Abstract
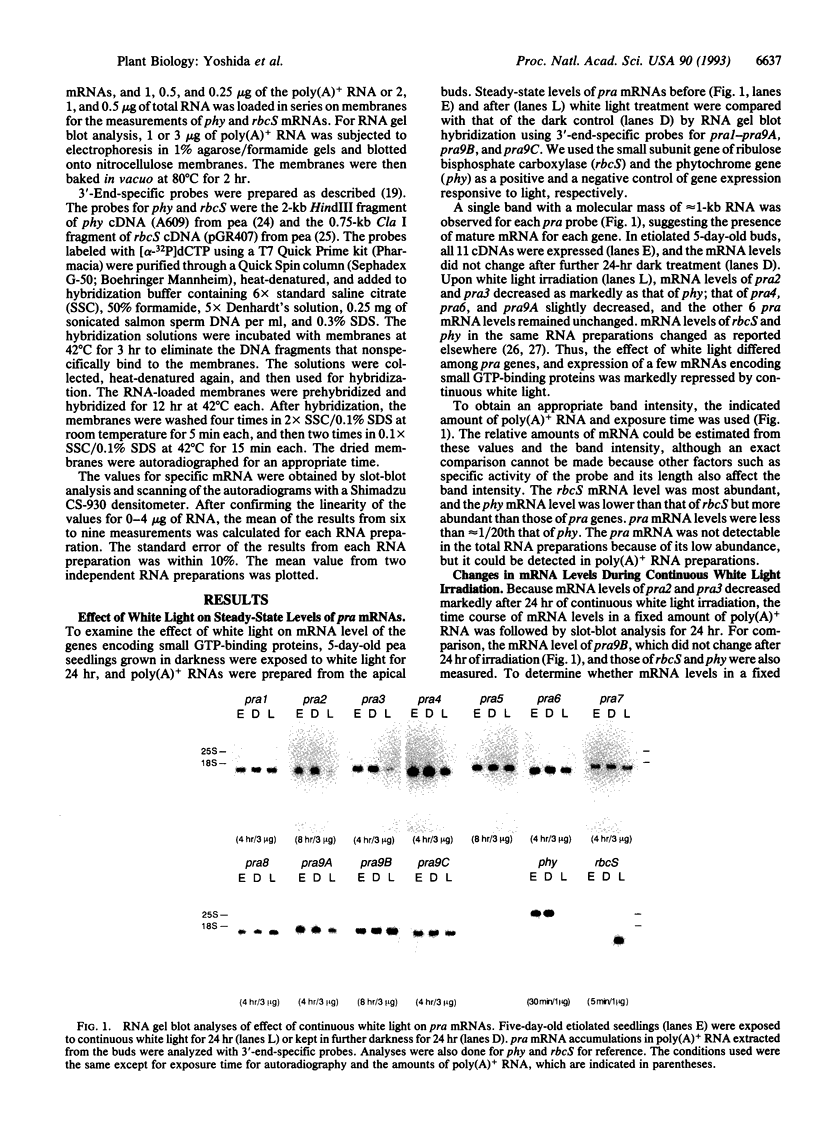
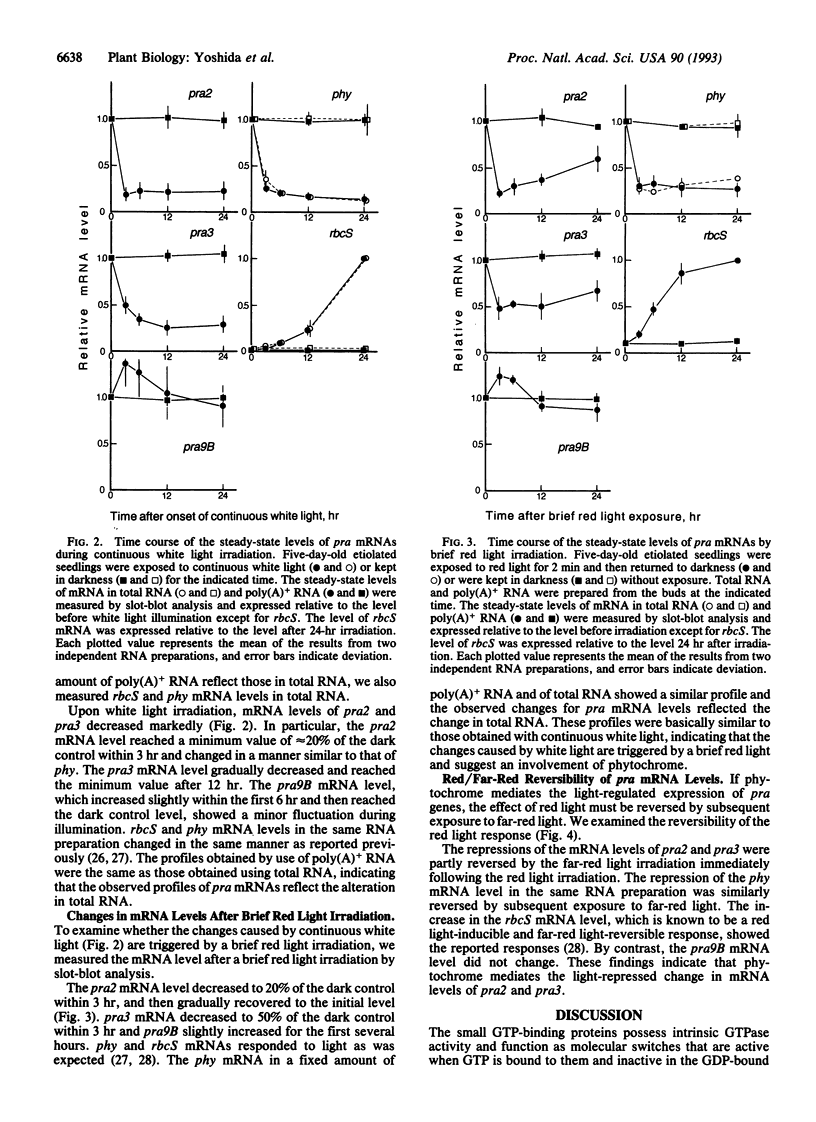
We examined the effect of light on the mRNA levels of 11 genes (pra1-pra9A, pra9B, and pra9C) encoding the small GTP-binding proteins that belong to the ras superfamily in Pisum sativum. When the dark-grown seedlings were exposed to continuous white light for 24 hr, the levels of several pra mRNAs in the pea buds decreased: pra2 and pra3 mRNAs decreased markedly; pra4, pra6, and pra9A mRNAs decreased slightly; the other 6 pra mRNAs did not decrease. We studied the kinetics of mRNA accumulation for pra2, pra3, and pra9B in detail during white light illumination and compared them with those of the phytochrome gene and the small subunit gene of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase: mRNA levels of pra2 and pra3 decreased in a manner similar to that of phytochrome while that of the small subunit increased as was expected. The decreases were triggered by a 2-min monochromatic red light (660 nm) irradiation. The effect of red light was reversed by subsequent exposure to far-red light, indicating an involvement of phytochrome as a photoreceptor in this light-regulated event. This work reports negative regulation of mRNA levels of small GTP-binding proteins by light, mediated by phytochrome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anai T., Hasegawa K., Watanabe Y., Uchimiya H., Ishizaki R., Matsui M. Isolation and analysis of cDNAs encoding small GTP-binding proteins of Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 1991 Dec 15;108(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90442-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., Smith S. M. Synthesis of the small subunit of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase from genes cloned into plasmids containing the SP6 promoter. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):709–715. doi: 10.1042/bj2400709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anuntalabhochai S., Terryn N., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Molecular characterization of an Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA encoding a small GTP-binding protein, Rha1. Plant J. 1991 Sep;1(2):167–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon R. A., Salminen A., Ruohola H., Novick P., Ferro-Novick S. The GTP-binding protein Ypt1 is required for transport in vitro: the Golgi apparatus is defective in ypt1 mutants. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallmann G., Sticher L., Marshallsay C., Nagy F. Molecular characterization of tobacco cDNAs encoding two small GTP-binding proteins. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Aug;19(5):847–857. doi: 10.1007/BF00027080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drobak B. K., Allan E. F., Comerford J. G., Roberts K., Dawson A. P. Presence of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in a plant hypocotyl microsomal fraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):899–903. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90713-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay S. A., Keith B., Shinozaki K., Chye M. L., Chua N. H. The rice phytochrome gene: structure, autoregulated expression, and binding of GT-1 to a conserved site in the 5' upstream region. Plant Cell. 1989 Mar;1(3):351–360. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X., Feng X. H., Watson J. C. Differential accumulation of transcripts encoding protein kinase homologs in greening pea seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6951–6955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissemore J. L., Quail P. H. Rapid transcriptional regulation by phytochrome of the genes for phytochrome and chlorophyll a/b-binding protein in Avena sativa. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4840–4850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui M., Sasamoto S., Kunieda T., Nomura N., Ishizaki R. Cloning of ara, a putative Arabidopsis thaliana gene homologous to the ras-related gene family. Gene. 1989;76(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mösinger E., Batschauer A., Schäfer E., Apel K. Phytochrome control of in vitro transcription of specific genes in isolated nuclei from barley (Hordeum vulgare). Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):137–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano Y., Murai N., Matsuno R., Sasaki Y. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs that encode eleven small GTP-binding proteins from Pisum sativum. Plant Cell Physiol. 1993 Apr;34(3):447–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo E. R., Sanders P. G., Padua R. A., Hughes D., Williamson R., Johnson K. J. The MEL gene: a new member of the RAB/YPT class of RAS-related genes. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1347–1351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubara P. A., Tobin E. M. Isolation and Characterization of Three Genes Negatively Regulated by Phytochrome Action in Lemna gibba. Plant Physiol. 1991 Aug;96(4):1237–1245. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.4.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palme K., Diefenthal T., Vingron M., Sander C., Schell J. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of genes from Zea mays (L.) coding for members of the ras-related ypt gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):787–791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quail P. H. Phytochrome: a light-activated molecular switch that regulates plant gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:389–409. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Youssefian S. A novel ras-related rgp1 gene encoding a GTP-binding protein has reduced expression in 5-azacytidine-induced dwarf rice. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):227–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00282470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Sekiguchi K., Nagano Y., Matsuno R. Detection of small GTP-binding proteins in the outer envelope membrane of pea chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 18;293(1-2):124–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Tomoda Y., Tomi H., Kamikubo T., Shinozaki K. Synthesis of ribulose biphosphate carboxylase in greening pea leaves. Coordination of mRNA level of two subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terryn N., Anuntalabhochai S., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Analysis of a Nicotiana plumbaginifolia cDNA encoding a novel small GTP-binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 16;299(3):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai F. Y., Coruzzi G. M. Dark-induced and organ-specific expression of two asparagine synthetase genes in Pisum sativum. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):323–332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Sluijs P., Hull M., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Goud B., Mellman I. The small GTP-binding protein rab4 is associated with early endosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6313–6317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]