Abstract
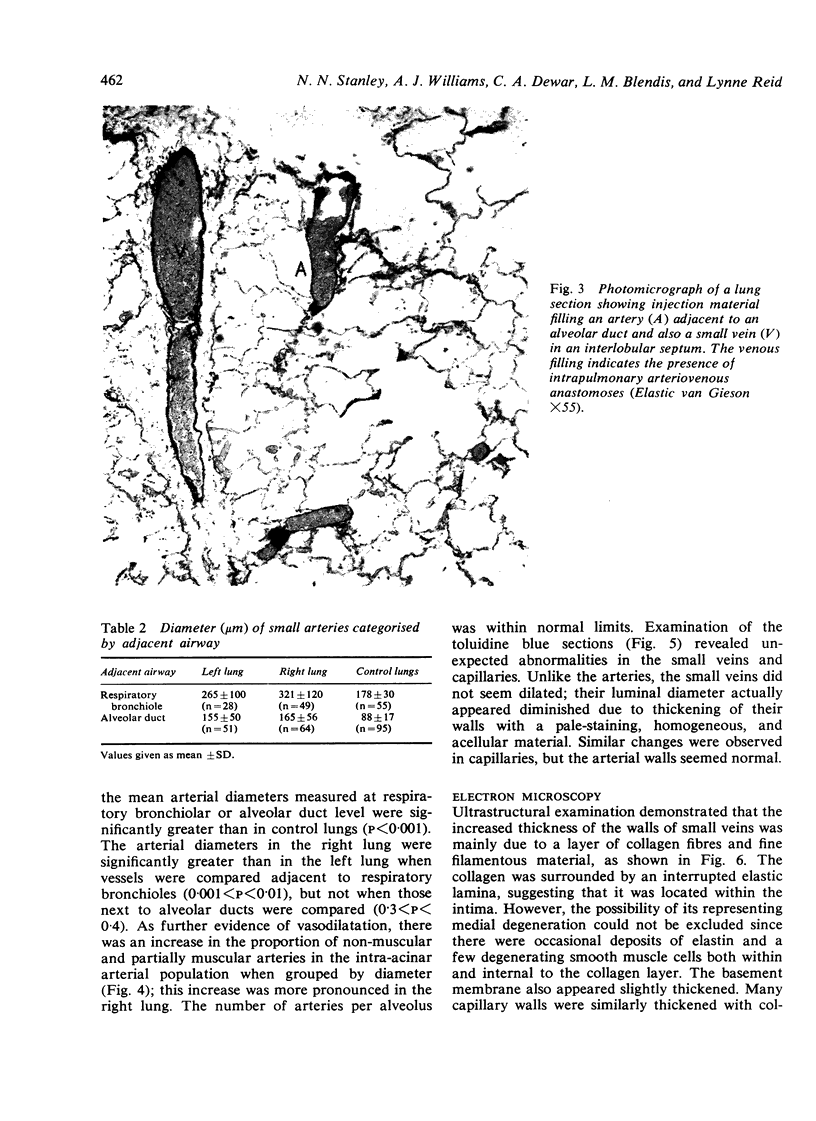
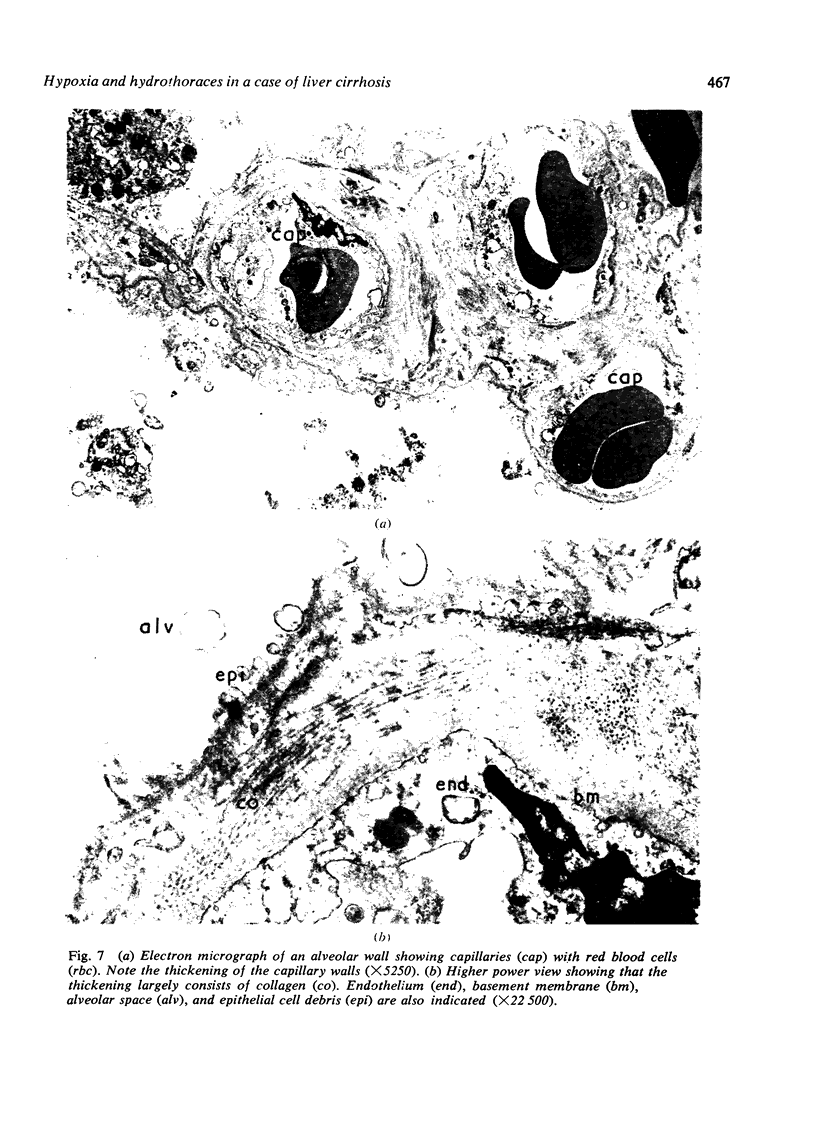
Stanley, N. N., Williams, A. J., Dewar, C. A., Blendis, L. M., and Reid, Lynne (1977).Thorax, 32, 457-471. Hypoxia and hydrothoraces in a case of liver cirrhosis: correlation of physiological, radiographic, scintigraphic, and pathological findings. A case is reported of liver cirrhosis complicated by cyanosis and recurrent right hydrothorax. A diagnostic pneumoperitoneum demonstrated that direct movement of ascites through a diaphragmatic defect was responsible for the hydrothoraces. Pulmonary function tests between episodes of hydrothorax showed severe arterial hypoxaemia, a 23% right-to-left shunt, and a reduction in the carbon monoxide transfer factor to less than half of the predicted value. Evidence of abnormal intrapulmonary arteriovenous communications was obtained by perfusion scanning. At necropsy the central tendon of the diaphragm showed numerous areas of thinning which were easily ruptured. Injection of the pulmonary arterial tree demonstrated precapillary arteriovenous anastomoses and pleural spider naevi. A morphometric analysis provided quantitative evidence of pulmonary vasodilatation limited to the intra-acinar arteries, consistent with the effect of a circulating vasodilator. The scintigraphic and pathological findings suggested that shunting had been greater in the right than the left lung. Examination of thin lung sections by light microscopy showed that the walls of small veins were thickened, and electron microscopy showed that this was due to a layer of collagen. The walls of capillaries were similarly thickened, which caused an approximately two-fold increase in the minimum blood-gas distance and contributed to the reduction in transfer factor.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelot P., Walker J. G., Sherlock S., Reid L. Arterial changes in the lungs in cirrhosis of the liver--lung spider nevi. N Engl J Med. 1966 Feb 10;274(6):291–298. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196602102740601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALABRESI P., ABELMANN W. H. Porto-caval and porto-pulmonary anastomoses in Laennec's cirrhosis and in heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1957 Aug;36(8):1257–1265. doi: 10.1172/JCI103523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Field G. B., Brown G. J., Read A. E. Impairment of lung function after portacaval anastomosis. Lancet. 1968 May 4;1(7549):952–955. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONT A. E., MULHOLLAND J. H. Flow rate and composition of thoracic-duct lymph in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1960 Sep 8;263:471–474. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196009082631001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G., Reid L. Growth of the alveoli and pulmonary arteries in childhood. Thorax. 1970 Nov;25(6):669–681. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT F. M., REID L. SOME NEW FACTS ABOUT THE PULMONARY ARTERY AND ITS BRANCHING PATTERN. Clin Radiol. 1965 Jul;16:193–198. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(65)80042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMERSON P. A., DAVIES J. H. Hydrothorax complicating ascites. Lancet. 1955 Mar 5;268(6862):487–488. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)90269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emirgil C., Sobol B. J., Heymann B., Shibutani K. Pulmonary function in alcoholics. Am J Med. 1974 Jul;57(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90770-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORG J., TYGSTRUP N., MELLEMGAARD K., WINKLER K. Venoarterial shunts in cirrhosis of the liver. Lancet. 1960 Apr 16;1(7129):852–854. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)90734-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES M. R. Multiple small arteriovenous fistulae of the lungs. Am J Pathol. 1956 Sep-Oct;32(5):927–943. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFBAUER F. W., RYDELL R. Multiple pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas in juvenile cirrhosis. Am J Med. 1956 Sep;21(3):450–460. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Haworth S. G., Shinebourne E. A., Reid L. Quantitative structural analysis of pulmonary vessels in isolated ventricular septal defect in infancy. Br Heart J. 1975 Oct;37(10):1014–1021. doi: 10.1136/hrt.37.10.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. Intra-pulmonary arterial development during fetal life-branching pattern and structure. J Anat. 1972 Oct;113(Pt 1):35–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON R. F., LOO R. V. HEPATIC HYDROTHORAX; STUDIES TO DETERMINE THE SOURCE OF THE FLUID AND REPORT OF THIRTEEN CASES. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Sep;61:385–401. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-3-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish A. J., Marshall R., Reid L., Sherlock S. Cyanosis with hepatic cirrhosis. A case with pulmonary arteriovenous shunting. Thorax. 1967 Nov;22(6):555–561. doi: 10.1136/thx.22.6.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravath R. E., Scarpelli E. M., Bernstein J. Hepatogenic cyanosis: arteriovenous shunts in chronic active hepatitis. J Pediatr. 1971 Feb;78(2):238–245. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman F. L., Hidemura R., Peters R. L., Reynolds T. B. Pathogenesis and treatment of hydrothorax complicating cirrhosis with ascites. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Feb;64(2):341–351. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-64-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman F. L., Peters R. L. Cirrhotic hydrothorax. Further evidence that an acquired diaphragmatic defect is at fault. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jan;125(1):114–117. doi: 10.1001/archinte.125.1.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORROW C. S., KANTOR M., ARMEN R. N. Hepatic hydrothorax. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Jul;49(1):193–203. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-49-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkin F. S., Brashear R. E. An experimental study of the effect of free pleural fluid on the lung scan. Radiology. 1970 Nov;97(2):283–287. doi: 10.1148/97.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAMURA T., NAKAMURA S., TAZAWA T., ABE S., AIKAWA T., TOKITA K. MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD FLOW THROUGH PORTOPULMONARY ANASTOMOSIS IN PORTAL HYPERTENSION. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Jan;65:114–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIDEN A. H., AVIADO D. M., Jr Effects of pulmonary embolism on the pulmonary circulation with special reference to arteriovenous shunts in the lung. Circ Res. 1956 Jan;4(1):67–73. doi: 10.1161/01.res.4.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovsky B. V., Milonov O. B. "Arterialization" and "venization" of vessels involved in traumatic arteriovenous fistulae: aetiology and pathogenesis. (An experimental study). J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1967 Sep-Oct;8(5):396–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN T., HURWITZ J. K., PASTOR B. H., CLOSE H. P. Cyanosis, clubbing and arterial oxygen unsaturation associated with Laennec's cirrhosis. Am J Med Sci. 1959 Nov;238:534–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin E. D., Horn B., Goris M. L., Theodore J., Kessel A. V., Mazoub J., Tilkian A. Detection, quantitation and pathophysiology of lung "spiders". Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1975;88:202–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff F., Hughes J. M., Stanley N., McCarthy D., Greene R., Aronoff A., Clayton L., Milic-Emili J. Regional lung function in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2403–2413. doi: 10.1172/JCI106739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKNER M. A., FEISAL K. A., KARSCH D. N. SIZE OF GAS EXCHANGE VESSELS IN THE LUNG. J Clin Invest. 1964 Sep;43:1847–1855. doi: 10.1172/JCI105058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORR E., ZWEIFACH B. W., FURCHGOTT R. F., BAEZ S. Hepatorenal factors in circulatory homeostasis. IV. Tissue origins of the vasotropic principles, VEM and VDM, which appear during evolution of hemorrhagi and tourniquet shock. Circulation. 1951 Jan;3(1):42–79. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.3.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAUB N. C. Microcirculation of the lung utilizing very rapid freezing. Angiology. 1961 Oct;12:469–472. doi: 10.1177/000331976101201006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Mutt V. Polypeptide with broad biological activity: isolation from small intestine. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1217–1218. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schomerus H., Buchta I., Arndt H. Pulmonary function studies and oxygen transfer in patients with liver cirrhosis and different degree of portasystemic encephalopathy. Respiration. 1975;32(1):1–20. doi: 10.1159/000193632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman A., Cooper M. D., Moller J. H., Good R. A. Syndrome of cyanosis, digital clubbing, and hepatic disease in siblings. J Pediatr. 1968 Jan;72(1):70–80. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley N. N., Ackrill P., Wood J. Lung perfusion scanning in hepatic cirrhosis. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 16;4(5841):639–643. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5841.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley N. N., Woodgate D. J. Mottled chest radiograph and gas transfer defect in chronic liver disease. Thorax. 1972 May;27(3):315–323. doi: 10.1136/thx.27.3.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley N. N., Woodgate D. J. The circulation, the lung, and finger clubbing in hepatic cirrhosis. Br Heart J. 1971 Jul;33(4):469–472. doi: 10.1136/hrt.33.4.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin C. E. Arteriovenous shunts in the peripheral pulmonary circulation in the human lung. Thorax. 1966 May;21(3):197–204. doi: 10.1136/thx.21.3.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toghill P. J., Smith P. G., Benton P., Brown R. C., Matthews H. L. Methyldopa liver damage. Br Med J. 1974 Aug 31;3(5930):545–548. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5930.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS M. H., Jr Pleural effusion produced by abdomino-pleural communication in a patient with Laennec's cirrhosis of the liver and ascites. Ann Intern Med. 1950 Jul;33(1):216–221. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-33-1-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON R. H., EBERT R. V., BORDEN C. W., PEARSON R. T., JOHNSON R. S., FALK A., DEMPSEY M. E. The determinations of blood flow through nonventilated portions of the normal and diseased lung. Am Rev Tuberc. 1953 Aug;68(2):177–187. doi: 10.1164/art.1953.68.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whimster W. F., Macfarlane A. J. Normal lung weights in a white population. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Oct;110(4):478–483. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.4.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]