Abstract
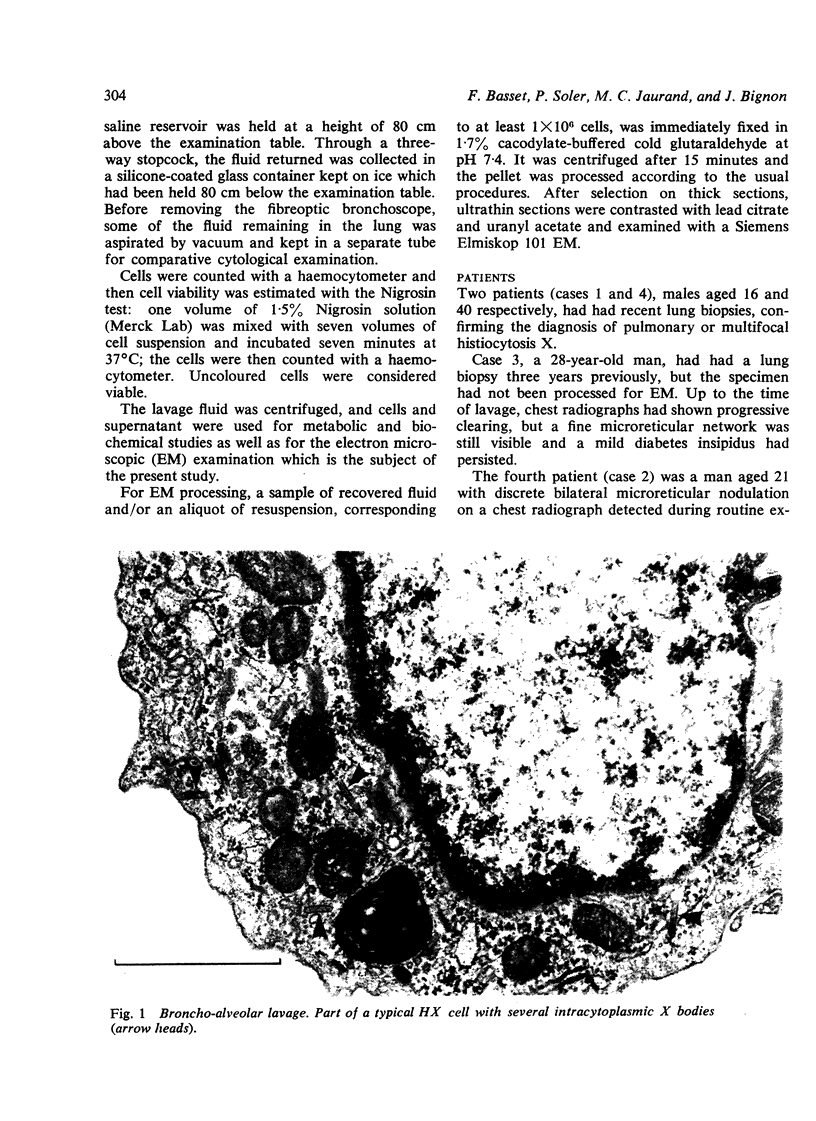
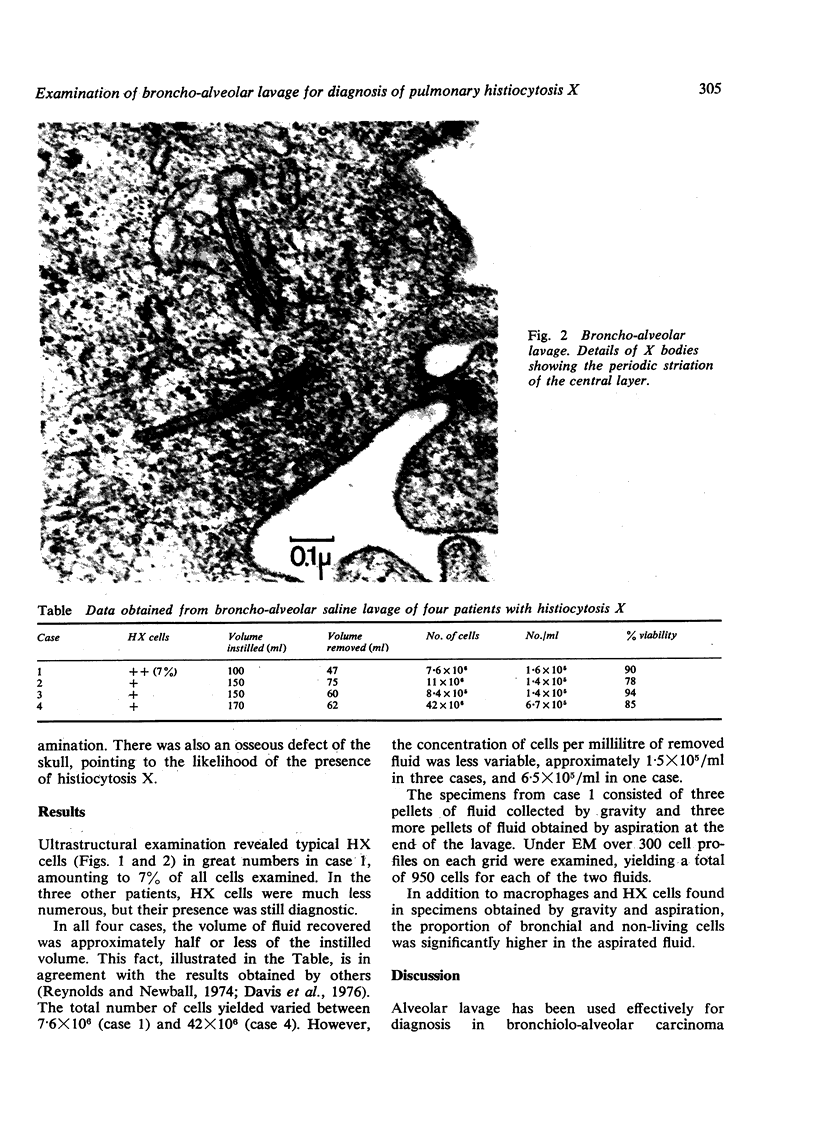
Fibreoptic broncho-alveolar lavage was used in four patients; the diagnosis of histiocytosis X had been established by lung biopsy in three and was suggested on clinical grounds in the remaining patient. Characteristic cells with an ultrastructural cytoplasmic marker (X body) were found in the washes of all four patients. In the patient without biopsy confirmation, the findings in the broncho-aleolar washes supplied the corroborating evidence for the diagnosis. From this preliminary study the technique seems able to provide a diagnosis in pulmonary histiocytosis X without the need for an open lung biopsy.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basset F., Nezelof C. L'histiocytose X. Microscopie électronique. Culture "in vitro" et histo-enzymologie. Discussion à propos de 21 cas. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1969 Jan;14(1):31–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset F., Nézelof C., Turiaf J. Présence en microscopie électronique de structures filamenteuses originales dans les lésions pulmonaires et osseuses de l'histiocytose x. Etat actuel de la question. Bull Mem Soc Med Hop Paris. 1966 Mar 25;117(5):413–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset F., Soler P., Wyllie L., Mazin F., Turiaf J. Langerhans' cells and lung interstitium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;278:599–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello J. F., Moriarty D. C., Branthwaite M. A., Turner-Warwick M., Corrin B. Diagnosis and management of alveolar proteinosis: the rôle of electron microscopy. Thorax. 1975 Apr;30(2):121–132. doi: 10.1136/thx.30.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S., Brody A. R., Landis J. N., Graham W. G., Craighead J. E., Green G. M. Quantitation of inflammatory activity in interstitial pneumonitis by bronchofiberscopic pulmonary lavage. Chest. 1976 Feb;69(2 Suppl):265–266. doi: 10.1378/chest.69.2_supplement.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins P. K., Swenson E. W., Hackett R. L., Coalson J. J. Alveolar cell carcinoma. Diagnosis by lobar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Apr;107(4):665–669. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley T. N., Swenson E. W., Curran W. S., Huber G. L., Ladman A. J. Bronchopulmonary lavage in normal subjects and patients with obstructive lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Apr;66(4):651–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-4-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Newball H. H. Analysis of proteins and respiratory cells obtained from human lungs by bronchial lavage. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):559–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K. The langerhans cell. Curr Probl Dermatol. 1972;4:79–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager H., Jr, Zimmet S. M., Schwartz S. L. Pinocytosis by human alveolar macrophages. Comparison of smokers and nonsmokers. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):247–251. doi: 10.1172/JCI107759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]