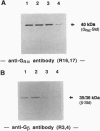
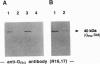
Abstract
Previous studies on the mechanism responsible for terminating the generation of second messengers induced by chemotactic factor-receptor complexes have, on one hand, suggested a direct role of a GTP-binding protein(s) (G protein), and, on the other hand, proposed that there is a lateral segregation of the ligand-receptor complexes into G protein-depleted domains of the plasma membrane. In the present investigation, which addresses these apparently contradictory findings, we found that a substantial part of the alpha subunits of the Gn protein (Gn alpha) in unstimulated neutrophils were associated with a cytoskeletal fraction and that release of these subunits occurred upon stimulation with the chemotactic factor fMet-Leu-Phe. An identical Gn alpha release could also be induced by direct activation of G proteins with guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate or AIF4-. In contrast, the alpha subunits of the stimulatory G protein (Gs alpha) also found associated with the cytoskeletal fraction of unstimulated cells were not released by fMet-Leu-Phe stimulation. However, they were effectively released by direct G-protein activation with guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. In addition, inhibition of the fMet-Leu-Phe-stimulated modulation of the actin network by pertussis toxin did not affect the fMet-Leu-Phe-induced release of Gn alpha from the cytoskeletal fraction. These observations indicate that fMet-Leu-Phe-induced activation of neutrophils involves a specific dissociation of Gn alpha from the cytoskeleton and that this release is not a consequence of the well-known effect of fMet-Leu-Phe on the cytoskeleton of neutrophils. The present data contribute ideas concerning the transducing properties of G proteins in cellular signaling and seem to reconcile the apparently contradictory concepts of how the cytoskeleton participates in the termination of the chemotactic-factor-induced generation of second messengers in human neutrophils.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengtsson T., Stendahl O., Andersson T. The role of the cytosolic free Ca2+ transient for fMet-Leu-Phe induced actin polymerization in human neutrophils. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;42(2):338–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson T., Särndahl E., Stendahl O., Andersson T. Involvement of GTP-binding proteins in actin polymerization in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2921–2925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Bickford K., Bohl B. P. Subcellular localization and quantitation of the major neutrophil pertussis toxin substrate, Gn. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1927–1936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommakanti R. K., Bokoch G. M., Tolley J. O., Schreiber R. E., Siemsen D. W., Klotz K. N., Jesaitis A. J. Reconstitution of a physical complex between the N-formyl chemotactic peptide receptor and G protein. Inhibition by pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7576–7581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fällman M., Gullberg M., Hellberg C., Andersson T. Complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis is associated with accumulation of phosphatidylcholine-derived diglyceride in human neutrophils. Involvement of phospholipase D and direct evidence for a positive feedback signal of protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2656–2663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Baldassare J. J., Pollard T. D. The actin-binding protein profilin binds to PIP2 and inhibits its hydrolysis by phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2157283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Bokoch G. M., Tolley J. O., Allen R. A. Lateral segregation of neutrophil chemotactic receptors into actin- and fodrin-rich plasma membrane microdomains depleted in guanyl nucleotide regulatory proteins. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):921–928. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Naemura J. R., Sklar L. A., Cochrane C. G., Painter R. G. Rapid modulation of N-formyl chemotactic peptide receptors on the surface of human granulocytes: formation of high-affinity ligand-receptor complexes in transient association with cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1378–1387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Tolley J. O., Allen R. A. Receptor-cytoskeleton interactions and membrane traffic may regulate chemoattractant-induced superoxide production in human granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13662–13669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Tolley J. O., Bokoch G. M., Allen R. A. Regulation of chemoattractant receptor interaction with transducing proteins by organizational control in the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2783–2790. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Tolley J. O., Painter R. G., Sklar L. A., Cochrane C. G. Membrane-cytoskeleton interactions and the regulation of chemotactic peptide-induced activation of human granulocytes: the effects of dihydrocytochalasin B. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(3):241–253. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Zahler-Bentz K., Dukes R. E. Regulation of the affinity state of the N-formylated peptide receptor of neutrophils: role of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins and the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):2959–2971. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Breton M., den Hartigh J. C., Plantavid M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Phosphoinositide kinase, diacylglycerol kinase, and phospholipase C activities associated to the cytoskeleton: effect of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):121–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of GTP-binding proteins in signal transduction: from the sublimely simple to the conceptually complex. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1992;32:1–47. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152832-4.50003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefcyk J., Yassin R., Volpi M., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Munoz J. J., Becker E. L., Feinstein M. B., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis but not cholera toxin inhibits the stimulated increase in actin association with the cytoskeleton in rabbit neutrophils: role of the "G proteins" in stimulus-response coupling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 15;126(3):1174–1181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Codina J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Gi2 mediates alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G alpha C-terminal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Särndahl E., Lindroth M., Bengtsson T., Fällman M., Gustavsson J., Stendahl O., Andersson T. Association of ligand-receptor complexes with actin filaments in human neutrophils: a possible regulatory role for a G-protein. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2791–2799. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Jaken S., Liao L., Fox J. E., Rittenhouse S. E. Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase associates with membrane skeleton in thrombin-exposed platelets. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4686–4692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]