Abstract
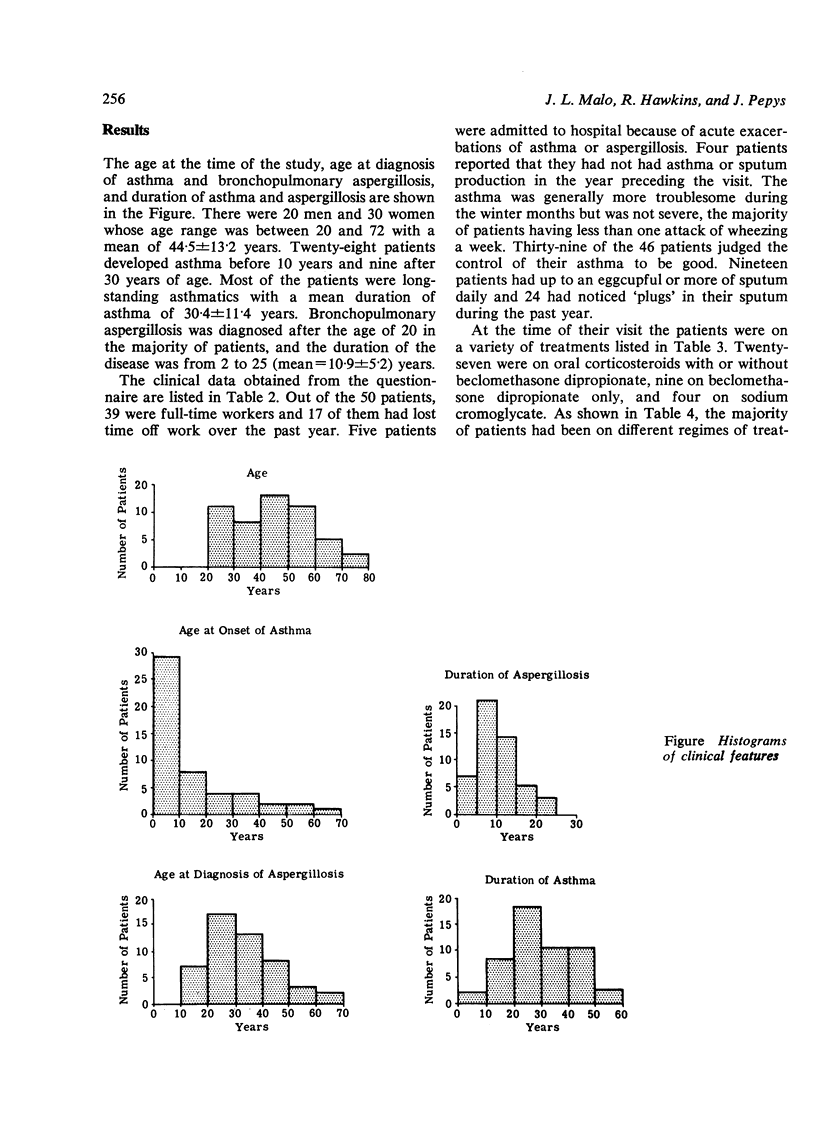
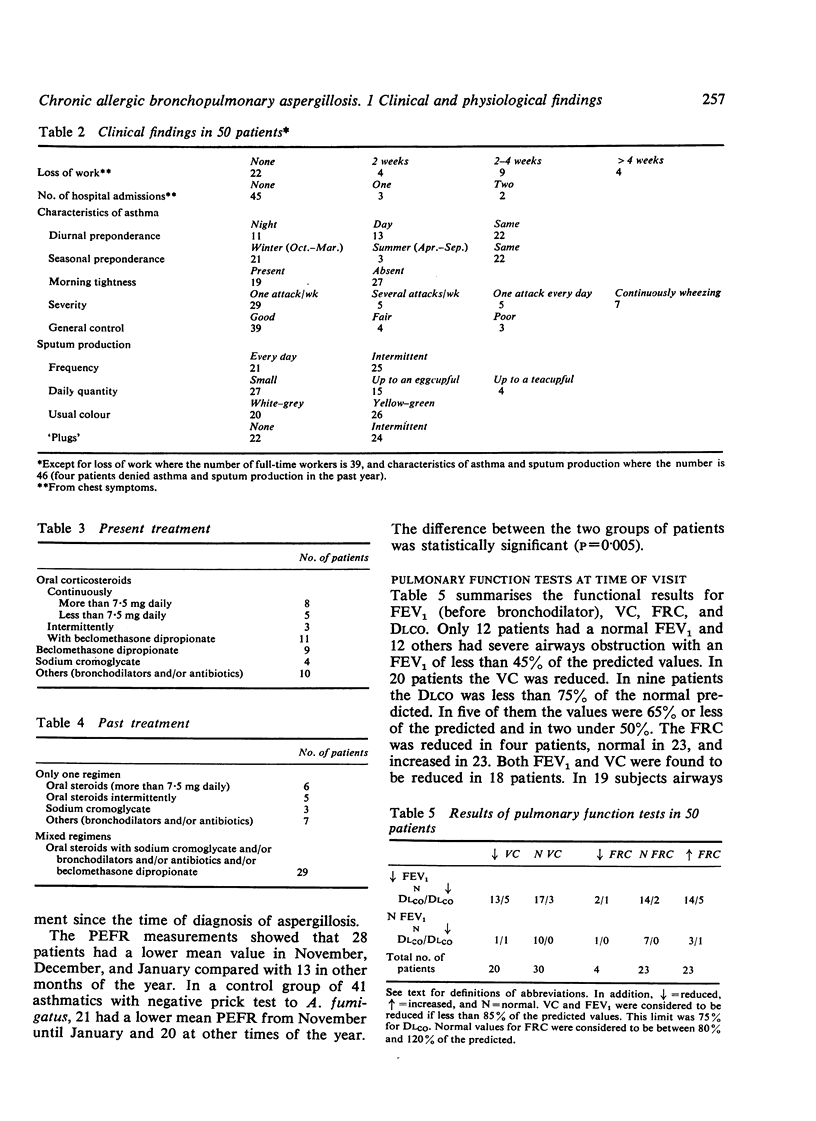
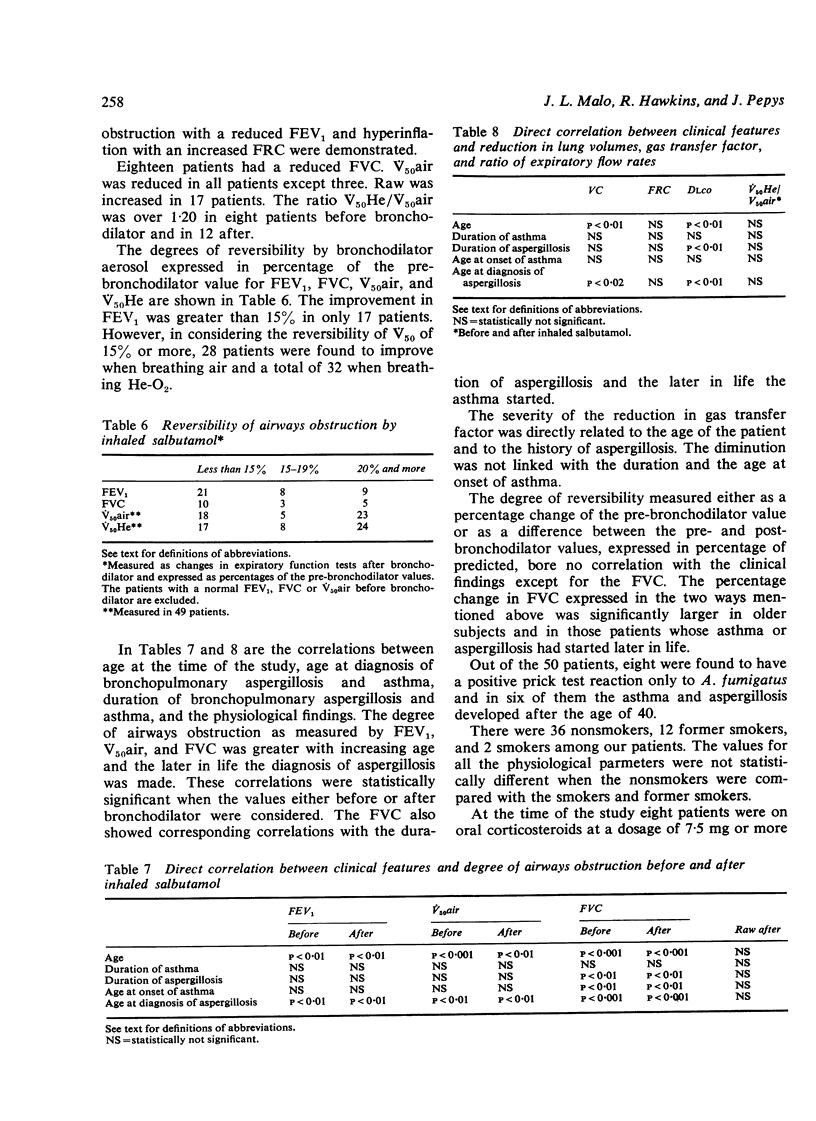
This report outlines the clinical and physiological features in 50 asthmatic patients with chronic allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in whom the diagnosis was made from 2 to 25 years ago (mean duration 10-9 years). From a questionnaire and analysis of the peak expiratory flow rate measurements it was found that they were worse in the winter months, corresponding to the maximal concentrations of Aspergillus fumigatus in the atmosphere. Nineteen patients reported daily sputum production of up to an eggcupful or more, and 24 had noticed sputum 'plugs' in the previous year. Reduction of vital capacity (VC) was found in 20 patients, of forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) in 38 patients, and of maximal expiratory flow at 50% VC breathing air (V50air) in 47 patients. Nine patients had significantly reduced gas transfer factor (DLCO). Significant improvement (more than 15%) in FEV1 after inhaled bronchodilator was shown by only 17 patients. There were statistically significant correlations between the degree of reduction in the physiological measurements of VC, FEV1, and V50air with the age of the patient at the time of the study and the later in life the diagnosis of aspergillosis was made, whereas the reduction in DLCO was also significantly related to the duration of aspergillosis. Prospective studies are needed for a proper assessment of any protective effect of treatment on the pathophysiological changes due to the disease over many years.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass H. The flow volume loop: normal standards and abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest. 1973 Feb;63(2):171–176. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benatar S. R., Clark T. J., Cochrane G. M. Clinical relevance of the flow rate response to low density gas breathing in asthmatics. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Feb;111(2):126–134. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.2.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherniack N. S., Carton R. W. Factors associated with respiratory insufficiency in bronchiectasis. Am J Med. 1966 Oct;41(4):562–571. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despas P. J., Leroux M., Macklem P. T. Site of airway obstruction in asthma as determined by measuring maximal expiratory flow breathing air and a helium-oxygen mixture. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3235–3243. doi: 10.1172/JCI107150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. I., BECKLAKE M. R. Respiratory function tests; normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Apr;79(4):457–467. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golbert T. M., Patterson R. Pulmonary allergic aspergillosis. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Mar;72(3):395–403. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Mead J., Hoppin F., Wohl M. E. Analysis of the forced expiratory maneuver. Chest. 1973 Apr;63(Suppl):33S–36S. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.4_supplement.33s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINSON K. F. W., MOON A. J., PLUMMER N. S. Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis; a review and a report of eight new cases. Thorax. 1952 Dec;7(4):317–333. doi: 10.1136/thx.7.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. H. Allergic aspergillosis: review of 32 cases. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):501–512. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Immunologic lung disease due to Aspergillus. Chest. 1975 Sep;68(3):346–355. doi: 10.1378/chest.68.3.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau L. I., Phelan P. D., Williams H. E. Ventilatory mechanics in patients with bronchiectasis starting in childhood. Thorax. 1974 May;29(3):304–312. doi: 10.1136/thx.29.3.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo J. L., Leblanc P. Functional abnormalities in young asymptomatic smokers with special reference to flow volume curves breathing various gases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 May;111(5):623–629. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.5.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo J. L., Pepys J., Simon G. Studies in chronic allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. 2. Radiological findings. Thorax. 1977 Jun;32(3):262–268. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.3.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. S., Pepys J. Allergic broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis. Clinical immunology. 2. Skin, nasal and bronchial tests. Clin Allergy. 1971 Dec;1(4):415–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb00793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. S., Simon G., Hargreave F. E. The radiological appearances in allergic broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis. Clin Radiol. 1970 Oct;21(4):366–375. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(70)80070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGRATH M. W., THOMSON M. L. The effect of age, body size and lung volume change on alveolar-capillary permeability and diffusing capacity in man. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 11;146(3):572–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBLE W. C., CLAYTON Y. M. FUNGI IN THE AIR OF HOSPITAL WARDS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:397–402. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPYS J., RIDDELL R. W., CITRON K. M., CLAYTON Y. M., SHORT E. I. Clinical and immunologic significance of Aspergillus fumigatus in the sputum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Aug;80:167–180. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pande J. N., Jain B. P., Gupta R. G., Guleria J. S. Pulmonary ventilation and gas exchange in bronchiectasis. Thorax. 1971 Nov;26(6):727–733. doi: 10.1136/thx.26.6.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safirstein B. H., D'Souza M. F., Simon G., Tai E. H., Pepys J. Five-year follow-up of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Sep;108(3):450–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.3.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


