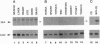Abstract
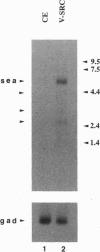
c-sea is the cellular homologue of the avian erythroblastosis virus S13-encoded oncogene v-sea. We have isolated and determined the nucleotide sequence of overlapping chicken cDNAs that encode the putative c-sea protooncogene product. The predicted reading frame encoded a 1404-aa polypeptide that had the structure of a receptor-like protein-tyrosine kinase and exhibited the highest degree of sequence similarity with the Met/hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Analysis of steady-state RNA expression revealed that c-sea mRNA levels were elevated approximately 5-fold in chicken embryo cells transformed by activated variants of the src nonreceptor protein-tyrosine kinase gene but not in cells transformed by the nuclear oncogenes v-myc or v-rel. A survey of c-sea expression in a variety of chicken tissues indicated that the highest levels of mRNA were located in peripheral white blood cell populations and in the intestine.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedict S. H., Maki Y., Vogt P. K. Avian retrovirus S13: properties of the genome and of the transformation-specific protein. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):154–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Hayman M. J., Graf T., Benedict S. H., Wallbank A. M., Vogt P. K. S13, a rapidly oncogenic replication-defective avian retrovirus. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):141–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. L., Parsons J. T. Amino acid alterations within a highly conserved region of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene product pp60src inactivate tyrosine protein kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):862–866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. M., King H. W., Deakin E. A., Tempest P. R., Hilkens J., Kroezen V., Edwards D. R., Wills A. J., Brookes P., Cooper C. S. Characterization of the mouse met proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., Stuart L. A., Han S., Jamison C. S. Characterization of the mouse cDNA and gene coding for a hepatocyte growth factor-like protein: expression during development. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9781–9791. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Renzo M. F., Narsimhan R. P., Olivero M., Bretti S., Giordano S., Medico E., Gaglia P., Zara P., Comoglio P. M. Expression of the Met/HGF receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):1997–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farina S. F., Huff J. L., Parsons J. T. Mutations within the 5' half of the avian retrovirus MC29 v-myc gene alter or abolish transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts and macrophages. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2698–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2698-2708.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferracini R., Longati P., Naldini L., Vigna E., Comoglio P. M. Identification of the major autophosphorylation site of the Met/hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19558–19564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Di Renzo M. F., Narsimhan R. P., Cooper C. S., Rosa C., Comoglio P. M. Biosynthesis of the protein encoded by the c-met proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1383–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S., Stuart L. A., Degen S. J. Characterization of the DNF15S2 locus on human chromosome 3: identification of a gene coding for four kringle domains with homology to hepatocyte growth factor. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9768–9780. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Kitchener G., Vogt P. K., Beug H. The putative transforming protein of S13 avian erythroblastosis virus is a transmembrane glycoprotein with an associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8237–8241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J. The sea oncogene of the avian erythroblastosis virus S13. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 1987;6(5-6):390–399. doi: 10.1159/000157065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A., Dull T. J., Bellot F., Van Obberghen E., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Biological activities of EGF-receptor mutants with individually altered autophosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3045–3052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Two retroviruses with similar transforming genes exhibit differences in transforming potential. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Narsimhan R. P., Gaudino G., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-MET. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):501–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M., Dean M., Kaul K., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Vande Woude G. Sequence of MET protooncogene cDNA has features characteristic of the tyrosine kinase family of growth-factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6379–6383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat M., Narsimhan R. P., Crepaldi T., Nicotra M. R., Natali P. G., Comoglio P. M. The receptor encoded by the human c-MET oncogene is expressed in hepatocytes, epithelial cells and solid tumors. Int J Cancer. 1991 Sep 30;49(3):323–328. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Vila J., Lansing T. J., Potts W. M., Weber M. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of the oncogenic potential of the avian cellular src protein by specific structural alteration of the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Oppermann H., Czernilofsky A. P., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L., Bishop J. M. Characterization of sites for tyrosine phosphorylation in the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus (pp60v-src) and its normal cellular homologue (pp60c-src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Vogt P. K., Hayman M. J. The v-sea oncogene of avian erythroblastosis retrovirus S13: another member of the protein-tyrosine kinase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5291–5295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. K., Weber M. J. Transformation by the src oncogene alters glucose transport into rat and chicken cells by different mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. P., Shipley J. P., Spurr N. K., Smith D. R., Hayman M. J., Goodfellow P. N. A human sequence homologous to v-sea maps to chromosome 11, band q13. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]