Abstract
Jastrzebski, J., Sykes, M. K., and Woods, D. G. (1974).Thorax, 29, 534-538. Cardiorespiratory effects of protamine after cardiopulmonary bypass in man. The cardiorespiratory changes following the injection of protamine sulphate (6 mg/kg) were studied in 15 patients who had undergone cardiopulmonary bypass. There was a transient fall in arterial pressure and a more prolonged increase in pulmonary artery pressure. There was a significant fall in arterial oxygen tension which was mainly due to a reduction in mixed venous oxygen tension resulting from a fall in cardiac output. Dead space/tidal volume ratio and percentage shunt did not change significantly.
Full text
PDF
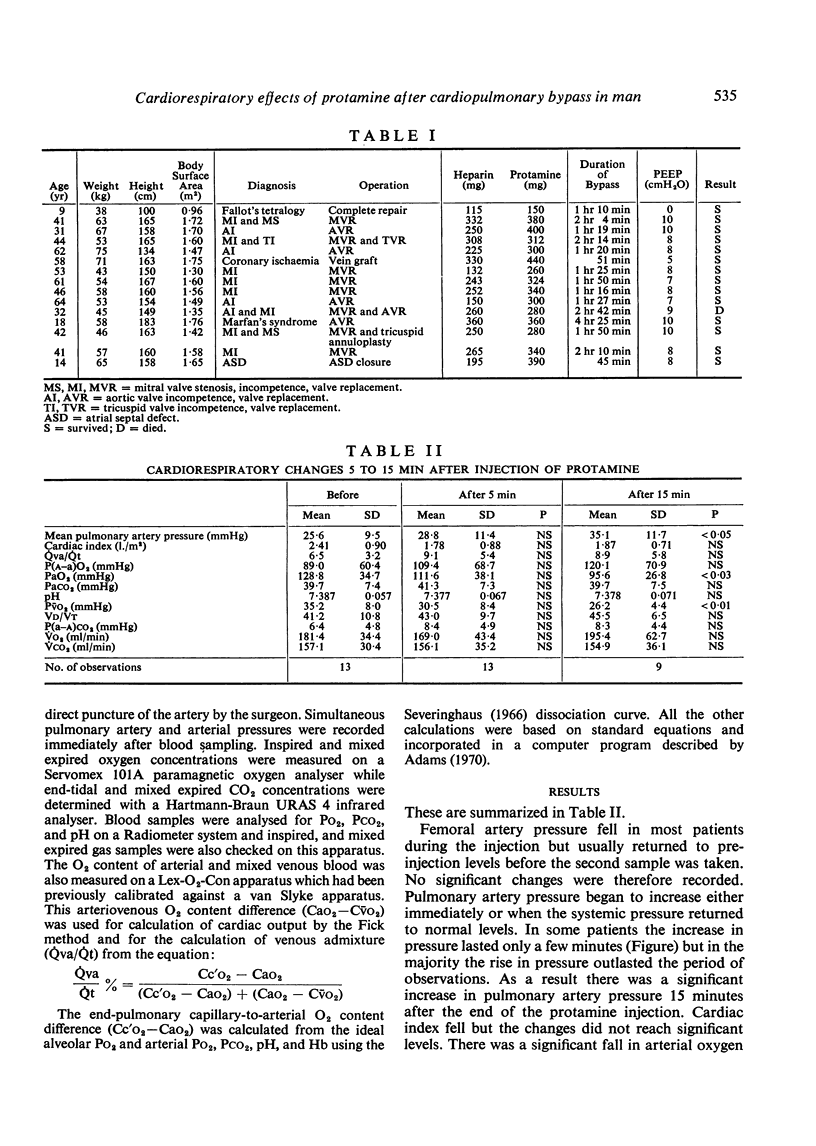


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd A. D., Engelman R. M., Beaudet R. L., Lackner H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation following extracorporeal circulation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1972 Nov;64(5):685–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda A. R., Gans H., Weber K. C., Fox I. J. Heparin neutralization: experimental and clinical studies. Surgery. 1967 Oct;62(4):686–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda A. R. Must heparin be neutralized following open-heart operations? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1966 Nov;52(5):716–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman B. S., Joison J., Austen W. G. Cardiovascular effects of protamine sulfate. Ann Thorac Surg. 1969 May;7(5):459–471. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)66210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourin A., Streisand R. L., Stuckey J. H. Total cardiopulmonary bypass, myocardial contractility, and the administration of protamine sulfate. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1971 Jan;61(1):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröttum K. A. Platelet surface charge and aggregation. Effects of polyelectrolytes. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Jun 15;21(3):450–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS H. A., HARKINS G., GERBODE F., ROLFS M. R., ACRA D. J. Comparison of effects of protamine and polybrene, with special emphasis on the factor VIII (antihemophilic globulin) deficiency induced. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1421–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI104373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. W. Role of carbon dioxide in changes in lung mechanics after protamine administration. Anesth Analg. 1972 Sep-Oct;51(5):733–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauca A., Sykes M. K. The elimination of carbon dioxide after total body perfusion. Br J Anaesth. 1966 Jan;38(1):39–49. doi: 10.1093/bja/38.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rådegran K., Taylor G. A., Olsson P. Mode of action of protamine in regard to its circulatory and respiratory side effects. Eur Surg Res. 1971;3(2):139–148. doi: 10.1159/000127560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed R. F., Sykes M. K., Finlay W. E. The effect of variations in end-expiratory inflation pressure on cardiorespiratory function before and after open-heart surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1970 Jun;42(6):488–496. doi: 10.1093/bja/42.6.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinghaus J. W. Blood gas calculator. J Appl Physiol. 1966 May;21(3):1108–1116. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.3.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M. K. A mixing device for expired gas. Anaesthesia. 1968 Jul;23(3):446–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1968.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M. K., Adams A. P., Finlay W. E., McCormick P. W., Economides A. The effects of variations in end-expiratory inflation pressure on cardiorespiratory function in normo-, hypo-and hypervolaemic dogs. Br J Anaesth. 1970 Aug;42(8):669–677. doi: 10.1093/bja/42.8.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker A. N., McKay D. G. Induction of hypotension in rhesus monkeys and rabbits by intravenous thrombin infusion. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):79–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. E., Kirklin J. W., Owen C. A., Jr, Thompson J. H., Jr, Taswell H. F. Effect of bypass surgery on coagulation-sensitive clotting factors. Mayo Clin Proc. 1967 Nov;42(11):724–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbinden G., Mehrishi J. N., Tomlin S. Assessment of damage to human platelets after aggregation and other injuries by microscopic observation and estimation of serotonin uptake. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 May 31;23(2):261–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]