Abstract
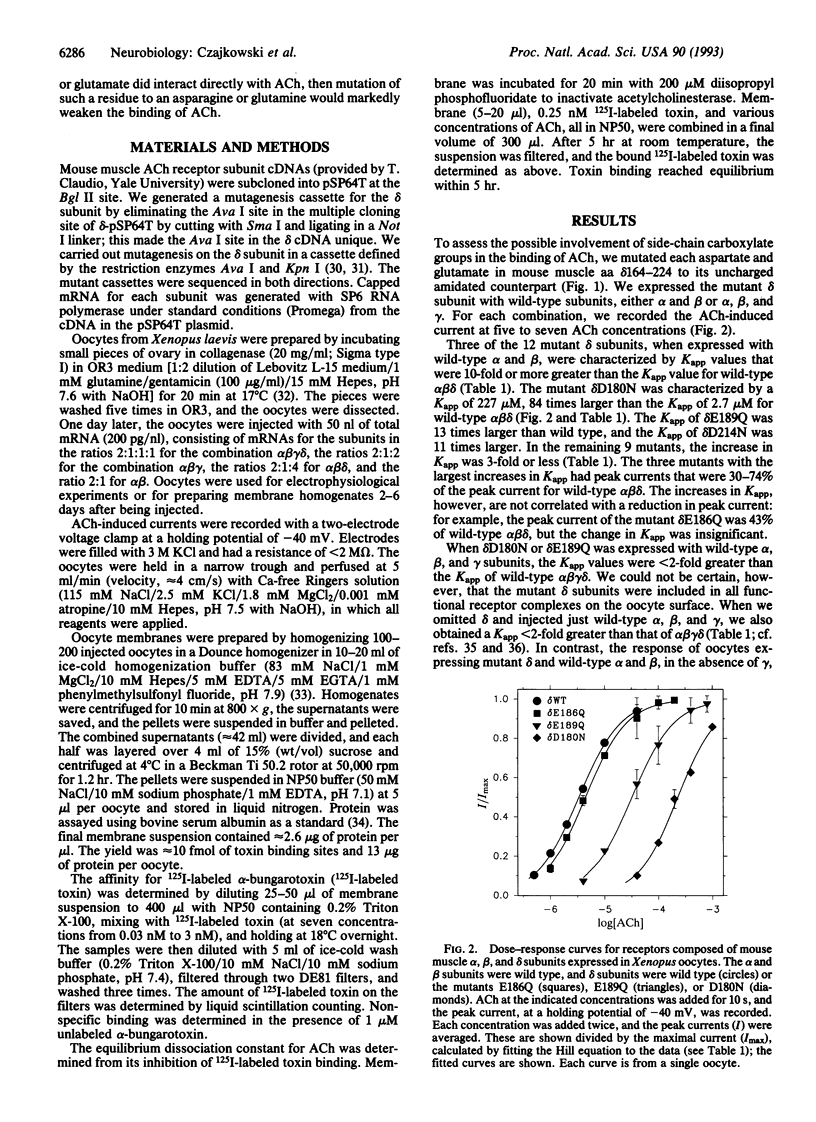
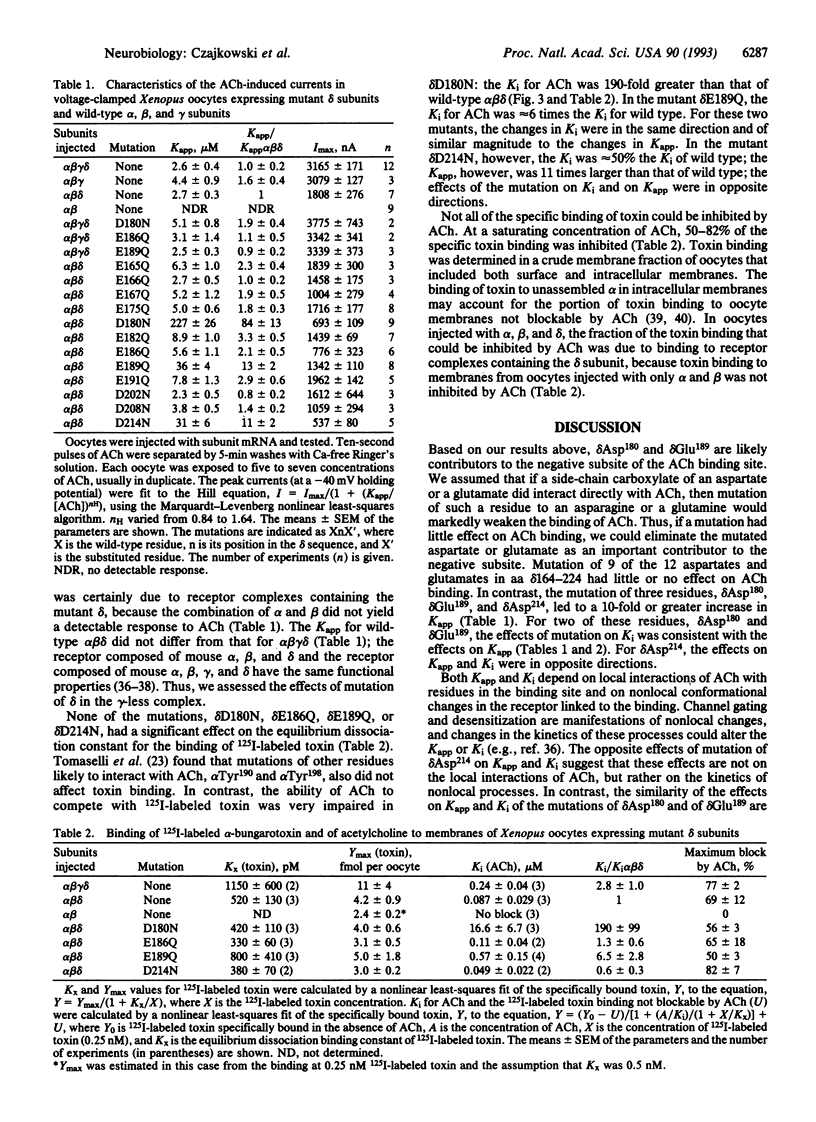
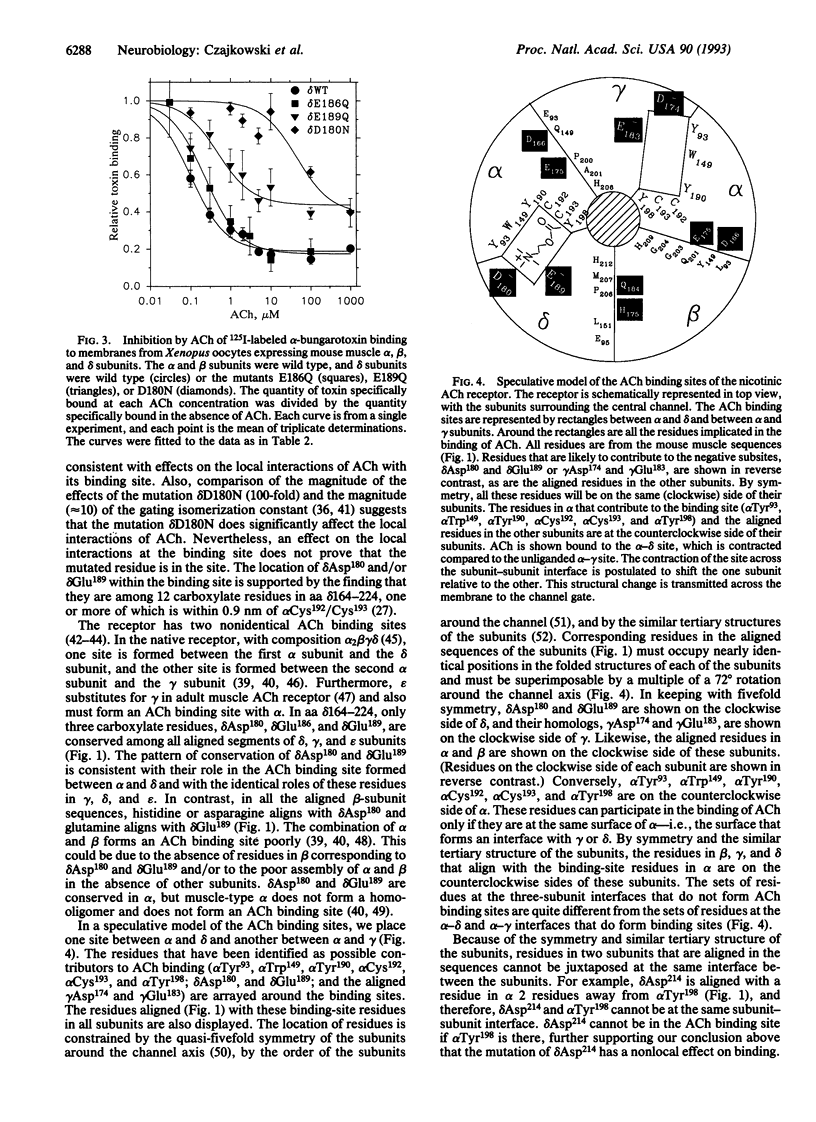
In nicotinic receptors, the binding sites for acetylcholine are likely to contain negatively charged amino acid side chains that interact with the positively charged quaternary ammonium group of acetylcholine and of other potent agonists. We previously found that a 61-residue segment of the delta subunit contains aspartate or glutamate residues within 1 nm of cysteines in the acetylcholine binding site on the alpha subunit. We have now mutated, one at a time, the 12 aspartates and glutamates in this segment of the mouse muscle delta subunit and have expressed the mutant receptors in Xenopus oocytes. Both the concentration of acetylcholine eliciting half-maximal current (Kapp) and the Ki for the inhibition by acetylcholine of alpha-bungarotoxin binding were increased 100-fold by the mutation of delta Asp180 to Asn and 10-fold by the mutation of delta Glu189 to Gln. These two residues, and their homologs in the gamma and epsilon subunits, are likely to contribute to the acetylcholine binding sites.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson S. N., Li Y., Culver P., Taylor P. An analog of lophotoxin reacts covalently with Tyr190 in the alpha-subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12666–12672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akabas M. H., Stauffer D. A., Xu M., Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):307–310. doi: 10.1126/science.1384130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Yoshihara C. M., Blackmer K., Kintner C. R., Burden S. J. Regulation of acetylcholine receptor transcript expression during development in Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):469–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeson D., Brydson M., Newsom-Davis J. Nucleotide sequence of human muscle acetylcholine receptor beta-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4391–4391. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P., Merlie J. P. Molecular basis of the two nonequivalent ligand binding sites of the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P., Merlie J. P. Native folding of an acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit expressed in the absence of other receptor subunits. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):1072–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Mudd J., Shah V., Merlie J. P. A universal oligonucleotide probe for acetylcholine receptor genes. Selection and sequencing of cDNA clones for the mouse muscle beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16451–16458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho P., Liu Y., Mandel G., Brehm P. The epsilon subunit confers fast channel gating on multiple classes of acetylcholine receptors. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):605–613. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00605.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnet P., Labarca C., Lester H. A. Structure of the gamma-less nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: learning from omission. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):708–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Sharp S. D., Liu W. S. Structure of the agonist-binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. [3H]acetylcholine mustard identifies residues in the cation-binding subsite. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23354–23364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criado M., Witzemann V., Koenen M., Sakmann B. Nucleotide sequence of the rat muscle acetylcholine receptor epsilon-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10920–10920. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski C., Karlin A. Agonist binding site of Torpedo electric tissue nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. A negatively charged region of the delta subunit within 0.9 nm of the alpha subunit binding site disulfide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22603–22612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., Karlin A. Affinity labeling of one of two alpha-neurotoxin binding sites in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2039–2045. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., Karlin A. Effects of agonists and antagonists on the reactivity of the binding site disulfide in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):3924–3932. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M., Giraudat J., Kotzyba-Hibert F., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Chang J. Y., Lazure C., Chrétien M., Changeux J. P. Amino acids of the Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit labeled by a photoaffinity ligand for the acetylcholine binding site. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2346–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty D. A., Stauffer D. A. Acetylcholine binding by a synthetic receptor: implications for biological recognition. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1558–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.2274786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowding A. J., Hall Z. W. Monoclonal antibodies specific for each of the two toxin-binding sites of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6372–6381. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Bertrand D., Devillers-Thiéry A., Revah F., Bertrand S., Changeux J. P. Functional significance of aromatic amino acids from three peptide loops of the alpha 7 neuronal nicotinic receptor site investigated by site-directed mutagenesis. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 9;294(3):198–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80668-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Revah F., Black D., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Changeux J. P. Identification of a novel amino acid alpha-tyrosine 93 within the cholinergic ligands-binding sites of the acetylcholine receptor by photoaffinity labeling. Additional evidence for a three-loop model of the cholinergic ligands-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10430–10437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Revah F., Bouet F., Ménez A., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Changeux J. P. Allosteric transitions of the acetylcholine receptor probed at the amino acid level with a photolabile cholinergic ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glockshuber R., Stadlmüller J., Plückthun A. Mapping and modification of an antibody hapten binding site: a site-directed mutagenesis study of McPC603. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 26;30(12):3049–3054. doi: 10.1021/bi00226a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golino M. D., Hamill O. P. Subunit requirements for Torpedo AChR channel expression: a specific role for the delta-subunit in voltage-dependent gating. J Membr Biol. 1992 Sep;129(3):297–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00232911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg K. E., Mudd J., Shah V., Merlie J. P. Nucleotide sequence of the mouse muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):5111–5111. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Dwork A. J., Kaldany R. R., Silver M. L., Wideman J., Stein S., Karlin A. Identification of the alpha subunit half-cystine specifically labeled by an affinity reagent for the acetylcholine receptor binding site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11662–11665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor binding site contains a disulfide cross-link between adjacent half-cystinyl residues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8085–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Holtzman E., Yodh N., Lobel P., Wall J., Hainfeld J. The arrangement of the subunits of the acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6678–6681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers O. P., Boot H. J., de Vos W. M. Improved site-directed mutagenesis method using PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4558–4558. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullberg R., Owens J. L., Camacho P., Mandel G., Brehm P. Multiple conductance classes of mouse nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki T., Fukuda K., Konno T., Mori Y., Tanaka K., Mishina M., Numa S. Functional properties of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits expressed in various combinations. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 20;214(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPolla R. J., Mayne K. M., Davidson N. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the complete protein coding region of the delta subunit of the mouse acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7970–7974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo D. C., Pinkham J. L., Stevens C. F. Influence of the gamma subunit and expression system on acetylcholine receptor gating. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90345-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton R. E., Cohen J. B. Mapping of the acetylcholine binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: [3H]nicotine as an agonist photoaffinity label. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6987–6997. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Takai T., Imoto K., Noda M., Takahashi T., Numa S., Methfessel C., Sakmann B. Molecular distinction between fetal and adult forms of muscle acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):406–411. doi: 10.1038/321406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Tobimatsu T., Imoto K., Tanaka K., Fujita Y., Fukuda K., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Morimoto Y., Hirose T. Location of functional regions of acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit by site-directed mutagenesis. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):364–369. doi: 10.1038/313364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Mauron A., Stalder R., Alliod C., Ballivet M. Structure linkage, and sequence of the two genes encoding the delta and gamma subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7975–7979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. M., Long G. L. A general method of site-specific mutagenesis using a modification of the Thermus aquaticus polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jul;180(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Cohen J. B. Equilibrium binding of [3H]tubocurarine and [3H]acetylcholine by Torpedo postsynaptic membranes: stoichiometry and ligand interactions. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5464–5475. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numa S. A molecular view of neurotransmitter receptors and ionic channels. Harvey Lect. 1987;83:121–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary M. E., White M. M. Mutational analysis of ligand-induced activation of the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8360–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. E., Cohen J. B. d-Tubocurarine binding sites are located at alpha-gamma and alpha-delta subunit interfaces of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradier L., Yee A. S., McNamee M. G. Use of chemical modifications and site-directed mutagenesis to probe the functional role of thiol groups on the gamma subunit of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 8;28(16):6562–6571. doi: 10.1021/bi00442a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radić Z., Gibney G., Kawamoto S., MacPhee-Quigley K., Bongiorno C., Taylor P. Expression of recombinant acetylcholinesterase in a baculovirus system: kinetic properties of glutamate 199 mutants. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 13;31(40):9760–9767. doi: 10.1021/bi00155a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter M. J., Cowburn D. A., Prives J. M., Karlin A. Affinity labeling of the acetylcholine receptor in the electroplax: electrophoretic separtion in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1168–1172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y., Cohen G. H., Padlan E. A., Davies D. R. Phosphocholine binding immunoglobulin Fab McPC603. An X-ray diffraction study at 2.7 A. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):593–604. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90245-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Claudio T. Gamma- and delta-subunits regulate the affinity and the cooperativity of ligand binding to the acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19369–19377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach J. H. Structural and functional diversity in vertebrate skeletal muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:353–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. L., Harel M., Frolow F., Oefner C., Goldman A., Toker L., Silman I. Atomic structure of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica: a prototypic acetylcholine-binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):872–879. doi: 10.1126/science.1678899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaselli G. F., McLaughlin J. T., Jurman M. E., Hawrot E., Yellen G. Mutations affecting agonist sensitivity of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):721–727. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82102-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii K., Yu L., Mayne K. M., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Equilibrium properties of mouse-Torpedo acetylcholine receptor hybrids expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Oct;90(4):553–573. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., LaPolla R. J., Davidson N. Mouse muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit: cDNA sequence and gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3539–3555. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., Leonard R. J., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Single-channel properties of mouse-Torpedo acetylcholine receptor hybrids expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jun;10(3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



