Abstract
Radioactive xenon-133 was used to study the pattern of regional lung function in 35 scoliotic patients and 10 normal subjects in the sitting posture. The scoliotic curves were classified into three anatomical sites: high, if the apical vertebra was located between Th1 and Th5; mid, between Th6 and Th10; and low, between Th11 and L4; only the primary curve was considered and in 70% of the patients this measured more than 60°.
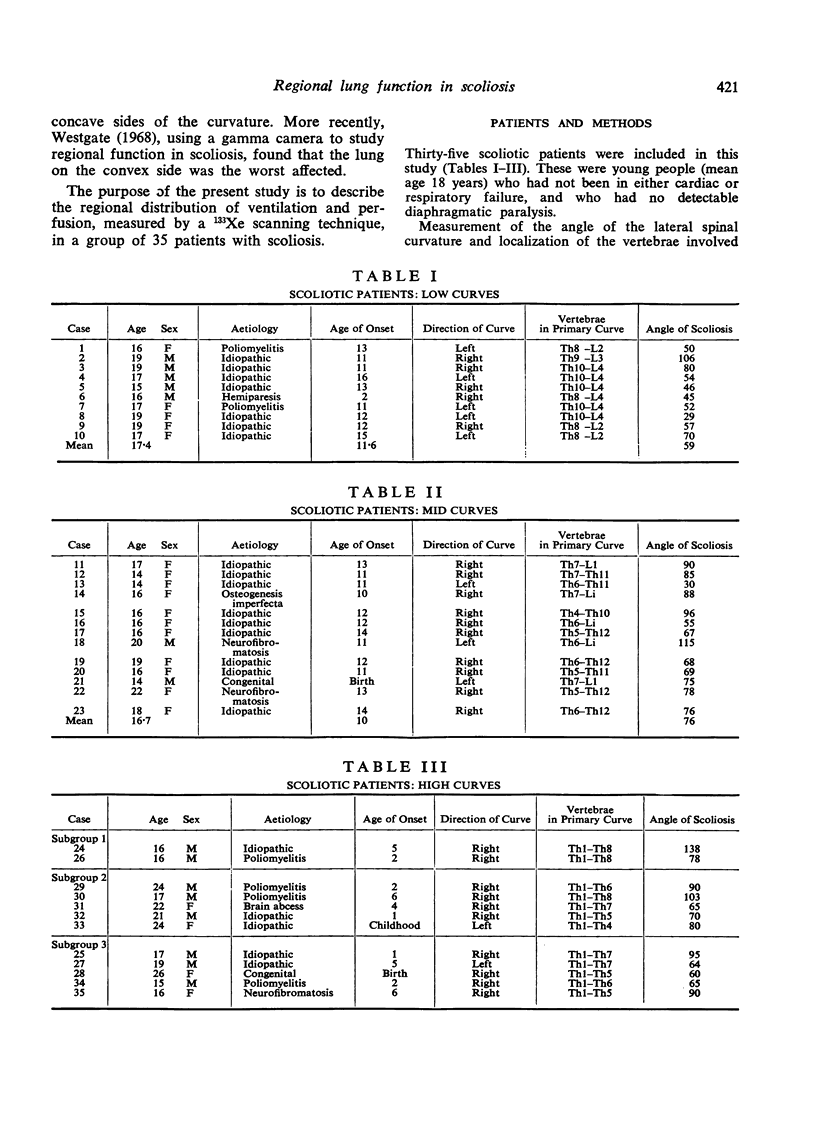
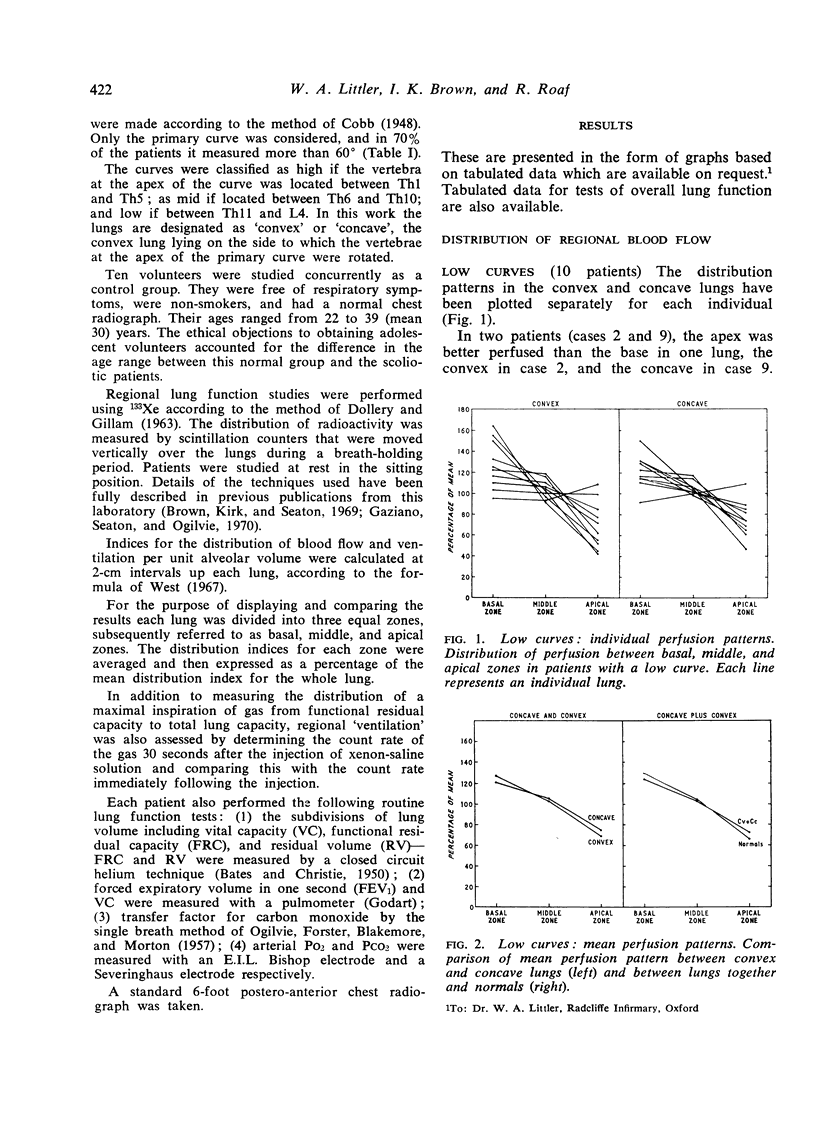
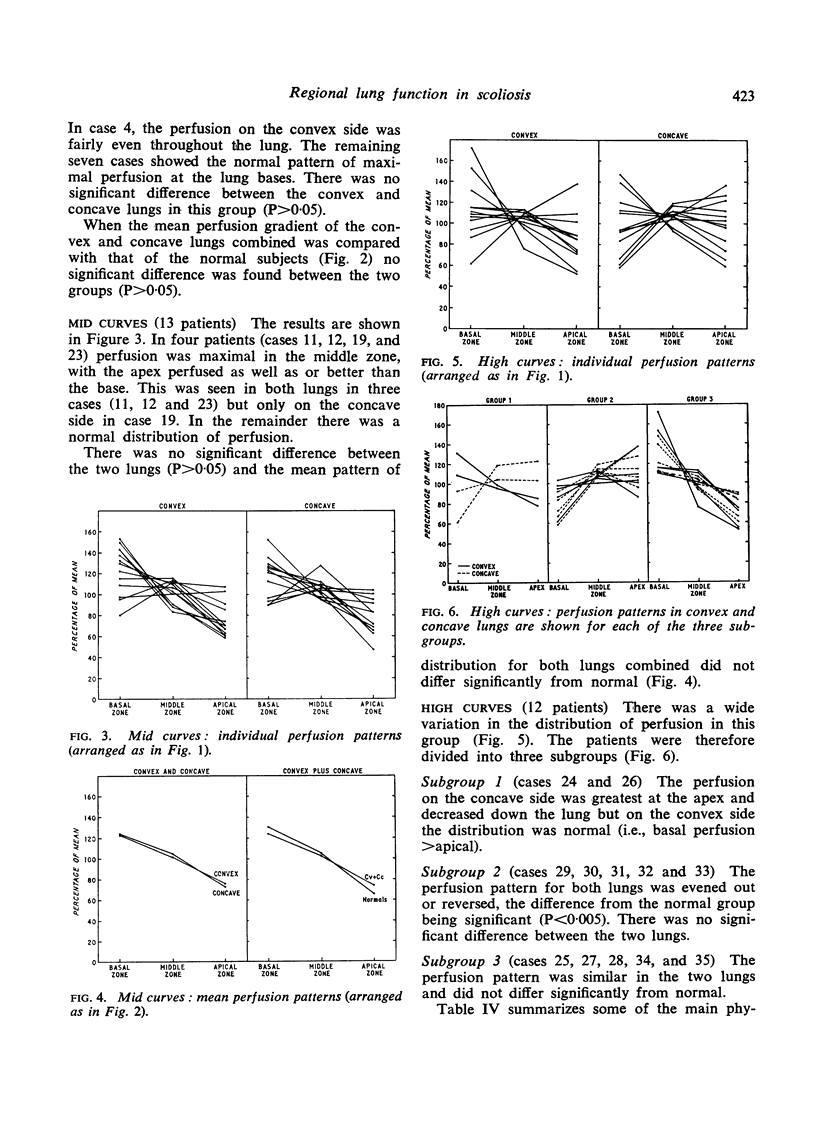
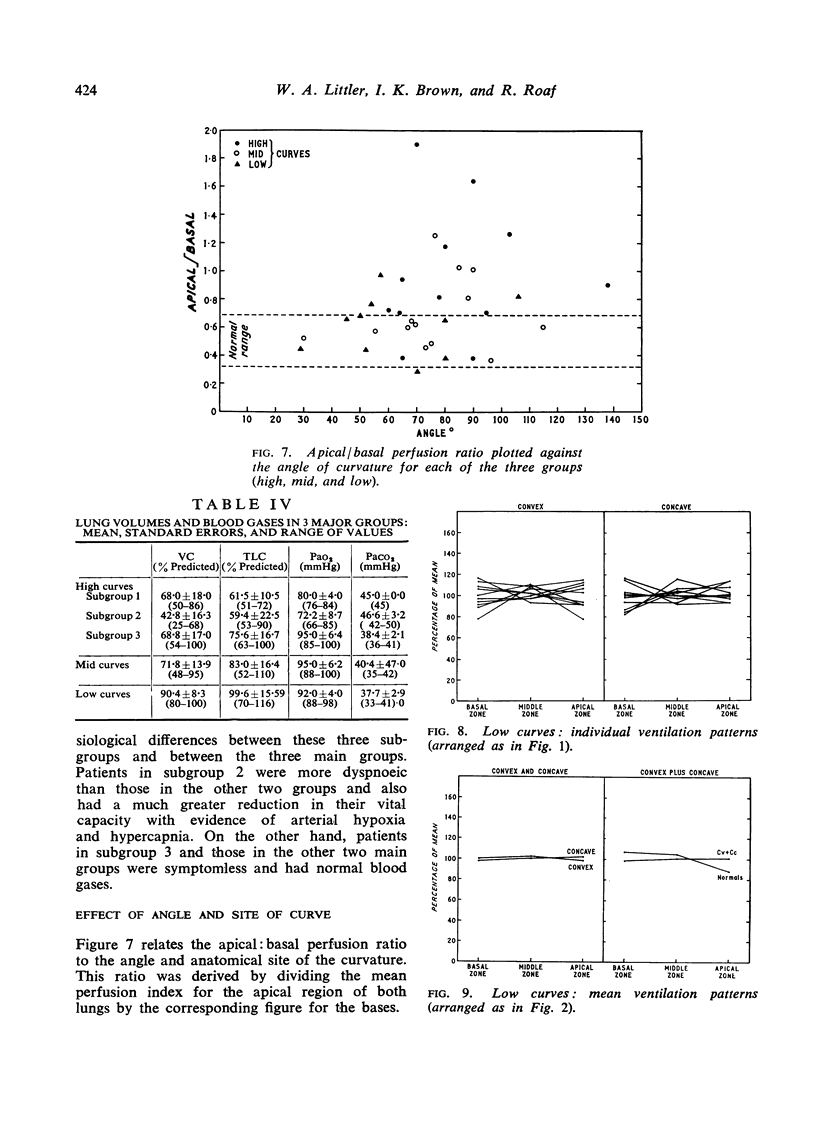
The mean pattern of perfusion in patients with low and mid curves was not significantly different from that of the normals, nor was there any significant difference between the convex and concave lungs in these two groups. Patients with high curves showed three distinct patterns: [List: see text]
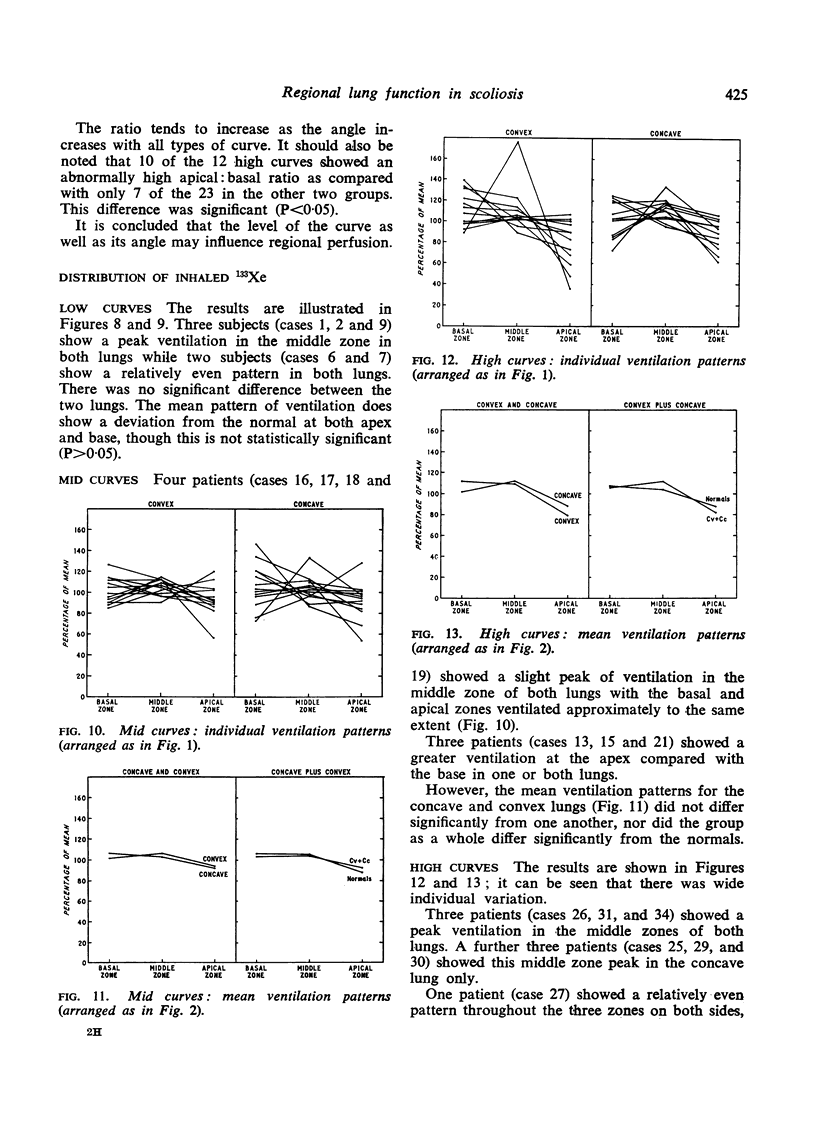
The mean pattern of ventilation in the three groups of scoliotic patients was not significantly different from that of the normals although there was wide individual variation. The only patients to show a significantly abnormal ventilation/perfusion ratio were the high group.
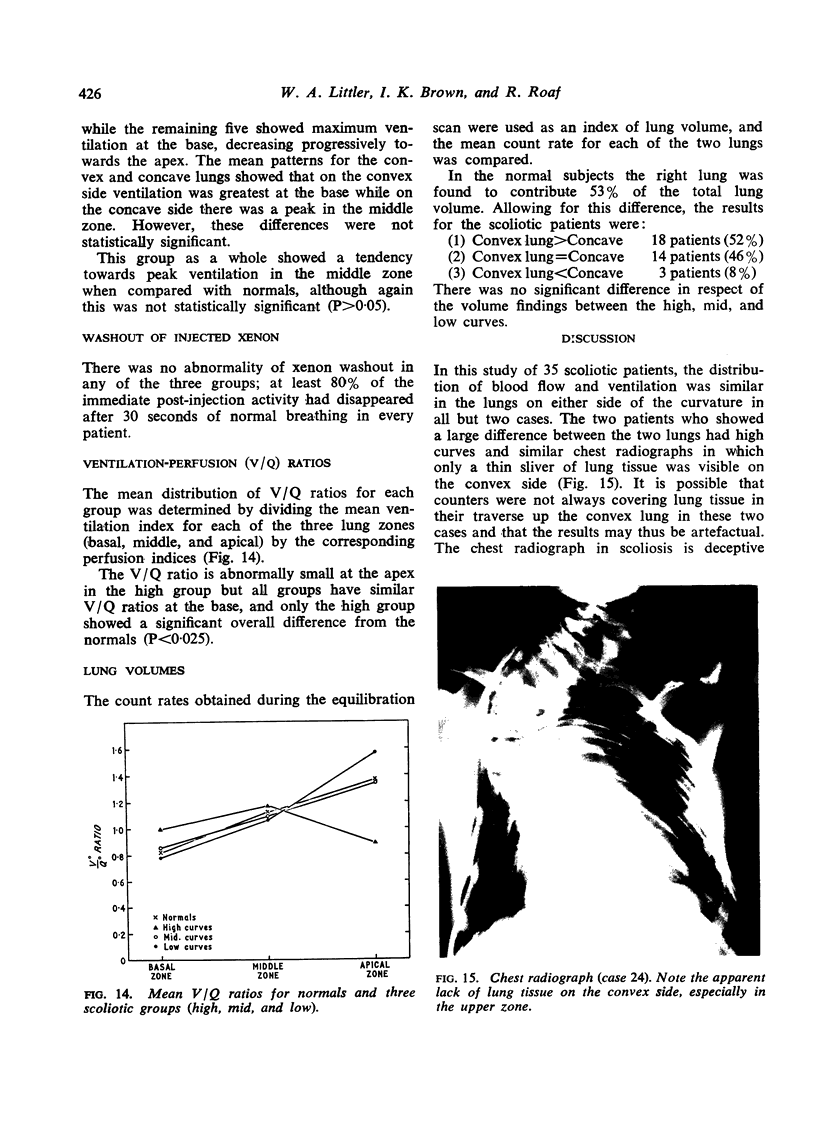
Regional lung volumes calculated from the equilibration scan indicated that in a majority of scoliotics the lung on the convex side of the curvature was larger than that on the concave side.
Our results suggest that both the anatomical site and the angle of the scoliotic curvature have an effect on regional lung function but that this effect falls equally on the convex and concave lungs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALL W. C., Jr, STEWART P. B., NEWSHAM L. G., BATES D. V. Regional pulmonary function studied with xenon 133. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:519–531. doi: 10.1172/JCI104505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGOFSKY E. H., TURINO G. M., FISHMAN A. P. Cardiorespiratory failure in kyphoscoliosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1959 Sep;38:263–317. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195909000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bwn I. K., Kirk F., Seaton A. A scanner stand for pulmonary function studies. Br J Radiol. 1969 Jul;42(499):545–548. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-42-499-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON A., KANEKO K., MCGREGOR M. REGIONAL LUNG FUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH MITRAL STENOSIS STUDIED WITH XENON-133 DURING AIR AND OXYGEN BREATHING. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jun;44:999–1008. doi: 10.1172/JCI105217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLLERY C. T., GILLAM P. M., HUGH-JONEP, ZORAB P. A. REGIONAL LUNG FUNCTION IN KYPHOSCOLIOSIS. Thorax. 1965 Mar;20:175–181. doi: 10.1136/thx.20.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLLERY C. T., GILLAM P. M. THE DISTRIBUTION OF BLOOD AND GAS WITHIN THE LUNGS MEASURED BY SCANNING AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF 133XE. Thorax. 1963 Dec;18:316–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.18.4.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLLERY C. T., HUGH-JONES P., MATTHEWS C. M. Use of radioactive xenon for studies of regional lung function. A comparison with oxygen-15. Br Med J. 1962 Oct 20;2(5311):1006–1016. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5311.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaziano D., Seaton A., Ogilvie C. Regional lung function in patients with obstructive lung diseases. Br Med J. 1970 May 9;2(5705):330–333. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5705.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANLEY T., PLATTS M. M., CLIFTON M., MORRIS T. L. Heart failure of the hunchback. Q J Med. 1958 Apr;27(106):155–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasleton P. S., Heath D., Brewer D. B. Hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease in states of chronic hypoxia. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(2):431–440. doi: 10.1002/path.1700950213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Glazier J. B., Maloney J. E., West J. B. Effect of lung volume on the distribution of pulmonary blood flow in man. Respir Physiol. 1968 Jan;4(1):58–72. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(68)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAEYE R. L. Kyphoscoliosis and cor pulmonale; a study of the pulmonary vascular bed. Am J Pathol. 1961 May;38:561–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINMANN E. P. Die Funktionsprufung der einzelnen Lunge bei der Kyphoskoliose. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1951;80(2):202–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UEDA H., IIO M., KAIHARA S. DETERMINATION OF REGIONAL PULMONARY BLOOD FLOW IN VARIOUS CARDIOPULMONARY DISORDERS. STUDY AND APPLICATION OF MACROAGGREGATED ALBUMIN (MAA) LABELLED WITH I-131 (I). Jpn Heart J. 1964 Sep;5:431–444. doi: 10.1536/ihj.5.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]