclear editing of rat brain using semiselective pulses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3115–3118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. W., Collins J. F., Anlezark G. M., Meldrum B. S. Convulsant and anticonvulsant actions in DBA/2 mice of compounds blocking the reuptake of GABA. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct 26;59(1-2):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippert B., Metcalf B. W., Jung M. J., Casara P. 4-amino-hex-5-enoic acid, a selective catalytic inhibitor of 4-aminobutyric-acid aminotransferase in mammalian brain. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 15;74(3):441–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H., Berger S. J., Chi M. M., Carter J. G., Blackshaw A., Outlaw W. Diversity of metabolic patterns in human brain tumors--I. High energy phosphate compounds and basic composition. J Neurochem. 1977 Dec;29(6):959–977. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb06500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. A. GABA as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in human cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Nov;62(5):1018–1027. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.5.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. S. GABAergic mechanisms in the pathogenesis and treatment of epilepsy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):3S–11S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B., Horton R. Blockade of epileptic responses in the photosensitive baboon, Papio papio, by two irreversible inhibitors of GABA-transaminase, gamma-acetylenic GABA (4-amino-hex-5-ynoic acid) and gamma-vinyl GABA (4-amino-hex-5-enoic acid). Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1978 Sep 15;59(1):47–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00428029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford J. P., Dam M. Meta-analysis of European placebo controlled studies of vigabatrin in drug resistant epilepsy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):101S–107S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfreyman M. G., Schechter P. J., Buckett W. R., Tell G. P., Koch-Weser J. The pharmacology of GABA-transaminase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 15;30(8):817–824. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(81)80001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry T. L., Hansen S., Gandham S. S. Postmortem changes of amino compounds in human and rat brain. J Neurochem. 1981 Feb;36(2):406–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroff O. A., Spencer D. D., Alger J. R., Prichard J. W. High-field proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human cerebrum obtained during surgery for epilepsy. Neurology. 1989 Sep;39(9):1197–1202. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.9.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard J., Rothman D., Novotny E., Petroff O., Kuwabara T., Avison M., Howseman A., Hanstock C., Shulman R. Lactate rise detected by 1H NMR in human visual cortex during physiologic stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5829–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remy C., Beaumont D. Efficacy and safety of vigabatrin in the long-term treatment of refractory epilepsy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):125S–129S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P. J., Ylinen A., Halonen T., Sivenius J., Pitkanen A. Cerebrospinal fluid GABA and seizure control with vigabatrin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27 (Suppl 1):87S–94S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman D. L., Behar K. L., Hetherington H. P., Shulman R. G. Homonuclear 1H double-resonance difference spectroscopy of the rat brain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6330–6334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman D. L., Hanstock C. C., Petroff O. A., Novotny E. J., Prichard J. W., Shulman R. G. Localized 1H NMR spectra of glutamate in the human brain. Magn Reson Med. 1992 May;25(1):94–106. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910250110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman D. L., Novotny E. J., Shulman G. I., Howseman A. M., Petroff O. A., Mason G., Nixon T., Hanstock C. C., Prichard J. W., Shulman R. G. 1H-[13C] NMR measurements of [4-13C]glutamate turnover in human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9603–9606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter P. J., Hanke N. F., Grove J., Huebert N., Sjoerdsma A. Biochemical and clinical effects of gamma-vinyl GABA in patients with epilepsy. Neurology. 1984 Feb;34(2):182–186. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.2.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segebarth C. M., Balériaux D. F., Luyten P. R., den Hollander J. A. Detection of metabolic heterogeneity of human intracranial tumors in vivo by 1H NMR spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Jan;13(1):62–76. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910130108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin C., Rigsbee L. C., McNamara J. O. Anti-seizure and anti-epileptogenic effect of gamma-vinyl gamma-aminobutyric acid in amygdaloid kindling. Brain Res. 1986 Nov 29;398(2):370–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. S., Joseph R. I., Chen C. N., Sank V. J., Hoult D. I. Selective population inversion in NMR. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):681–683. doi: 10.1038/310681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivenius J., Ylinen A., Murros K., Mumford J. P., Riekkinen P. J. Vigabatrin in drug-resistant partial epilepsy: a 5-year follow-up study. Neurology. 1991 Apr;41(4):562–565. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. S. Surgical options for uncontrolled epilepsy. Neurol Clin. 1986 Aug;4(3):669–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gelder N. M., Sherwin A. L., Rasmussen T. Amino acid content of epileptogenic human brain: focal versus surrounding regions. Brain Res. 1972 May 26;40(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Johnson D. D., Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Schousboe A. Anticonvulsant activity of the glial-selective GABA uptake inhibitor, THPO. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Jan;22(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



