Abstract
Patients with severe temporal lobe epilepsy lose neurons within the CA3 and hilar regions of the hippocampus. Loss of CA3 and hilar neurons was also induced by transducing organotypic hippocampal slice cultures with a replication-defective herpes simplex virus (HSV) vector expressing the GluR6 kainate subtype of the glutamate receptor (HSVGluR6). In transduced fibroblasts, HSVGluR6 expressed a M(r) 115,000 protein that reacted with anti-GluR6 serum. After exposure of fibroblast to HSVGluR6, a kainate-dependent toxicity appeared in cells that were previously resistant to kainate. Microapplication of nanoliter amounts of recombinant HSV stocks into organotypic hippocampal slice cultures resulted in localized transduction and gene transfer at the site of microapplication. Microapplication of 100 HSVGluR6 virions into CA3 stratum pyramidale induced a large loss of CA3 pyramidal cells and hilar neurons, despite the small number of transduced neurons. This effect was not seen when 100 virions of HSVGluR6 were microapplied to CA1 stratum pyramidale. Tetrodotoxin or N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists inhibited the large loss of CA3 and hilar neurons, suggesting that the small cluster of HSVGluR6-transduced cells induced an N-methyl-D-aspartate-dependent transsynaptic loss of non-transduced neurons.
Full text
PDF

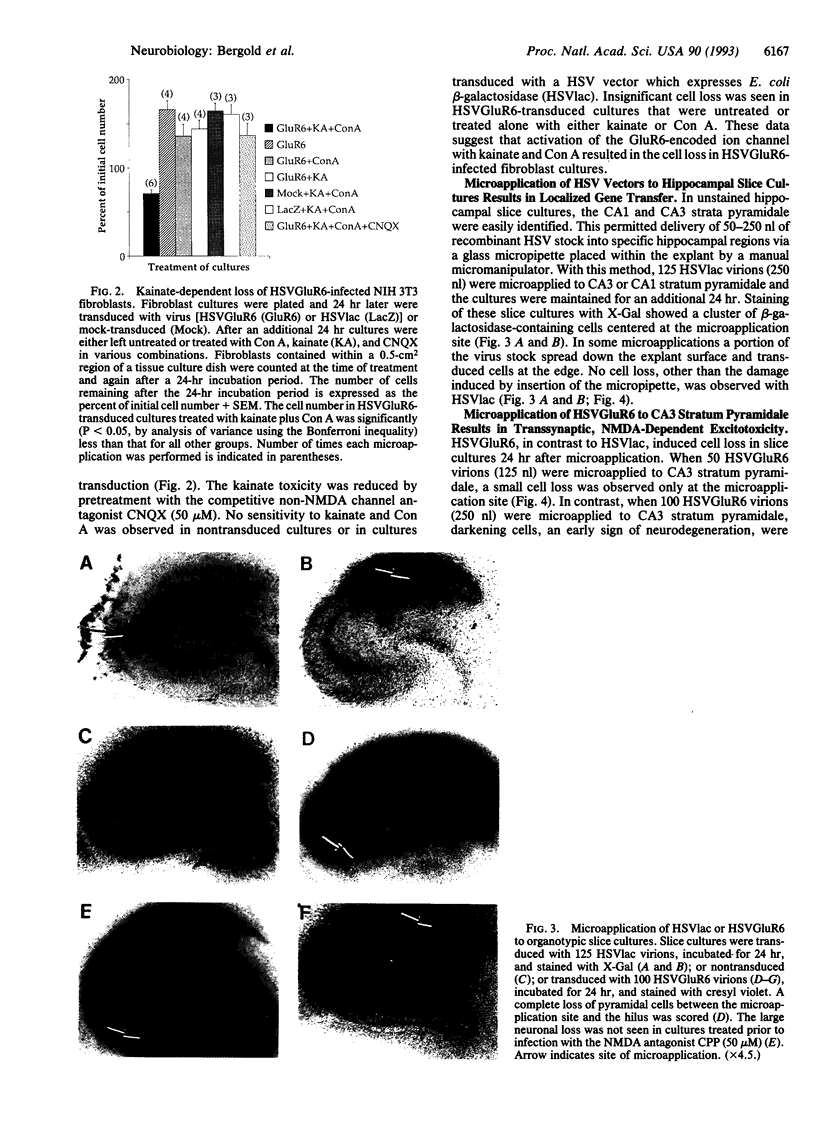
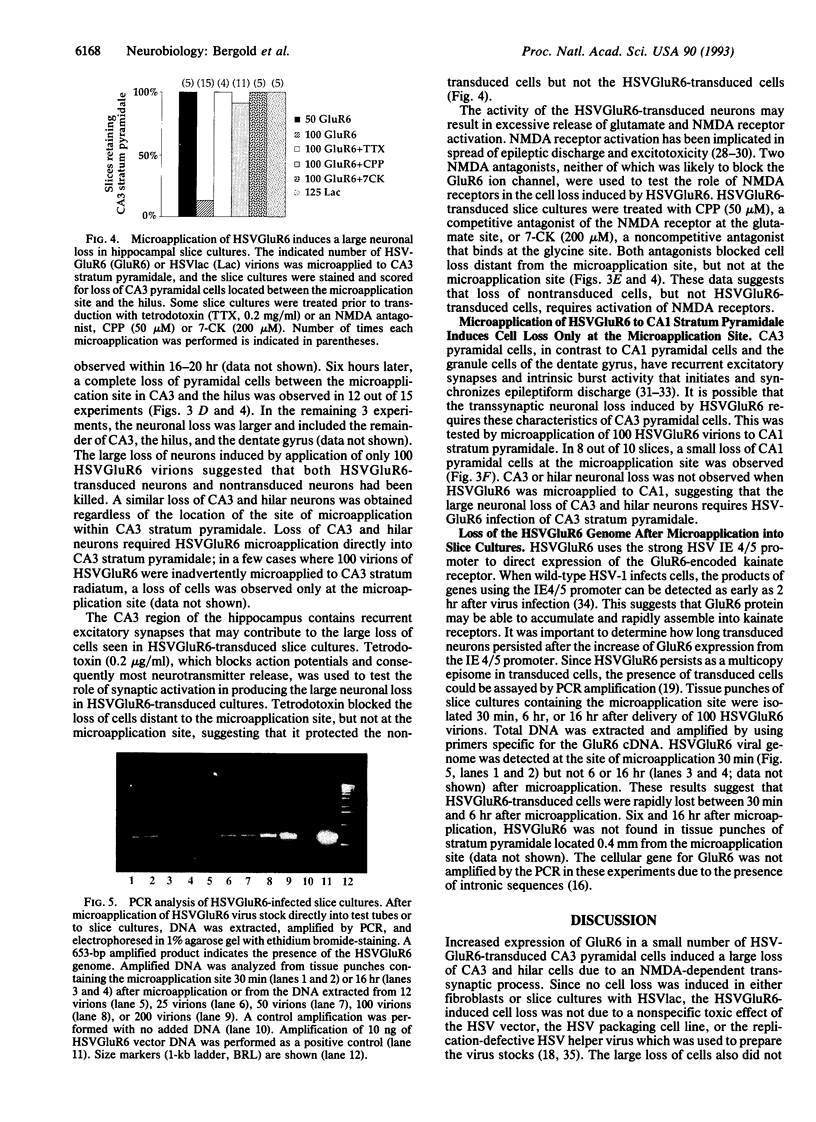

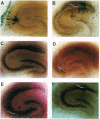
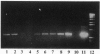
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babb T. L., Lieb J. P., Brown W. J., Pretorius J., Crandall P. H. Distribution of pyramidal cell density and hyperexcitability in the epileptic human hippocampal formation. Epilepsia. 1984 Dec;25(6):721–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1984.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y. Limbic seizure and brain damage produced by kainic acid: mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1985 Feb;14(2):375–403. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergold P. J., Beushausen S. A., Sacktor T. C., Cheley S., Bayley H., Schwartz J. H. A regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase down-regulated in aplysia sensory neurons during long-term sensitization. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):387–397. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90304-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Boulter J., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Deneris E. S., Moll C., Borgmeyer U., Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloning of a novel glutamate receptor subunit, GluR5: expression in the nervous system during development. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90213-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Egebjerg J., Sharma G., Pecht G., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Moll C., Stevens C. F., Heinemann S. Cloning of a putative glutamate receptor: a low affinity kainate-binding subunit. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90292-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caeser M., Aertsen A. Morphological organization of rat hippocampal slice cultures. J Comp Neurol. 1991 May 1;307(1):87–106. doi: 10.1002/cne.903070109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Molliver M. E., Kuhar M. J. In situ injection of kainic acid: a new method for selectively lesioning neural cell bodies while sparing axons of passage. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Jul 15;180(2):301–323. doi: 10.1002/cne.901800208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federoff H. J., Geschwind M. D., Geller A. I., Kessler J. A. Expression of nerve growth factor in vivo from a defective herpes simplex virus 1 vector prevents effects of axotomy on sympathetic ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frotscher M., Gähwiler B. H. Synaptic organization of intracellularly stained CA3 pyramidal neurons in slice cultures of rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1988 Feb;24(2):541–551. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Breakefield X. O. A defective HSV-1 vector expresses Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase in cultured peripheral neurons. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1667–1669. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Freese A. Infection of cultured central nervous system neurons with a defective herpes simplex virus 1 vector results in stable expression of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1149–1153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herb A., Burnashev N., Werner P., Sakmann B., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The KA-2 subunit of excitatory amino acid receptors shows widespread expression in brain and forms ion channels with distantly related subunits. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosford D. A., Crain B. J., Cao Z., Bonhaus D. W., Friedman A. H., Okazaki M. M., Nadler J. V., McNamara J. O. Increased AMPA-sensitive quisqualate receptor binding and reduced NMDA receptor binding in epileptic human hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1991 Feb;11(2):428–434. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-02-00428.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. A., Foster A. C., Leeson P. D., Priestley T., Tridgett R., Iversen L. L., Woodruff G. N. 7-Chlorokynurenic acid is a selective antagonist at the glycine modulatory site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6547–6550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder S., Brown K., Qiu F. H., Besmer P. c-kit protein, a transmembrane kinase: identification in tissues and characterization. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4896–4903. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Excitatory synaptic interactions between CA3 neurones in the guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:397–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Single neurones can initiate synchronized population discharge in the hippocampus. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):371–373. doi: 10.1038/306371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Represa A., Robain O., Tremblay E., Ben-Ari Y. Hippocampal plasticity in childhood epilepsy. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 8;99(3):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90472-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar H. J., Oxbury J. M. Hippocampal neuron loss in temporal lobe epilepsy: correlation with early childhood convulsions. Ann Neurol. 1987 Sep;22(3):334–340. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin C., Tamaki Y., Wilson J. T., Butler L., Sakaguchi T. NMDA-receptor mediated electrical epileptogenesis in the organotypic culture of rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1992 Aug 28;589(1):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91171-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Köhler M., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H. RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90568-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasheff S. F., Anderson W. W., Clark S., Wilson W. A. NMDA antagonists differentiate epileptogenesis from seizure expression in an in vitro model. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):648–651. doi: 10.1126/science.2569762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppini L., Buchs P. A., Muller D. A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Apr;37(2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90128-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swann J. W., Smith K. L., Brady R. J. Age-dependent alterations in the operations of hippocampal neural networks. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;627:264–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb25930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. D., Miles R., Wong R. K. Models of synchronized hippocampal bursts in the presence of inhibition. I. Single population events. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Oct;58(4):739–751. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.4.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. D., Wong R. K. Cellular mechanism of neuronal synchronization in epilepsy. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):745–747. doi: 10.1126/science.7079735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner P., Voigt M., Keinänen K., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Cloning of a putative high-affinity kainate receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampal CA3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):742–744. doi: 10.1038/351742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Miles R., Traub R. D. Local circuit interactions in synchronization of cortical neurones. J Exp Biol. 1984 Sep;112:169–178. doi: 10.1242/jeb.112.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer J., Gähwiler B. H. Cellular and connective organization of slice cultures of the rat hippocampus and fascia dentata. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Sep 20;228(3):432–446. doi: 10.1002/cne.902280310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lanerolle N. C., Kim J. H., Robbins R. J., Spencer D. D. Hippocampal interneuron loss and plasticity in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Res. 1989 Aug 28;495(2):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]