Abstract
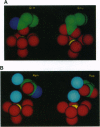
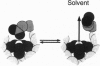
EF-hand Ca(II) binding sites share a conserved architecture and are prevalent in Ca(II) signaling pathways. The ion binding kinetics of these sites are carefully tuned to provide the physiologically appropriate activation and inactivation time scales. Here we examine kinetic tuning by the side chain at the ninth position of the EF-loop. A model is proposed in which both the size and charge of the side chain contribute to kinetic tuning. To test this model, the ninth loop position of the EF-hand-like site in the Escherichia coli D-galactose binding protein has been engineered and the Tb(III) dissociation kinetics of the resulting sites have been analyzed. Substitutions at this position are observed to generate up to 10(4)-fold changes in Tb(III) dissociation rates, with little effect on Tb(III) affinity. Furthermore, the observed pattern of rate changes confirm the model's predictions; long side chains at the ninth loop position yield slow dissociation kinetics as predicted for a steric block, whereas acidic side chains yield slow dissociation kinetics as expected for an electrostatic barrier.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed F. R., Przybylska M., Rose D. R., Birnbaum G. I., Pippy M. E., MacManus J. P. Structure of oncomodulin refined at 1.85 A resolution. An example of extensive molecular aggregation via Ca2+. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 5;216(1):127–140. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley C. C., Mulligan I. P., Lea T. J. Ca2+ and activation mechanisms in skeletal muscle. Q Rev Biophys. 1991 Feb;24(1):1–73. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu Y. S., Bugg C. E., Cook W. J. Structure of calmodulin refined at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):191–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90608-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baimbridge K. G., Celio M. R., Rogers J. H. Calcium-binding proteins in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Aug;15(8):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90081-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen P. J., Johnson K. A., Horrocks W. D., Jr Stopped-flow kinetic studies of metal ion dissociation or exchange in a tryptophan-containing parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):4997–5004. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain H. G., Richardson F. S., Martin R. B. Terbium (III) emission as a probe of calcium(II) binding sites in proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Dec 8;98(25):8255–8260. doi: 10.1021/ja00441a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Careaga C. L., Falke J. J. Thermal motions of surface alpha-helices in the D-galactose chemosensory receptor. Detection by disulfide trapping. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1219–1235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91063-u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavé A., Daures M. F., Parello J., Saint-Yves A., Sempere R. NMR studies of primary and secondary sites of parvalbumins using the two paramagnetic probes Gd (III) and Mn (II). Biochimie. 1979;61(7):755–765. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao S. H., Suzuki Y., Zysk J. R., Cheung W. Y. Activation of calmodulin by various metal cations as a function of ionic radius. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):75–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corson D. C., Williams T. C., Sykes B. D. Calcium binding proteins: optical stopped-flow and proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the binding of the lanthanide series of metal ions to parvalbumin. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):5882–5889. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. N., Urdea M. S., Masiarz F. R., Thorner J. Isolation of the yeast calmodulin gene: calmodulin is an essential protein. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declercq J. P., Tinant B., Parello J., Rambaud J. Ionic interactions with parvalbumins. Crystal structure determination of pike 4.10 parvalbumin in four different ionic environments. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 20;220(4):1017–1039. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90369-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Snyder E. E., Thatcher K. C., Voertler C. S. Quantitating and engineering the ion specificity of an EF-hand-like Ca2+ binding. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8690–8697. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser J. R., van Tuinen D., Brockerhoff S. E., Neff M. M., Davis T. N. Can calmodulin function without binding calcium? Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):949–959. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90547-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabarek Z., Tao T., Gergely J. Molecular mechanism of troponin-C function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1992 Aug;13(4):383–393. doi: 10.1007/BF01738034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Schulman H. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:559–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Common structural framework of the two Ca2+/Mg2+ binding loops of troponin C and other Ca2+ binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5298–5302. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Refined crystal structure of troponin C from turkey skeletal muscle at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):761–779. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou T. T., Johnson J. D., Rall J. A. Effect of temperature on relaxation rate and Ca2+, Mg2+ dissociation rates from parvalbumin of frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:399–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden B. J., Shaw G. S., Sykes B. D. Calcium binding proteins. Elucidating the contributions to calcium affinity from an analysis of species variants and peptide fragments. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;68(3):587–601. doi: 10.1139/o90-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., Andersson Teleman A., Bayley P. M., Drakenberg T., Forsen S. Kinetics of calcium dissociation from calmodulin and its tryptic fragments. A stopped-flow fluorescence study using Quin 2 reveals a two-domain structure. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., Linse S., Johansson C., Bayley P. M., Forsén S. Protein surface charges and Ca2+ binding to individual sites in calbindin D9k: stopped-flow studies. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4188–4193. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador W. E., Means A. R., Quiocho F. A. Target enzyme recognition by calmodulin: 2.4 A structure of a calmodulin-peptide complex. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1251–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1519061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Kretsinger R. H. Terbium replacement of calcium in carp muscle calcium-binding parvalbumin: an x-ray crystallographic study. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama S., Moncrief N. D., Kretsinger R. H. Evolution of EF-hand calcium-modulated proteins. II. Domains of several subfamilies have diverse evolutionary histories. J Mol Evol. 1992 May;34(5):416–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00162998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham J. V., Chen T. Y., Falke J. J. Novel ion specificity of a carboxylate cluster Mg(II) binding site: strong charge selectivity and weak size selectivity. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3363–3367. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onek L. A., Smith R. J. Calmodulin and calcium mediated regulation in prokaryotes. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jun;138(6):1039–1049. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-6-1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechère J. F., Derancourt J., Haiech J. The participation of parvalbumins in the activation-relaxation cycle of vertebrate fast skeletal-muscle. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roquet F., Declercq J. P., Tinant B., Rambaud J., Parello J. Crystal structure of the unique parvalbumin component from muscle of the leopard shark (Triakis semifasciata). The first X-ray study of an alpha-parvalbumin. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):705–720. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90985-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekharudu Y. C., Sundaralingam M. A structure-function relationship for the calcium affinities of regulatory proteins containing 'EF-hand' pairs. Protein Eng. 1988 Jul;2(2):139–146. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder E. E., Buoscio B. W., Falke J. J. Calcium(II) site specificity: effect of size and charge on metal ion binding to an EF-hand-like site. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 24;29(16):3937–3943. doi: 10.1021/bi00468a021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strynadka N. C., James M. N. Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:951–998. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. A., Sack J. S., Maune J. F., Beckingham K., Quiocho F. A. Structure of a recombinant calmodulin from Drosophila melanogaster refined at 2.2-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21375–21380. doi: 10.2210/pdb4cln/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas M. N., Jacobson B. L., Quiocho F. A. The calcium-binding site in the galactose chemoreceptor protein. Crystallographic and metal-binding studies. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20817–20821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas N. K., Vyas M. N., Quiocho F. A. A novel calcium binding site in the galactose-binding protein of bacterial transport and chemotaxis. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):635–638. doi: 10.1038/327635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]