Abstract
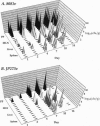
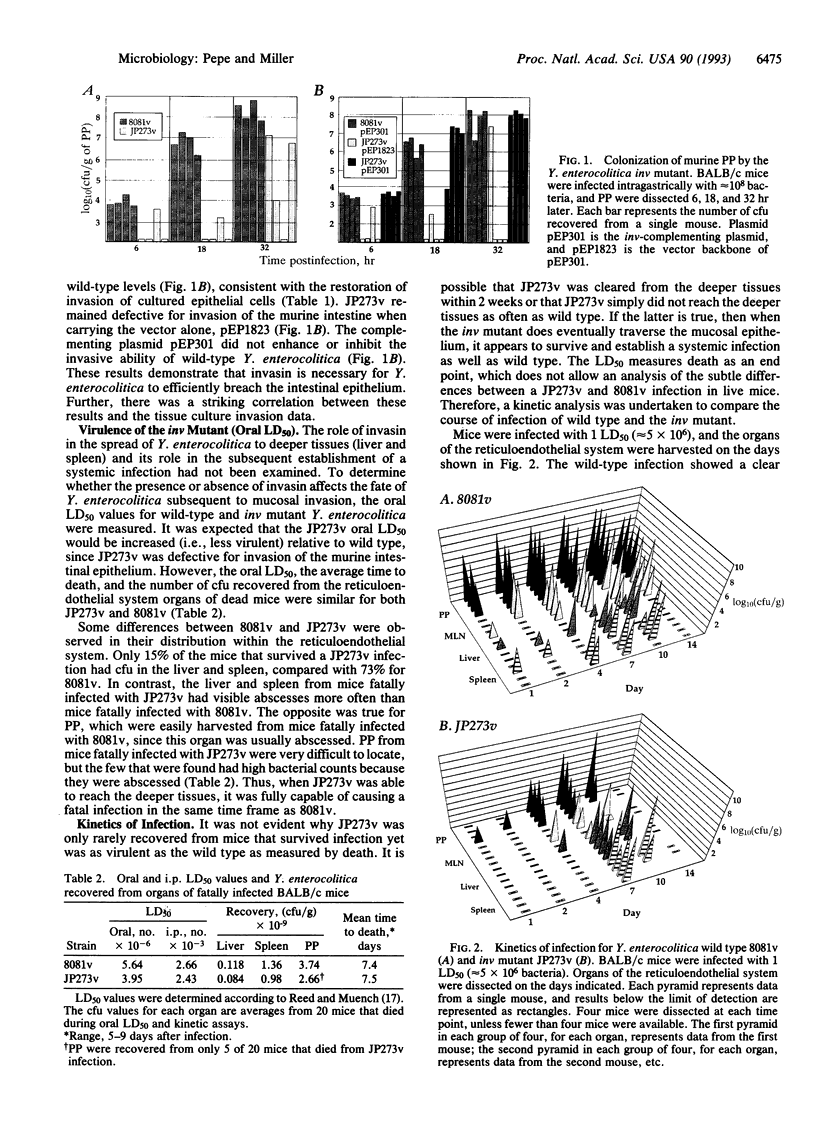
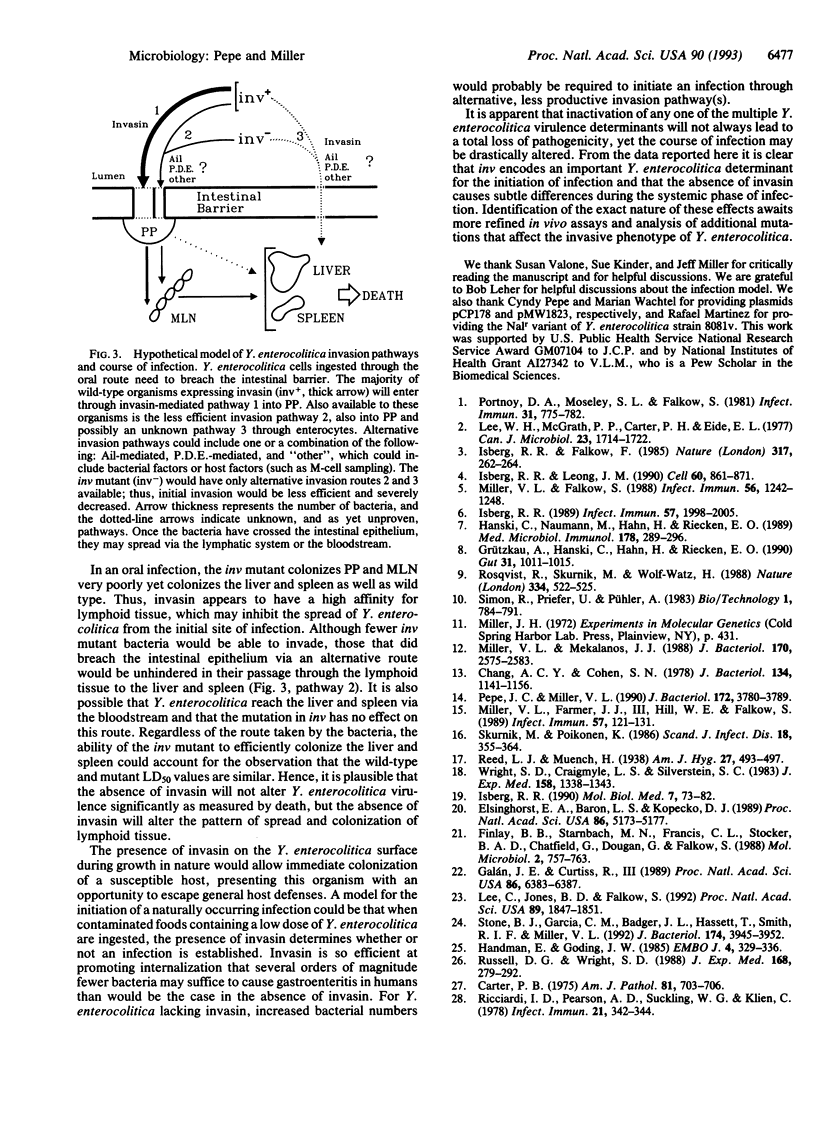
The ability to invade the intestinal epithelium of mammals is an essential virulence determinant of Yersinia enterocolitica. The chromosomally encoded Y. enterocolitica 8081v invasion gene, inv, was disrupted to assess its role in pathogenesis. The inv mutant (JP273v) was approximately 80-fold less invasive than wild type for cultured epithelial cells. When mice were infected intragastrically, up to 10(7) fewer JP273v were recovered from Peyer's patches early (6-18 hr) after infection compared with wild type. Analysis of the course of infection revealed that the inv mutant had distinct differences relative to wild type in the distribution of visible infectious foci and in tissue colonization; however, the mutant and wild-type strains had similar LD50 values for both orally and intraperitoneally infected mice. The invasion defect of the inv mutant was fully complemented in vitro and in vivo by introduction of the wild-type inv gene in trans. The inv gene product, invasin, appears to play a vital role in promoting entry during the initial stage of infection. During the subsequent establishment of a systemic infection, invasin may be of secondary importance, since the Y. enterocolitica inv mutant was as proficient as wild type at causing a fatal infection in mice. Based on these data, we discuss the role of invasin in a naturally occurring Y. enterocolitica infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter P. B. Animal model of human disease. Yersinia enteritis. Animal model: oral Yersinia enterocolitica infection of mice. Am J Pathol. 1975 Dec;81(3):703–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Starnbach M. N., Francis C. L., Stocker B. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of TnphoA mutants of Salmonella that are unable to pass through a polarized MDCK epithelial cell monolayer. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):757–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grützkau A., Hanski C., Hahn H., Riecken E. O. Involvement of M cells in the bacterial invasion of Peyer's patches: a common mechanism shared by Yersinia enterocolitica and other enteroinvasive bacteria. Gut. 1990 Sep;31(9):1011–1015. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.9.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Goding J. W. The Leishmania receptor for macrophages is a lipid-containing glycoconjugate. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):329–336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski C., Naumann M., Hahn H., Riecken E. O. Determinants of invasion and survival of Yersinia enterocolitica in intestinal tissue. An in vivo study. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1989;178(5):289–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00191063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Determinants for thermoinducible cell binding and plasmid-encoded cellular penetration detected in the absence of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1998–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1998-2005.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Pathways for the penetration of enteroinvasive Yersinia into mammalian cells. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Feb;7(1):73–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Jones B. D., Falkow S. Identification of a Salmonella typhimurium invasion locus by selection for hyperinvasive mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1847–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McGrath P. P., Carter P. H., Eide E. L. The ability of some Yersinia enterocolitica strains to invade HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1714–1722. doi: 10.1139/m77-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe J. C., Miller V. L. The Yersinia enterocolitica inv gene product is an outer membrane protein that shares epitopes with Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3780–3789. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3780-3789.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi I. D., Pearson A. D., Suckling W. G., Klein C. Long-term fecal excretion and resistance induced in mice infected with Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):342–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.342-344.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Increased virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by two independent mutations. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):522–524. doi: 10.1038/334522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G., Wright S. D. Complement receptor type 3 (CR3) binds to an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing region of the major surface glycoprotein, gp63, of Leishmania promastigotes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):279–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Poikonen K. Experimental intestinal infection of rats by Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3. A follow-up study with specific antibodies to the virulence plasmid specified antigens. Scand J Infect Dis. 1986;18(4):355–364. doi: 10.3109/00365548609032347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone B. J., Garcia C. M., Badger J. L., Hassett T., Smith R. I., Miller V. L. Identification of novel loci affecting entry of Salmonella enteritidis into eukaryotic cells. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3945–3952. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3945-3952.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Craigmyle L. S., Silverstein S. C. Fibronectin and serum amyloid P component stimulate C3b- and C3bi-mediated phagocytosis in cultured human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1338–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]