Abstract
Hutchison, D. C. S., Barter, C. E., and Martelli, N. A. (1973).Thorax, 28, 584-587. Errors in the measurement of vital capacity: a comparison of three methods in normal subjects and in patients with pulmonary emphysema. Three methods of measuring the vital capacity have been compared in six normal subjects and in six with pulmonary emphysema, according to a randomized design. The methods were (a) the inspiratory vital capacity (IVC), (b) the expiratory vital capacity (EVC), and (c) the forced vital capacity (FVC).
In normal subjects, there was a small but significant difference between the methods. The residual standard deviation derived from analysis of variance was 94 ml (coefficient of variation 1.7%). A slight but significant rise in vital capacity with repeated effort was observed.
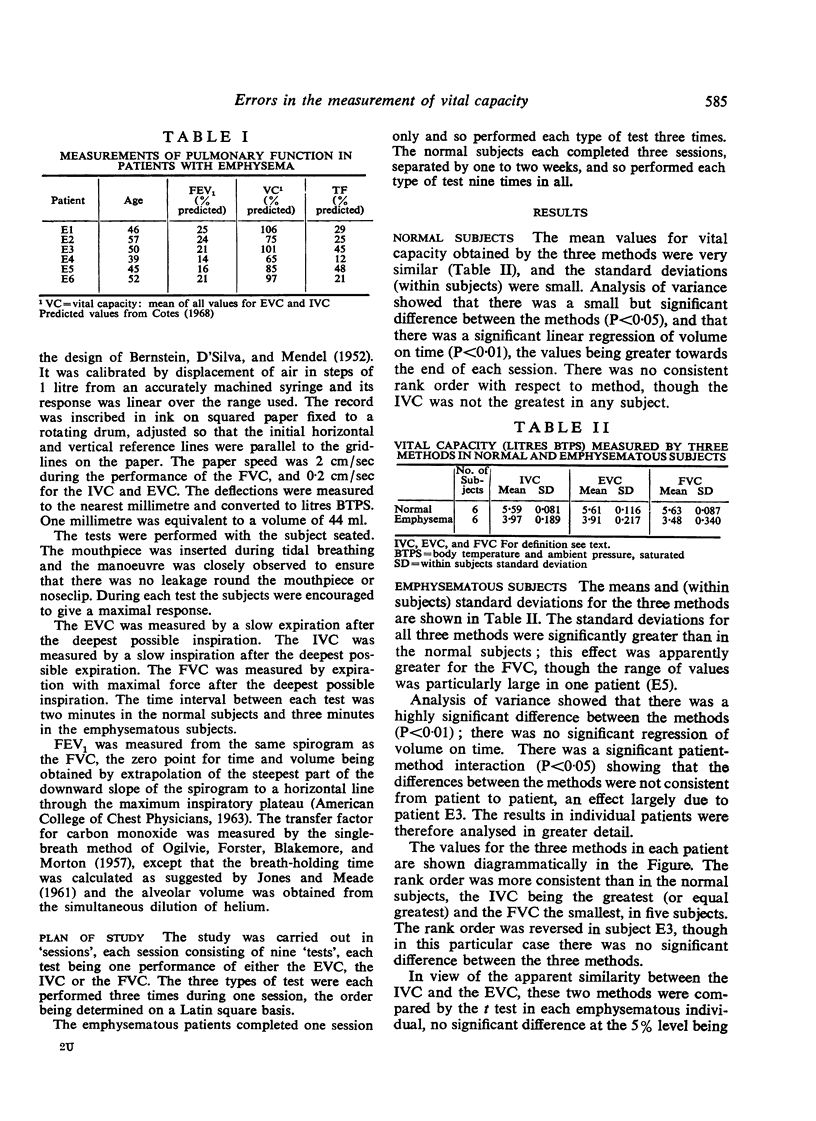
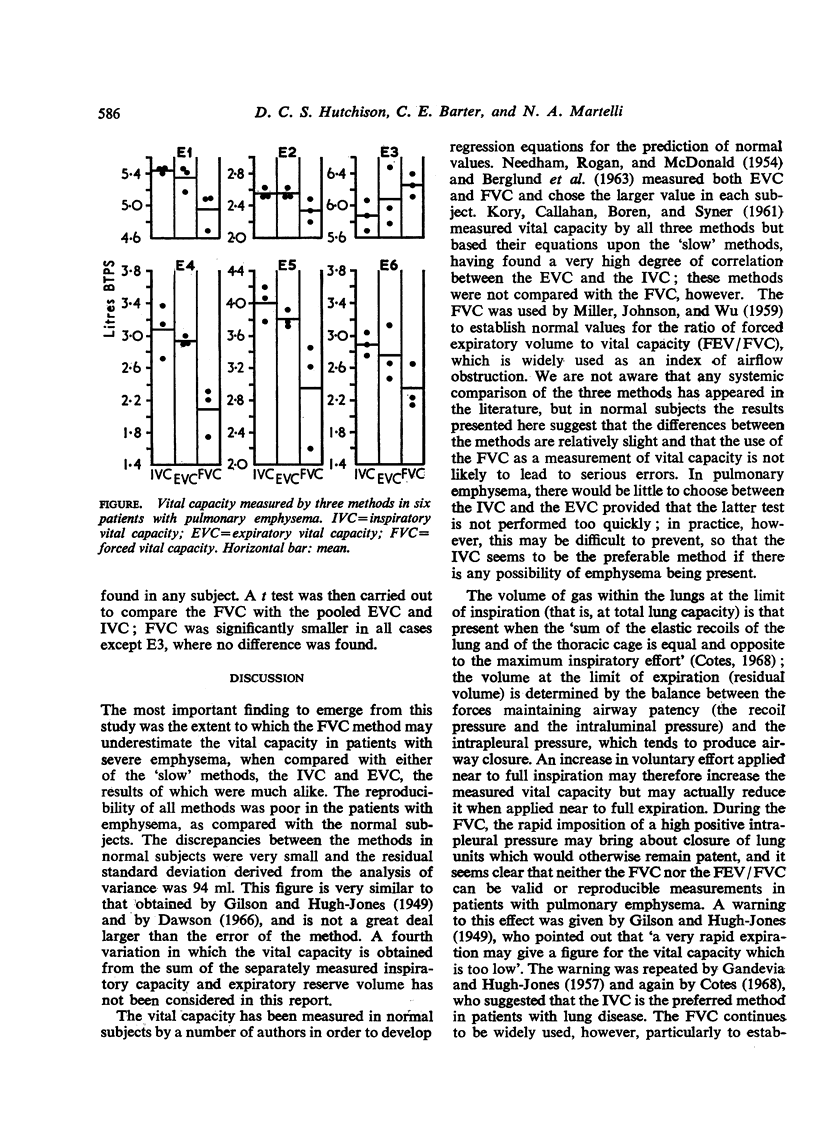
In emphysematous subjects, there was no significant difference between the IVC and EVC methods. The FVC gave values which were, on average, approximately 0.5 litre less than those obtained by the other methods. The standard deviation in all three methods was substantially greater than for the normal subjects.
The FVC is not a suitable method for the measurement of vital capacity in patients with pulmonary emphysema. The EVC is satisfactory, provided it is used with caution, but in practice the IVC is the preferred method.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGLUND E., BIRATH G., BJURE J., GRIMBY G., KJELLMER I., SANDQVIST L., SODERHOLM B. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. I. Forced expirograms in subjects between 7 and 70 years of age. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Feb;173:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSTEIN L., D'SILVA J. L., MENDEL D. The effect of the rate of breathing on the maximum breathing capacity determined with a new spirometer. Thorax. 1952 Sep;7(3):255–262. doi: 10.1136/thx.7.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. Reproducibility of spirometric measurements in normal subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Feb;93(2):264–268. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.93.2.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANDEVIA B., HUGH-JONES P. Terminology for measurements of ventilatory capacity; a report to the thoracic society. Thorax. 1957 Dec;12(4):290–293. doi: 10.1136/thx.12.4.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison D. C., Cook P. J., Barter C. E., Harris H., Hugh-Jones P. Pulmonary emphysema and alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency. Br Med J. 1971 Mar 27;1(5751):689–694. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5751.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. S., MEADE F. A theoretical and experimental analysis of anomalies in the estimation of pulmonary diffusing capacity by the single breath method. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1961 Apr;46:131–143. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1961.sp001525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORY R. C., CALLAHAN R., BOREN H. G., SYNER J. C. The Veterans Administration-Army cooperative study of pulmonary function. I. Clinical spirometry in normal men. Am J Med. 1961 Feb;30:243–258. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER W. F., JOHNSON R. L., Jr, WU N. Relationships between fast vital capacity and various timed expiratory capacities. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Mar;14(2):157–163. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


