Abstract
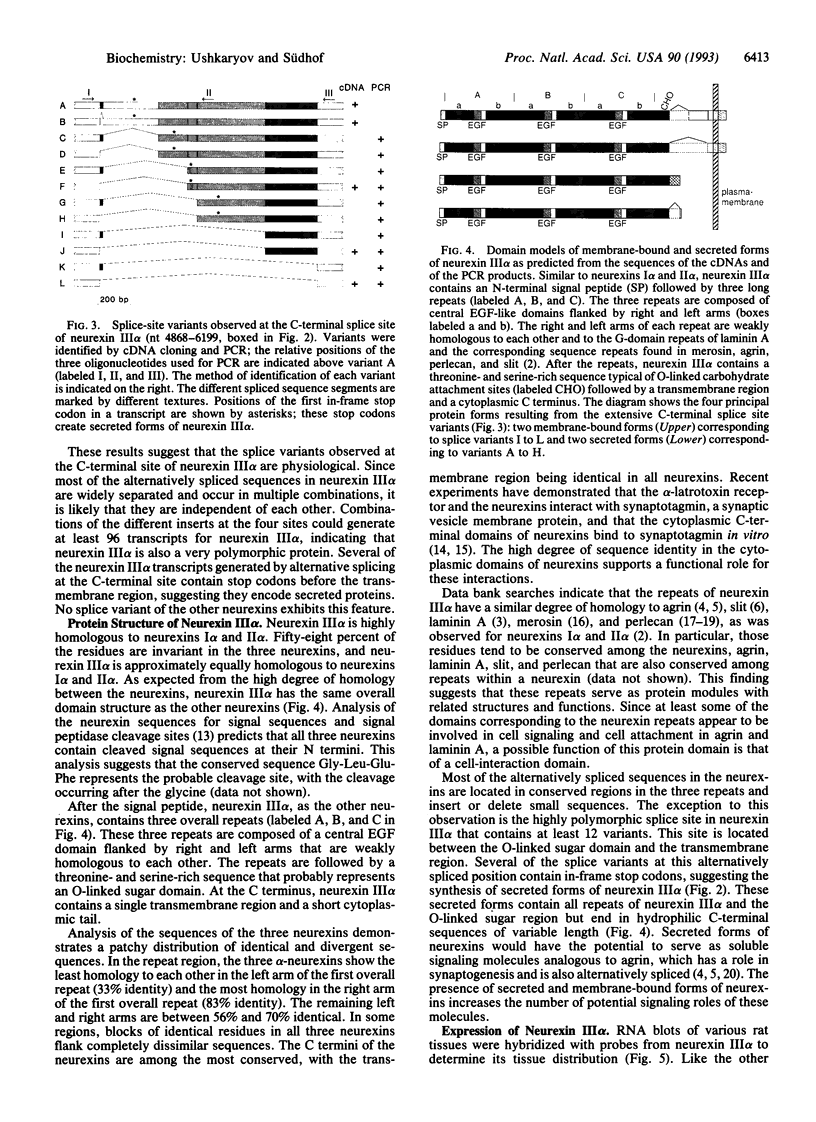
The structure of neurexin III alpha was elucidated from overlapping cDNA clones. Neurexin III alpha is highly homologous to neurexins I alpha and II alpha and shares with them a distinctive domain structure that resembles a cell surface receptor. cDNA cloning and PCR experiments revealed alternative splicing at four positions in the mRNA for neurexin III alpha. Alternative splicing was previously observed at the same positions in either neurexin I alpha or neurexin II alpha or both, suggesting that the three neurexins are subject to extensive alternative splicing. This results in hundreds of different neurexins with variations in small sequences at similar positions in the proteins. The most extensive alternative splicing of neurexin III alpha was detected at its C-terminal site, which exhibits a minimum of 12 variants. Some of the alternatively spliced sequences at this position contain in-frame stop codons, suggesting the synthesis of secreted proteins. None of the sequences of the other splice sites in this or the other two neurexins include stop codons. RNA blot analysis demonstrate that neurexin III alpha is expressed in a brain-specific pattern. Our results suggest that the neurexins constitute a large family of polymorphic cell surface proteins that includes secreted variants, indicating a possible role as signaling molecules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ehrig K., Leivo I., Argraves W. S., Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. Merosin, a tissue-specific basement membrane protein, is a laminin-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3264–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M. J., Hall Z. W. How many agrins does it take to make a synapse? Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90525-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata Y., Davletov B., Petrenko A. G., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Interaction of synaptotagmin with the cytoplasmic domains of neurexins. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90320-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallunki P., Tryggvason K. Human basement membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein: a 467-kD protein containing multiple domains resembling elements of the low density lipoprotein receptor, laminin, neural cell adhesion molecules, and epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):559–571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch A. D., Dodge G. R., Cohen I., Tuan R. S., Iozzo R. V. Primary structure of the human heparan sulfate proteoglycan from basement membrane (HSPG2/perlecan). A chimeric molecule with multiple domains homologous to the low density lipoprotein receptor, laminin, neural cell adhesion molecules, and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8544–8557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noonan D. M., Fulle A., Valente P., Cai S., Horigan E., Sasaki M., Yamada Y., Hassell J. R. The complete sequence of perlecan, a basement membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan, reveals extensive similarity with laminin A chain, low density lipoprotein-receptor, and the neural cell adhesion molecule. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22939–22947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrenko A. G., Lazaryeva V. D., Geppert M., Tarasyuk T. A., Moomaw C., Khokhlatchev A. V., Ushkaryov Y. A., Slaughter C., Nasimov I. V., Südhof T. C. Polypeptide composition of the alpha-latrotoxin receptor. High affinity binding protein consists of a family of related high molecular weight polypeptides complexed to a low molecular weight protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1860–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrenko A. G., Perin M. S., Davletov B. A., Ushkaryov Y. A., Geppert M., Südhof T. C. Binding of synaptotagmin to the alpha-latrotoxin receptor implicates both in synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):65–68. doi: 10.1038/353065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg J. M., Jacobs J. R., Goodman C. S., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. slit: an extracellular protein necessary for development of midline glia and commissural axon pathways contains both EGF and LRR domains. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2169–2187. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg M. A., Tsim K. W., Horton S. E., Kröger S., Escher G., Gensch E. M., McMahan U. J. The agrin gene codes for a family of basal lamina proteins that differ in function and distribution. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90090-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp F., Payan D. G., Magill-Solc C., Cowan D. M., Scheller R. H. Structure and expression of a rat agrin. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):811–823. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Huber H., Deutzmann R., Yamada Y. Laminin, a multidomain protein. The A chain has a unique globular domain and homology with the basement membrane proteoglycan and the laminin B chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16536–16544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Lottspeich F., Greengard P., Mehl E., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle protein with a novel cytoplasmic domain and four transmembrane regions. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1142–1144. doi: 10.1126/science.3120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushkaryov Y. A., Petrenko A. G., Geppert M., Südhof T. C. Neurexins: synaptic cell surface proteins related to the alpha-latrotoxin receptor and laminin. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):50–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1621094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]