Abstract
Increased ploidy is common in tumors but treatments for tumors with excess chromosome sets are not available. Here, we characterize high-ploidy breast cancers and identify potential anticancer compounds selective for the high-ploidy state. Among 354 human breast cancers, 10% have mean chromosome copy number exceeding 3, and this is most common in triple negative and HER2-positive types. Women with high-ploidy breast cancers have higher risk of recurrence and death in two patient cohorts, demonstrating that it represents an important group for improved treatment. Because high-ploidy cancers are aneuploid, rather than triploid or tetraploid, we devised a two-step screen to identify selective compounds. The screen was designed to assure both external validity on diverse karyotypic backgrounds and specificity for high-ploidy cell types. This screen identified novel therapies specific to high-ploidy cells. First, we discovered 8-azaguanine, an antimetabolite that is activated by hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT), suggesting an elevated gene-dosage of HPRT in high-ploidy tumors can control sensitivity to this drug. Second, we discovered a novel compound, 2,3-Diphenylbenzo[g]quinoxaline-5,10-dione (DPBQ). DPBQ activates p53 and triggers apoptosis in a polyploid-specific manner, but does not inhibit topoisomerase or bind DNA. Mechanistic analysis demonstrates that DPBQ elicits a hypoxia gene signature and its effect is replicated, in part, by enhancing oxidative stress. Structure-function analysis defines the core benzo[g]quinoxaline-5,10 dione as being necessary for the polyploid-specific effects of DPBQ. We conclude that polyploid breast cancers represent a high-risk subgroup and that DPBQ provides a functional core to develop polyploid-selective therapy.
Keywords: polyploidy, genome doubling, NCI-60, high throughput screen, Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase, 8-azaguinine, Diphenylbenzo[g]quinoxaline-dione
Introduction
Cancers are commonly aneuploid, with irregular karyotypes. In some cases, during tumor evolution, cancers gain entire chromosome sets and the resulting cells are polyploid (1, 2). Polyploidy confers characteristic alterations to cellular physiology that could be exploited for cancer therapy (3-5), but clinical characteristics of these tumors is unclear. One confounding factor in analysis is that few cancers harbor precise triploid or tetraploid chromosome sets. Instead, tumors may double their genome at an incipient point in oncogenic transformation, by cell-cell fusion, endoreduplication, or cytokinesis failure (6) (7-9). This genome doubling produces tetraploid cells that are buffered from haploinsufficiency, thereby permitting chromosome losses. In addition to permitting genomic abnormalities, the mechanism of genome doubling will generally double centrosomes in concert. The resulting supernumerary centrosomes can promote tumor evolution by enhancing chromosomal gains/losses (10). By buffering against haploinsufficiency and enhancing chromosomal instability, the tetraploid state permits selection of high-ploidy aneuploid states most permissive of tumor growth and resistance (11, 12). It is unsurprising, therefore, that a genome doubling event can promote oncogenic transformation in model systems (13, 14).
The tumor suppressor, p53 places an important restraint on genome doubling. After genome-doubling event, human cells typically elicit a p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest(15). This activation can promote apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Additionally a fraction of cells may undergo interphase cytofission to resolve to a diploid state (16). Nevertheless, some tetraploid cells enter the cell cycle and continue to proliferate (17). Loss of p53 is permissive of continued cell cycle progression after genome doubling (18), but this loss is not strictly required (17, 19). P53-mediated arrest can also be bypassed by sustained mitogenic signaling or by downregulation of the hippo tumor suppressor pathway (15). The loss or bypass of p53 effect can further enhance permissiveness of chromosomal instability. Thus, genome doubling events can be oncogenic, enhance chromosomal instability, and biologic restraints are incomplete.
Here, our goal is to elucidate the clinical characteristics of polyploid breast cancer. We accomplish this by analyzing the ploidy status of two sets of breast cancer, and characterizing their clinical behavior. Additionally, we develop laboratory models of genome-doubled human cells and compare with the tumors. Finally, we develop a two-step screen to identify compounds that are specific for high-ploidy cell types, can be effective on cells with diverse karyotypes. Our findings provide an important basis for the idea of developing polyploid-selective cancer therapies.
Materials and Methods
Patient samples and FISH
The tissue microarray (TMA) used in this analysis has been described previously (20). Briefly, primary tumor samples were arrayed and annotated under protocol OS10111 (IRB approval 2010-0405). For fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH), slides were deparaffinized, and treated with 0.2N HCl, 1M sodium thiocyanate, Protease I, 10% formalin, and dehydrating ethanol series. In situ DNA and probe were denatured by heating at 73°C for 2 minutes. Hybridization was performed over 2 nights at 37°C with human-specific alpha-satellite labeled centromere probes for chromosomes 3(D3Z1), 4(D4Z1), 7(D7Z1), 9(D9Z1), 10(D10Z1), and 17(D17Z1) (Abbott Molecular). Slides were mounted with Vectashield with DAPI (Vector Laboratories Inc., Burlingame, CA). Chromosomes 4, 10, and 17 were probed on one section, and chromosomes 3, 7, and 9 on a second section. Chromosomes were counted by observers blinded to patient conditions in a minimum of 10 cells per case. A small fraction of samples were not evaluable due to loss of tissue, insufficient cellularity, or other technical issues and were excluded. Similarly a subset of samples had a single probe that was poorly visualized; these were evaluated if two probes per slide were visualized. FISH data were linked to de-identified clinical data by position on the tissue microarray and analyzed using the R statistical package and Excel (Microsoft).
To validate findings, a second patient cohort was obtained from clinical laboratory FISH analysis using the chromosome 17 centromeric probe. Clinical laboratory ploidy data were linked to outcome data from the UWCCC Tumor Registry, which was audited for accuracy prior to removal of identifiers. This study was reviewed and approved as OS12105 (IRB approval 2012-0196).
Data analysis
Karyotypes for 7 distinct cancer types were downloaded from the Mitelman database and analyzed for mean chromosome number, and plotted in Prism (Graphpad software, La Jolla, CA).
Ploidy from the NCI-60 cell lines was obtained from the modal chromosome number (21). Drug sensitivity data was obtained from the NCI Developmental Therapeutics Program (http://dtp.nci.nih.gov). The cell lines have known ploidy with modal chromosome numbers that range from 43 (2N; KM12 line) to 116 (5N; SF-295 line) (21). For each chemical, we calculated the correlation, ρ, of GI50 with cell line ploidy: ρ = Σ (g-gavg)/(c-cavg) where g= –log(GI50) (GI50 is the concentration that elicits 50% growth inhibition), c is the modal number of chromosomes in the cell line, and gavg and cavg are the mean values of g and c across all cell lines. Thus, ρ is positive for chemicals that selectively inhibit growth of polyploid cells. Data was analyzed using a script generated in Perl with an output of each chemical by NSC and associated value of ρ. These data were further processed and displayed graphically using Excel (Microsoft).
Cell culture, chromosome analysis and microscopy
Cell lines were obtained from American Type Culture Collection in 2005 for RPE1, and MCF10a; both were authenticated by karyotype in this study. RPE1 and MCF10a cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) mixed with Ham's F-12 modified medium (HyClone). Media was supplemented with 100 U/mL of penicillin/streptomycin and 10% (vol/vol) FBS (RPE1) or 5% (vol/vol) horse serum (MCF10a). For MCF10a, media also included 20 ng/mL EGF, 0.5 mL/mL hydrocortisone, 100 ng/mL cholera toxin, and 10 μg/mL insulin. MCF7 was obtained from V.C. Jordan in 2010 and verified by STR-15 analysis in 2015. MCF7 cells were cultured in DMEM with 10% FBS. Chromosome spreads and karyotypes were performed as previously described(16).
For FISH, microscopy was performed on Olympus BX41 and BX60 fluorescent microscopes using single and dual band filters for fluorophores DAPI, Spectrum Green, Spectrum Orange, and Spectrum Aqua. Other microscopy was performed by paraformaldehyde cell fixation on coverslips followed by staining and indirect immunohistochemistry, and analyzed on an automated inverted Nikon Ti-E fluorescence microscope as described previously (16).
Proliferation Assays
Cells were plated and treated with chemicals the following day. For proliferation assays, adherent and non-adherent cells were collected every 24 h and counted via trypan blue exclusion with a hemocytometer in three independent replicates. For automated fluorescent analysis, cells were plated into 96-well plates, and treated the following day with chemicals. After 72 h, SYBR green (Lonza) was added to a final volume of 140 μl, and incubated overnight. Fluorescence was read using a BioTek Synergy 4 plate reader. Assays were performed in triplicate. For long-term cell proliferation assays cells were exposed for 8 days to chemical treatment, washed with PBS and stained with crystal violet fixative solution for 20 min. Cells were then rinsed and dried. A 1:1 methanol-water solution was added to each well for 15 min. The solution was transferred to a 96-well plate and absorbance (570nm) was read on the Molecular Devices Spectra Max plus plate reader.
For dose-response analysis, data was normalized using function zi=[xi-min(x)]/[max(x)-min(x)]. Normalized data from at least 3 independent replicates were averaged and standard deviation was calculated. For evaluation of ΔAUC we estimated area under curve for both the 2N and 4N and calculated the difference. For calculation of dose-response curves, data was analyzed in Prism, normalized to logarithmic concentration, and fit with a four-parameter dose response curve (fitting bottom, top, IC50 and slope). Fit curves are shown and displayed IC50 values were obtained from the fit.
Protein analysis and immunoblotting
For Western blot analysis, 2N and 4N RPE1 cells were treated with DMSO, 50ng/ml doxorubicin, or 1μM DPBQ for 48 hours. Western blotting was performed with a SDS-PAGE Electrophoresis and semidry transfer. Samples were analyzed by chemiluminescence. β-actin was used as a protein loading control.
Flow cytometry
For Apoptosis assays, 2N and 4N RPE1 cells were treated with DMSO, 60nM staurosporine, or 1μM DPBQ for 48 hours. Apoptosis was evaluated by an Annexin V-PE/7-AAD apoptosis detection kit (Ebiosciences, Pittsburg, PA, USA). For the flow cytometry analysis, the percent positive cells in the upper right (Annexin V+/7-AAD+; late apoptotic cells) and lower right quadrants (Annexin V+/7-AAD; early apoptotic cells) were summed to give the total number of apoptotic cells. Three independent replicates were performed.
Gene expression analysis
RNA was isolated from MCF7s +/- 6 hour treatment with 10μM DPBQ using TRIzol. cDNA was synthesized from 200ng RNA and isolated using Ambion MessageAmp™ Premier IVT kit (37°C for 8 hours). Hybridization cocktail prepared according to protocols & procedures in the AFX Expression Analysis Technical Manual (P/N 702232 Rev. 3) for the U133A 2.0 array. 6.5 μg of fragmented labeled aRNA applied to AFX HG U133A 2.0 array & hybridized at 45°C for 16 hours in AFX 640 Hyb oven. Human U133A 2.0 GeneChips were post processed on the AFX 450 Fluidics Station according to all AFX protocols and procedures defined for the U133A 2.0 array (FS450_0002) in the GeneChip® Hybridization, Wash, and Stain Kit User Manual (P/N 702231 Rev. 3). All GC's scanned on AFX GC3000 G7 scanner (S/N 50208130). Data extracted from GC3000 G7 scanned images using the AFX Expression Console v 1.2.0.20 software. Sample preparation and scanning was performed at the University of Wisconsin Biotechnology—Gene Expression Center. Array data was normalized by RMA method and the data exported to GSEA for analysis (22). Data were deposited in the GEO archive, accession GSE73710 (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE73710).
Chemicals and reagents
DPBQ and other chemicals were obtained from the National Cancer Institute, diluted in stock DMSO solutions and used at the concentrations shown. Other chemicals used include doxorubicin (ThermoFisher, Waltham MA), etoposide (Topogen, Port Orange, FL), paclitaxel (ThermoFisher/Acros), BI-2536 (Selleck Chemical, Houston, TX), chloroquine, 17-AAG, and Nutlin-3a (Fisher). Antibodies used include β-actin (ab6276 WB 1:10,000; Abcam,Cambridge, MA), pericentrin (ab4448 IF 1:1000; Abcam), p53 (#9282, WB 1:2000; Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA), phospho-P15 p53 (#9284 WB 1:2000; Cell Signaling Technology), p21 (sc6246, WB 1:500; Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX)
The topoisomerase assay was performed using the Topo II Assay kit per the manufacturer instructions (TopoGEN, Port Orange, FL). Circular dichroism of 0.5 mg/ml salmon sperm DNA was performed using an AVIV Model 420 CD Spectrometer at room temperature. To analyze DNA binding, 100 μM ethidium bromide or DPBQ was added to the sample to evaluate changes in spectrum consistent with intercalation.
Statistical analysis
The clinical outcomes analyzed in this study were relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS). Relapse-free survival was defined as the time from initial breast cancer diagnosis to recurrence or death; stage IV patients were excluded. Overall survival was defined as the time from diagnosis to the date of death or last follow-up. RFS and OS were plotted using the Kaplan–Meier method, and log-rank tests were used to compare patients with tumors that were polyploid (ploidy≥3) versus not polyploid (ploidy<3). Cox proportional hazards model included ploidy, stage, tumor grade, hormone receptor status, and HER2 status. Associations between these factors and either RFS or OS were analyzed and presented as hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). SAS (version 9.4, SAS Institute, Cary, NC) and R (version 3.1.1, Vienna, Austria) software packages were used for these analyses. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
To characterize diversity in chromosome number across diverse cancers, we visualized the mean chromosome numbers of diverse human cancers from the Mitelman database (23). Significant fractions of diverse tumors have greater than 3 chromosome sets, including breast, ovary, pancreas, lung, and diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma (Fig. 1A). Interestingly, the lack of samples with 92 chromosomes demonstrates that true tetraploidy is rare. We conclude that high-ploidy aneuploid states are common and may represent a targetable feature of some cancers.
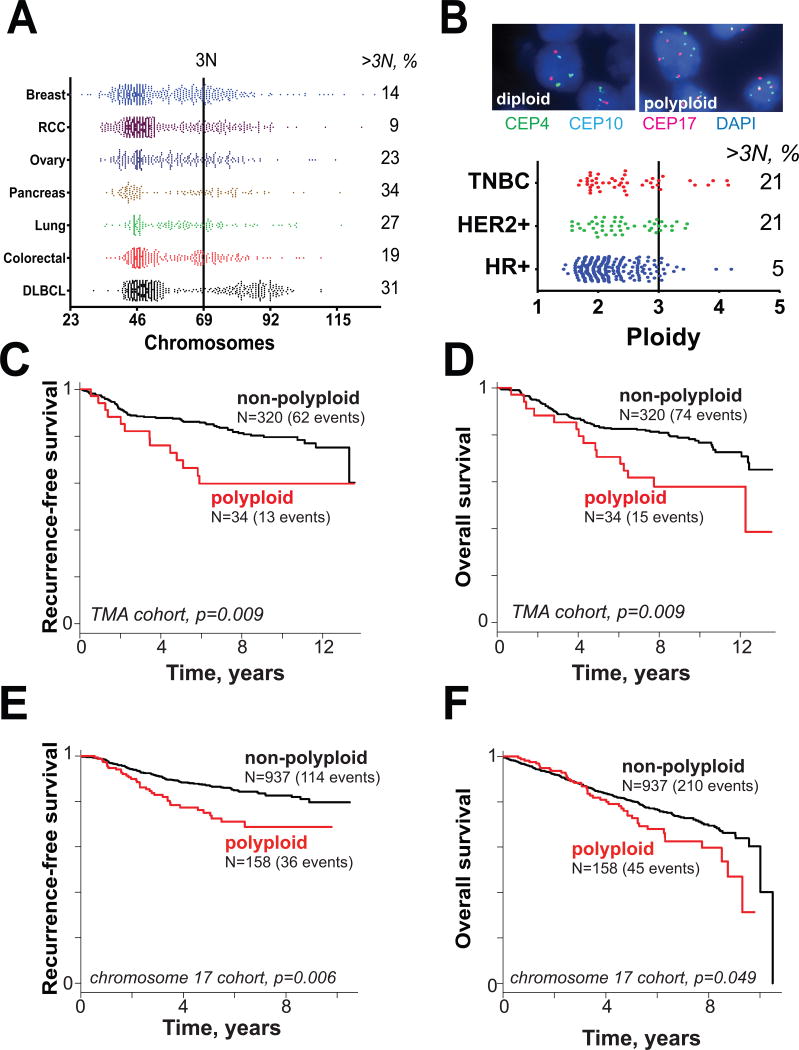
Figure 1.
Polyploidy is a feature of many cancers. A. Chromosome number in multiple cancer types from Mitelman database. RCC = renal cell carcinoma; DLBCL = diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. B. (top) Representative 3-color centromeric FISH images from breast cancer tissue microarray analysis of 354 distinct breast cancers. A total of 6 chromosomes were sampled by centromeric probes (4, 10, 17 on one section and 3, 7, 9 on a separate section). (bottom) Mean ploidy status by 6-chromosome sampling of 354 breast cancers by subtype. C-F. Kaplan-Meier survival curves for polyploid versus non-polyploid cancers. C. Recurrence-free survival for tissue microarray (TMA) cohort where polyploid tumors are defined as those that have mean ≥3 centromere signals per cell among 6 centrosomes counted. D. Overall survival for TMA cohort. E. Relapse-free survival in single-chromosome FISH cohort where polyploid tumors are those defined as those that have mean ≥3 centromere 17 per cell. F. Overall survival for single-chromosome FISH cohort.
Polyploid cells are prone to genetic instability due to both aberrations of division (10) and are permissive of chromosomal losses (12). We therefore hypothesized that polyploid breast cancers would constitute a subtype with distinct clinical features. To address this, we employed a clinically annotated tissue microarray of 354 unique primary stage I-III breast cancer specimens from patients treated at the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center. We performed FISH analysis of six chromosomes using centromeric probes (Fig. 1B, top). Polyploid cancers were defined as those that had mean chromosome numbers of ≥3 and 10% met this criterion. Clinically, breast cancer is categorized as hormone receptor positive (having estrogen or progesterone receptor), HER2-positive (regardless of hormone receptor status) or triple negative. High-ploidy breast cancers were found among all three subsets. However, high ploidy is common in tumors of the triple-negative and HER2+ subtypes (21% of each; Fig. 1B).
Given increased permissiveness to genomic alterations, we anticipated that high tumor ploidy would confer worse clinical outcomes. To test this, we employed the Kaplan-Meier method (Fig. 1C-F). As predicted, patients with high ploidy had a significantly higher risk of cancer relapse (p=0.009) and of death (p=0.009; Fig. 1C-D). To validate this in an additional cohort, we retrospectively reviewed outcomes for 1095 individuals treated at UW Cancer Center in which FISH was performed for the centromere of chromosome 17 as part of a standard clinical assay, and matched to a database of clinical outcomes. Importantly, the ploidy of chromosome 17 correlates well with 6-chromosome ploidy in the first cohort (Supplementary Fig. S1), suggesting that this chromosome is a reasonable surrogate for tumor ploidy. Again, high tumor ploidy is associated with higher risk of cancer relapse (p=0.006) and death (p=0.049). Our findings led us to consider that high-ploidy status of a tumor might impart aggressive phenotypes leading to high tumor grade and stage in breast cancer. To test this, we performed a Cox proportional hazard analysis in both patient cohorts (Supplementary Table). Indeed tumor stage and grade remained strong predictors of poor clinical outcomes and subsumed the prognostic effect of polyploidy. We conclude that polyploid breast cancers represent a high risk subtype. Prognostically, this risk is captured in clinically observable variables used for prognosis, suggesting that polyploidy may promote advanced tumor grade and stage. Yet, the finding that tumors with high ploidy have worse clinical outcomes provides a strong clinical rationale for improving treatment, and a biological basis for specific anticancer therapy.
Physiologic effects of polyploidy
There is considerable evidence that polyploidy alters cell physiology in diverse biological systems (24, 25). To characterize the effects in human epithelial cells, we obtained two diploid human epithelial cell lines, RPE1 and MCF10a. RPE1 is an hTERT immortalized retinal pigment epithelial cell line, and MCF10a is a spontaneously immortalized breast epithelial cell line (26). To obtain genetically matched high-ploidy cells, we synchronized cells in mitosis with brief nocodazole treatment, then chemically interrupted cytokinesis using blebbistatin and generated subclones. As reported previously, many resulting binucleated cells spontaneously undergo cytofission to resolve to a normal diploid type (16). However, a fraction of the subclones recovered are near tetraploid (4N). These near-tetraploid cells can undergo further alterations in chromosome number due to centrosome amplification and increased permissiveness of aneuploidy (10, 12). Because such genome evolution could complicate later analyses, we selected lines that maintained a near-tetraploid chromosome number through >10 passages. As reported previously (11, 27, 28), we found our polyploid cells to be enlarged compared to their diploid counterparts (Fig. 2A). Flow cytometry and chromosome analysis confirmed tetraploid DNA content in the 4N cells (Fig. 2B-C, and Supplementary Fig. S2). Similarly, the tetraploid cells nearly double the protein content of diploids, consistent with expected gene dosage effects (Fig. 2D-E). Although loss of p53 is permissive of continued cycling after tetraploidization (29), our 4N cells retained the ability to express and activate p53 (see below). Cells arrested at the G1/S boundary commonly showed two pericentrin foci, suggesting supernumerary centrosomes (Fig. 2F). These findings demonstrate significant alterations in cell physiology occur with tetraploidization, consistent with prior reports.
Figure 2.
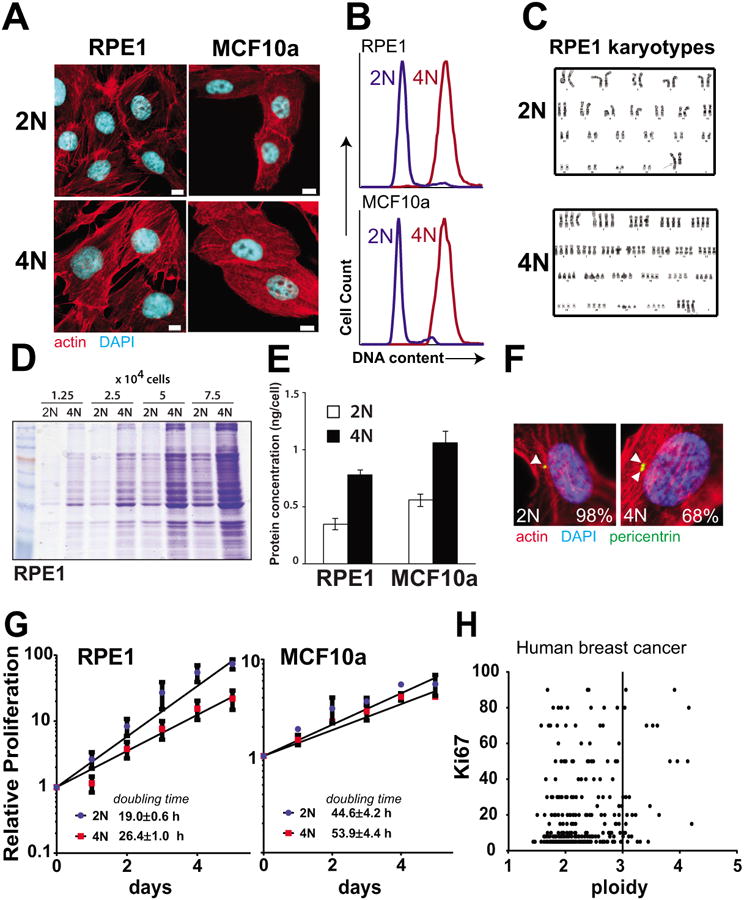
Matched pairs of diploid-polyploid cells were generated from epithelial breast cell types. A. Representative images of diploid (2N) and polyploid (4N) cells derived from RPE1 and MCF10a cell lines. Scale bar = 10 μm. B. Flow cytometry demonstrating double DNA content of tetraploid cells after staining with propidium iodide. C. Karyotype of diploid and polyploid matched RPE1 cells. D-E. Protein levels are higher in tetraploid cells relative to diploid as determined by coomassie staining of extracts (D) and Bradford Assay (E). F. Polyploid RPE1 cells have supernumerary centrosomes. Cells were synchronized using aphidicolin and stained. Pericentrin foci are marked with arrows and percentage of cells that harbor the indicated number of centrosomes is indicated (n>40). G. 4N cells proliferate more slowly than 2N cells. Cell number was quantified in proliferating 2N and 4N cells and doubling time was calculated. H. High ploidy in human breast cancer samples does not correlate strongly with the Ki67 proliferation marker.
Given the association of high-ploidy with high-risk breast cancer subtypes, we hypothesized that polyploidy might confer a proliferative advantage. However, both tetraploid cell lines proliferated more slowly than their diploid counterparts, although the difference is modest for MCF10a (Fig. 2G). The slowed proliferation of polyploid cells could arise from non-optimal regulation of gene expression. If so, polyploid cancers might adapt to recover rapid proliferation and polyploidy would not correlate with proliferation in human cancers. To test this, we determined correlation of the ploidy of the human breast cancers with Ki67, a standard marker of proliferation rate. High ploidy does not correlate with decreased proliferation (Fig. 2H). Thus high tumor ploidy does not necessarily slow proliferation, likely because of additional genetic adaptations that control proliferation independent of ploidy.
Ploidy-specific antiproliferative compounds
Previous work identified specific treatments that can have differential effects on specific polyploid versus diploid cell types (4, 24). To test whether existing drugs might have this property, we evaluated detailed response curves for several anticancer agents. We first evaluated standard anticancer agents including doxorubicin, paclitaxel, and etoposide, but these lacked a selective effect on tetraploid cells (Supplementary Fig. S3A-C). Previous work suggested that polyploid yeast are more dependent than diploids on Cdc5, the yeast homolog of human Plk1 (25); however we did not observe a selective effect of BI-2536, an inhibitor of Plk1, on polyploid human cells (Supplementary Fig. S3D). Chloroquine, 17-AAG are aneuploidy-selective compounds (5), so we hypothesized that these might also operate selectively on polyploid tumors. Yet chloroquine and 17-AAG did not show polyploid-selective effects in our matched pair of diploid- and tetraploid RPE1 cells (Supplementary Fig. S3E-F). These agents may be selective for cells with near-diploid aneuploidy, generating an unbalanced gene dose not found in our tetraploid cell line models. Thus, existing or potentially predicted anticancer agents lack polyploid-specific anticancer effects.
We sought to identify anticancer agents specific for high cell ploidy, but not necessarily specific to the near-tetraploid state of our model cell types, since many high-ploidy tumors have diverse aneuploid karyotypes. Thus, we designed a two-step screen that inherently addresses the diversity of high-ploidy karyotypes found in human cancer. To do this, we obtained chemical sensitivity data from the NCI-60 database (30). The data consists of 50% growth-inhibitory concentrations (GI50) of 45,342 chemicals across ∼60 human cancer cell lines. For each chemical, we calculated the correlation of drug sensitivity (GI50) against ploidy and plotted distribution of this score, ρ, against the interline-variance in GI50 (Fig. 3A). A high interline variance (vertical axis in Fig. 3A) indicates that other factors in addition to polyploidy contribute to drug selectivity (e.g. p53 with DPBQ—see below). Of note, the vast majority of chemicals had little differential effect for polyploid- versus non-polyploid cells. Those chemicals that lack selectivity include doxorubicin, etoposide, and paclitaxel; of standard chemotherapy drugs, only vincristine is found to have weak correlation with increased sensitivity of polyploid cells (Table 1). Nevertheless, a small proportion of compounds elicit sensitivity that correlates highly with ploidy on a diverse set of human cancer cell types, and are worthy of further analysis.
Figure 3.
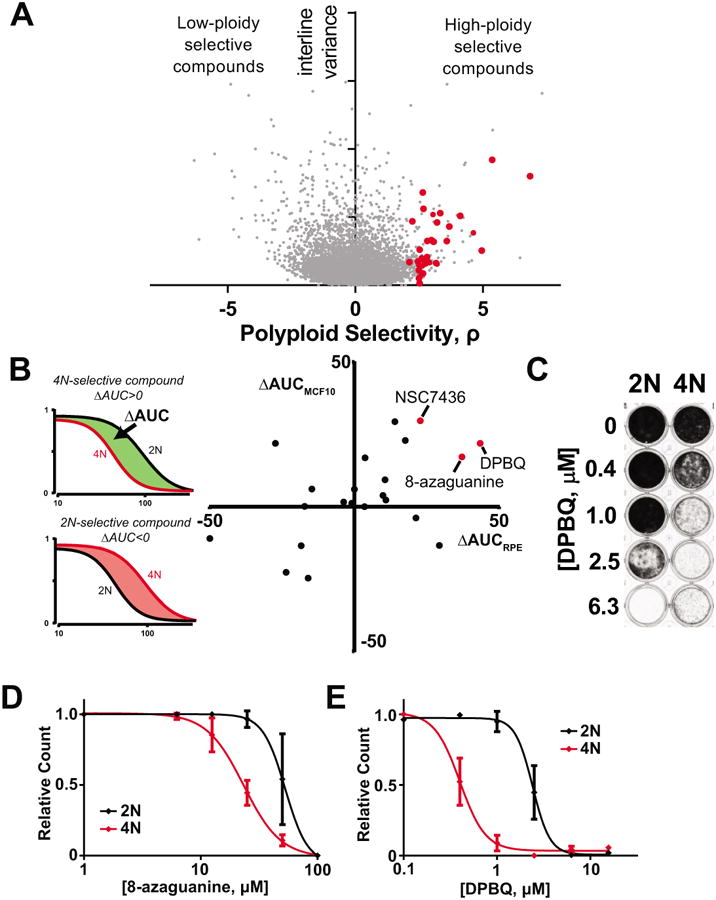
Discovery of DPBQ and 8-azaguanine as polyploid-specific disruptors of proliferation. A. Correlation with drug sensitivity and cell ploidy from NCI-60 data of over 45,342 chemicals across ∼60 cell lines. Polyploid selectivity, ρ, is plotted against interline variance for each chemical. Red circles indicate chemicals obtained for secondary screens. B. Secondary screen to test selectivity of hits in matched pairs of diploid and polyploid RPE1 and MCF10a cells. Red circles indicate hits that are polyploid selective in both MCF10a and RPE1 cell types. C. DPBQ 8-day proliferation assay in RPE1 cells. Crystal violet staining marks viable cells remaining. D-E. Quantification of proliferation assay as in C. plotting absorbance for 8-azaguanine (D) and DPBQ (E) in RPE1. n=3, SD shown.
Table 1. Correlation of sensitivity with ploidy for standard cancer therapies.
| Drug | ρ |
|---|---|
| vincristine | 1.7 |
| Chloroquine | 0.7 |
| Doxorubicin | 0.4 |
| Etoposide | 0.1 |
| Paclitaxel | -0.4 |
| 17-AAG | -0.6 |
| Methotrexate | -0.8 |
| 5-FU | -1.1 |
| Gemcitabine | -1.9 |
Although this analysis identifies compounds with sensitivity that correlates with cell ploidy, it does not demonstrate that ploidy per se controls selectivity since it does not exclude unknown confounding variables. To determine if the response to these compounds is intrinsic to polyploidy, we validated them in matched diploid-polyploid human cells. We procured available chemicals with the highest ploidy-specific growth inhibition scores (red circles in Fig. 3A) and established concentration-response curves on the matched 2N and polyploid (4N) RPE1 and MCF10a cells. We measured the difference in the areas under the curve between 2N and 4N lines (Fig. 3B, left) and plotted results for each chemical. As shown, few chemicals have confirmed polyploid selectivity in both paired cell lines (Fig. 3B, right), suggesting that the correlation with ploidy for most chemicals is due to confounding factors. However, a small number of compounds had confirmed selectivity in both polyploid RPE1 and MCF10a lines.
One intriguing hit is 8-azaguanine, an antimetabolite that is activated by the purine salvage enzyme HPRT (hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase), encoded on the X-chromosome. 8-azaguanine can be used to select cells that lack HPRT, which are then resistant. Our data here suggest that polyploid cells, which have additional X chromosomes, have enhanced sensitivity to 8-azaguanine possibly due to elevated expression of HPRT; excess X chromosomes are not inactivated in polyploid cells (31). Second, we identified NSC7436 (4-amino-N-(4-tert-butylphenyl)benzenesulfonamide), a sulfonamide compound which was not further characterized here. A third hit discovered is 2,3-Diphenylbenzo[g]quinoxaline-5,10-dione (DPBQ). To quantify the magnitude of the 8-azaguanine and DPBQ effects, we performed detailed concentration-response curves in 8-day proliferation assays on matched diploid-polyploid cells (Fig. 3C-E). This confirmed significant selectivity for polyploid cell types. We conclude that these are bona fide polyploid-selective compounds.
DPBQ does not have a known mechanism of action, so we first tested the hypothesis that it may operate similarly to existing cancer therapeutics. To identify potential matches, we used the Prediction of Activity Spectra for Substances (PASS) score which is available for all compounds in the NCI-60 database (32). PASS estimates the probability that a given compound has one of 565 biological activities based on known activities of a learning set of ∼35,000 compounds. We obtained a PASS score of 0.8 (range 0 - 1) for DPBQ as a topoisomerase inhibitor. We were initially puzzled by this finding because other topoisomerase inhibitors lacked selectivity in our in silico screen and both doxorubicin and etoposide failed to exhibit any differential effect in diploid and tetraploid RPE1 in separate assays (Supplementary Fig. S2). Nevertheless, we directly evaluated DPBQ activity in a Topoisomerase II assay, and found no activity (Supplementary Fig. S4A). Moreover, we observed that the planar aromatic structure of DPBQ resembles DNA intercalators, but we did not detect binding a direct assay by circular dichroism (Supplementary Fig. S4B). We conclude that DPBQ mechanism appears distinct from DNA binding or inhibition of topoisomerase II.
Mechanism of DPBQ action
Preliminary data suggested that DPBQ caused cancer cell death rather than inhibition of proliferation. To evaluate the cell biologic effects of DPBQ, we evaluated mechanisms of death by Annexin and 7-AAD staining to detect apoptotic/necrotic cell populations (Fig. 4A-B). These results demonstrate that DPBQ elicits apoptosis and cell death and is selective for effects in 4N cells. The tumor suppressor p53 is a central mediator of apoptosis from chemically induced stress (33). We therefore reasoned that DPBQ may elicit p53 activation to produce the observed apoptosis. Indeed, DPBQ elicits expression and phosphorylation of p53 and this effect is specific to tetraploid cells (Fig. 4C). Additionally, this is bona fide activation of p53 transcriptional activity as it results in expression of p21, a downstream effector. In contrast, doxorubicin causes activation of p53 in both diploid and tetraploid cells, consistent with the lack of cell-line specific selectivity. To test if p53 mediates the antiproliferative effect of DPBQ in polyploid cells, we knocked down p53 and re-analyzed antiproliferative effects. Indeed, knockdown of TP53 restores proliferation of tetraploid cells in the presence of DPBQ (Fig. 4D). We conclude that DPBQ elicits 4N-selective apoptosis mediated by p53.
Figure 4.
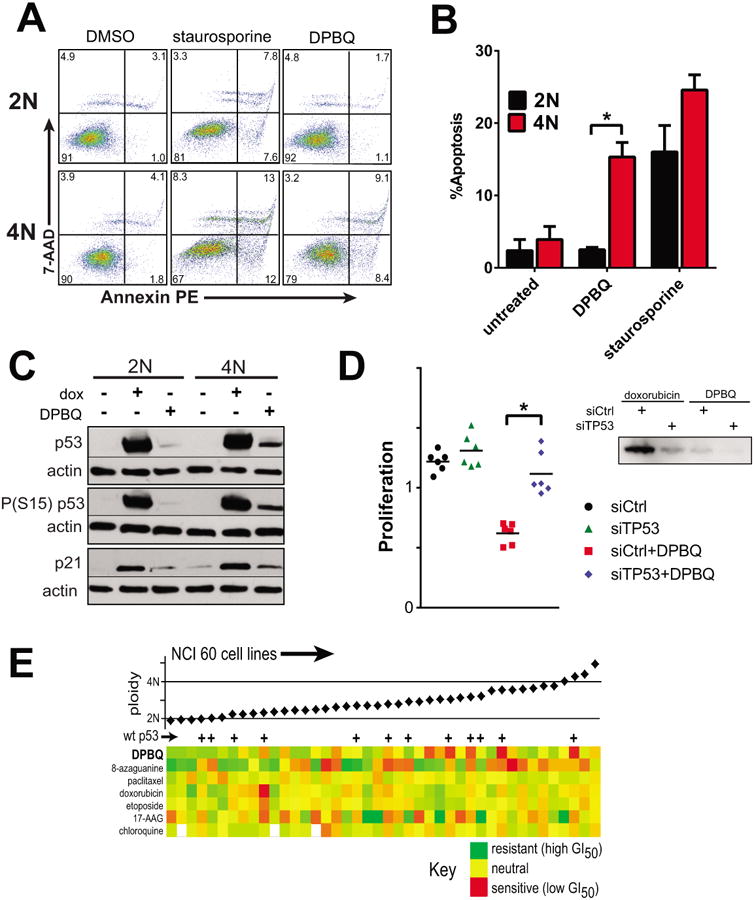
Mechanism of DPBQ. A-B. DPBQ elicits polyploid-specific apoptosis. A. Apoptosis by representative Annexin assay. B. Averaged apoptosis (early and late) for n=3 assays, SD shown. *p<0.05 by T-test. C. 1 μM DPBQ elicits 4N-specific p53 induction and activation; dox=doxorubicin. D. p53 is required for the DPBQ effect. 4N RPE1 cells were transfected with siRNA against p53 (siTP53) or control (siCtrl) and then exposed to DPBQ or vehicle. DPBQ restrained prolilferation only when p53 was present (red). Right: blot demonstrating suppression of phospho(S15)-p53 with knockdown. *p<0.05 by T-test. E. Among NCI-60 lines, DPBQ has its strongest effects against polyploid cell lines that express wildtype p53.
If p53 is indeed a mediator of DPBQ effect on polyploid cells, then we would anticipate that cell lines with high ploidy and intact p53 would be most sensitive to DPBQ. The p53 status is known for most cell lines in the NCI-60 panel (34). Considering those for which p53 is known to be wildtype, we find that sensitivity to DPBQ is highest in cells that have both intact p53 and high ploidy (Fig. 4E). In contrast, there is no correlation of drug sensitivity with p53 status or ploidy for other agents including 8-azaguanine and the agents in Supplementary Fig. S2. We conclude that DPBQ activates p53 and induces apoptosis in a polyploid-selective manner.
To further elucidate mechanism of polyploid-selective p53 activation, we tested how 6h DPBQ alters gene expression. We initially matched the conditions of the connectivity map in the hopes of identifying a matching pharmacophore (35). Although we identified DPBQ-matching pharmacophores, these did not match the polyploid-selective effect of DPBQ. These results suggest that this agent operates by a unique mechanism. To narrow down specific mechanisms, we reviewed the effects of DPBQ on gene expression (Fig. 5A) and. performed gene set enrichment analysis against standardized hallmark profiles (22). As expected, the enrichment profile matched the canonical effect of p53 activation, but we also identified the hypoxia hallmark, which could explain mechanism of p53 activation (Fig. 5B). Hypoxia is known to induce oxidative stress and can have a reciprocal effect on p53 activation (36). We therefore evaluated whether oxidative stress can have polyploid-selective effects. In contrast to other methods of activating p53, we found that oxidative stress from H2O2 and is modestly polyploid-selective in inducing antiproliferative effects (Fig. 5C) and induces polyploid-selective p53 activation (Fig. 5D). Thus, DPBQ activates p53 in a polyploid-selective manner at least partially through oxidative stress.
Figure 5.
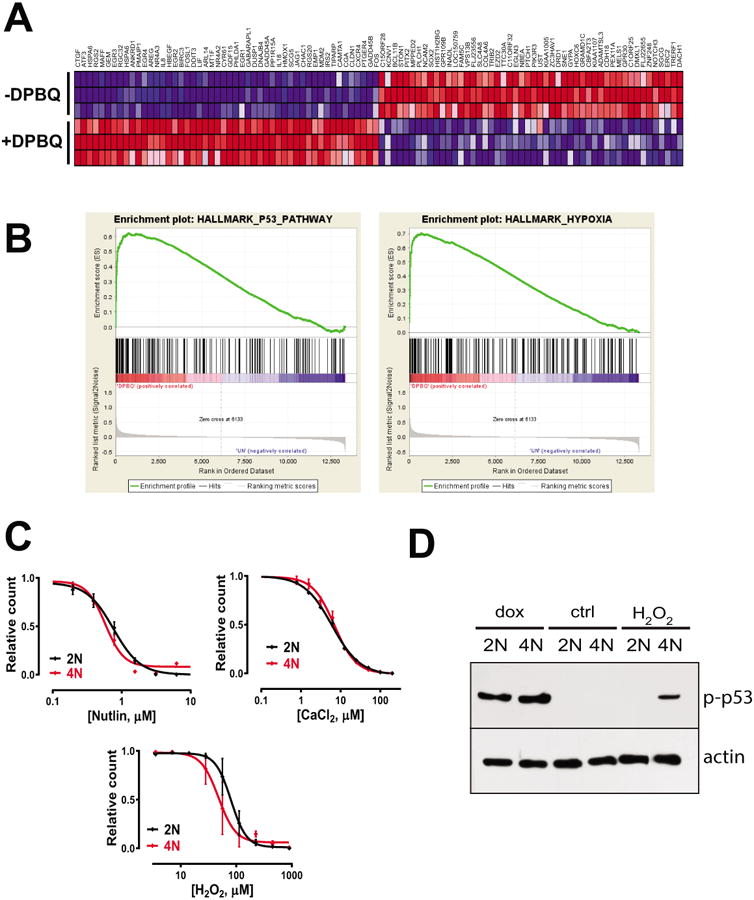
Evaluation of DPBQ mechanism by gene expression analysis. A. Top gene expression altered by DPBQ is shown, both upregulated (red) and downregulated (blue) in 3 technical replicates. B. Gene set enrichment analysis showing strong enrichment of hallmark pathways for p53 and hypoxia. C. Concentration-response curves for nutlin, CaCl2, and H2O2 on diploid and tetraploid cells. D. Expression of phospho-P53 (top) and actin after treatment with doxorubicin, control, or H2O2.
Structure-function analysis
DPBQ has a planar oxidized tricyclic structure with benzyl substituents. To evaluate which components of the structure are critical for its polyploid-specific effects, we procured related compounds that were readily available (Fig. 6A). First, we tested two related compounds that are missing the complete benzo[g]quinoxaline-5,10-dione structure, DQD and QXD (Fig. 6B,C). However, these lacked not only selectivity but also potency, as demonstrated by the high concentrations required to elicit antiproliferative effects. Similarly, potency and selectivity were lost in BQD (Fig. 6D), which lacks both the phenyl substituents and a heterocyclic nitrogen. In contrast, selectivity and potency were maintained in NQD (Fig. 6E), in which the core benzo[g]quinoxaline-5,10 dione structure was retained. Importantly, this suggests that the phenyl groups are dispensable and that modifications of the nitro- group could be made to improve potency, selectivity, or pharmacologic properties. Thus, this benzo-quinoxaline-dione structure represents a core structure for development of polyploid-selective therapeutics.
Figure 6.
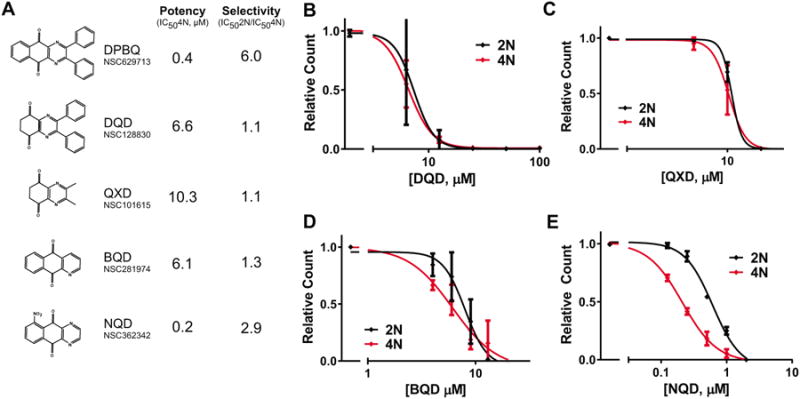
Structure-function analysis of DPBQ. A. DPBQ-like molecules were tested for potency and specificity for in paired diploid-polyploid RPE1 cells. B-E. Concentration response curves for DPBQ-like molecules for 8-day proliferation assays, as in Fig. 3C-E. n=2, SD shown.
Discussion
Cancers have diverse karyotypes with highly divergent chromosome numbers ranging from 33 to 133 in common cancers (23). The presence of supernumerary chromosome sets alters cell physiology in replication, cell size, mitosis, gene expression, and tolerance for mutation.(1, 11, 12, 24, 25, 27, 28). Previous work demonstrates that human tetraploid cells have elevated sensitivity to certain drugs, resistance to others, and altered regulation of apoptosis (4, 24). Although tetraploid-specific drugs could be useful for prevention, cancer cells often have additional mutations, chromosomal aberrations, or epigenetic changes that result in deviation from a purely tetraploid karyotype. In support of this idea, no human cancer cells of the common types shown Fig. 1A have strictly tetraploid chromosome content, as all have one or more chromosome gains/losses, creating a high-ploidy aneuploid state. Moreover, high ploidy does not correlate with low proliferation in human breast cancer, although laboratory-derived near-tetraploid lines do proliferate more slowly. These observations suggest that human cancers with high-ploidy aneuploid states have additional adaptations that need to be accounted for in discovery of polyploid-selective cancer therapies.
Polyploidy is found in a significant fraction of high risk breast cancers. Although it comprises only 10-14% of breast cancer, this represents 20-28,000 cases per year. Moreover, we find that polyploid breast cancers have worse clinical outcomes than non-polyploid cancers, indicating a need for effective and specific therapies for these patients. This study associates polyploidy with poor clinical outcomes, but other evidence suggests that polyploidy causes cancer. For example, polyploidy is common in early stages of malignant transformation of the esophagus (37) and of the cervix (38). Certain hereditary cancer syndromes also increase the rate of cytokinesis failure and concomitant tetraploid tumors; these include hereditary mutations in BRCA2 (39, 40) and APC (41-43). Once cells are tetraploid, supernumerary centrosomes can promote abnormal chromosome segregation leading to gains and losses of chromosomes(2, 30). Polyploid cells have a greater propensity for oncogenic transformation than diploid cells in zebrafish (14) and in p53-/- mice (13). Together, these observations support the idea that genome doubling is an early event in oncogenic transformation in some cancers, and suggests that high ploidy may also produces aggressive cancer phenotypes.
DPBQ is a novel a lead compound discovered to exhibit selective lethality for polyploid cells. The screen used is innovative in that the primary screen accounts for the genetic and physiologic diversity of cancer, thereby reducing the likelihood of finding a hit restricted to a specific genetic background or cell type. Moreover, the secondary screen distinguishes polyploid specific effects by testing in matched diploid-polyploid cell line pairs. Of note, many of the chemical hits in the primary screen do not have specificity for polyploid cells, demonstrating that other factors sometimes underlie the correlation seen with drug sensitivity and polyploidy for certain chemicals. Thus, this two-step screen provides validation that is both intrinsic (polyploid-specific) and extrinsic (diverse cancer cell types and genetic backgrounds).
In addition to DPBQ, we identified 8-azaguinine as an additional compound with polyploid-specific effects. 8-azaguanine is an antimetabolite that interferes with nucleotide synthesis after it is activated by HPRT. Similar compounds such as mercaptopurine and 6-thioguanine are used to treat acute lymphocytic leukemia(44). Cells with inactive HPRT are resistant to the effects to these antimetabolites, but heretofore it has not been demonstrated that polyploid tumors might have enhanced sensitivity to these agents. The increased sensitivity of polyploid tumors here suggests a novel biomarker for sensitivity to existing anticancer drugs. In addition, polyploidy would decrease the likelihood of secondary resistance through HPRT loss of function since human polyploid cells have multiple activated X chromosomes (31).
The finding of enhanced sensitivity of tetraploid cells to H2O2 is consistent with prior observations that tumorigenic polyploid cells have enhanced reactive oxidative species (ROS) signaling (45). However, this does not completely account for the mechanism by which DPBQ elicits p53 activation. First, we find no selectivity with other ROS activators, such as doxorubicin. Second, the preferential effect of DPBQ on polyploid versus diploid cells is larger than that of H2O2. These findings suggest that DPBQ either elicits a particular type of oxidative stress or that it also operates in additional ways that have a strong selectivity to polyploid cells. It will be important to elucidate the details of this mechanism.
Despite the strength of the screen, there are some limitations of the findings. The effects of DPBQ appear to be limited to high-ploidy cell types with intact p53, and a significant fraction of cancers have lost the function of this tumor suppressor. However, there is good reason to anticipate that some polyploid cancers will retain p53. Loss of p53 is not strictly required for development of polyploid cancers, and can be overcome by mitogenic growth signals or loss of hippo pathway (46). Indeed, cell cycle progression and mitotic entry has been observed in p53-wildtype cells after cytokinesis failure as reported by others(17, 19). Finally, we identify high-ploidy NCI-60 cell lines reported to have wildtype p53. A substantial fraction of high-risk breast cancer subtypes appear to have wildtype p53, although it remains unclear how this overlaps with the polyploidy fraction. Thus it is plausible that a significant fraction of breast and other cancers may have the characteristics required for sensitivity to DPBQ-like drugs.
We anticipate that the therapeutic window for DPBQ (6 fold-selectivity) is sufficient for an effective therapeutic, and might be enhanced by pharmacologic modification.
We conclude that polyploidy correlates with, and may cause, high stage and high grade breast cancer with worse clinical outcomes. This finding provides insight into an underlying cause of some high-risk breast cancers. Moreover, we have discovered compounds that exploit the underlying differences of polyploid-versus-diploid cell types, and may serve as a lead compound for novel cancer therapy. Given that high-ploidy aneuploid states exist in a significant numbers of cancers, targeting polyploidy could be an effective therapeutic strategy.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the UW Biophysics Instrumentation Facility (NSF BIR-9512577 and NIH S10 RR13790), and the University of Wisconsin Biotechnology Center—Gene Expression Center for equipment and expertise. We acknowledge Amy Fothergill, Ross Fedenia, John Feltenberger, Melissa Martowicz, Robert Millholland for contributions of clinical data, reagents and preliminary analyses.
Financial Support: This work was supported by R01 GM097245, the Mary Kay Foundation, American Cancer Society IRG-58-011-48, the Wisconsin Partnership New Investigator Program Award #2261, and Effcansah to M.E. Burkard, and R01 CA140458 to B.A. Weaver. Additional support was provided by a training grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences UL1TR000427 to M.E. Burkard, and Cancer Center Support P30 CA014520 supporting collaborative resources for all investigators.
Footnotes
Conflict of interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Storchova Z, Kuffer C. The consequences of tetraploidy and aneuploidy. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:3859–66. doi: 10.1242/jcs.039537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Storchova Z, Pellman D. From polyploidy to aneuploidy, genome instability and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:45–54. doi: 10.1038/nrm1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Janssen A, Kops GJ, Medema RH. Elevating the frequency of chromosome mis-segregation as a strategy to kill tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:19108–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904343106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lissa D, Senovilla L, Rello-Varona S, Vitale I, Michaud M, Pietrocola F, et al. Resveratrol and aspirin eliminate tetraploid cells for anticancer chemoprevention. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:3020–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1318440111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tang YC, Williams BR, Siegel JJ, Amon A. Identification of aneuploidy-selective antiproliferation compounds. Cell. 2011;144:499–512. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Duelli DM, Hearn S, Myers MP, Lazebnik Y. A primate virus generates transformed human cells by fusion. J Cell Biol. 2005;171:493–503. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200507069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Edgar BA, Orr-Weaver TL. Endoreplication cell cycles: more for less. Cell. 2001;105:297–306. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lacroix B, Maddox AS. Cytokinesis, ploidy and aneuploidy. J Pathol. 2011;226:338–51. doi: 10.1002/path.3013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lanni JS, Jacks T. Characterization of the p53-dependent postmitotic checkpoint following spindle disruption. Molecular and cellular biology. 1998;18:1055–64. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.2.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ganem NJ, Godinho SA, Pellman D. A mechanism linking extra centrosomes to chromosomal instability. Nature. 2009;460:278–82. doi: 10.1038/nature08136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Comai L. The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid. Nature reviews Genetics. 2005;6:836–46. doi: 10.1038/nrg1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dewhurst SM, McGranahan N, Burrell RA, Rowan AJ, Gronroos E, Endesfelder D, et al. Tolerance of whole-genome doubling propagates chromosomal instability and accelerates cancer genome evolution. Cancer discovery. 2014;4:175–85. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fujiwara T, Bandi M, Nitta M, Ivanova EV, Bronson RT, Pellman D. Cytokinesis failure generating tetraploids promotes tumorigenesis in p53-null cells. Nature. 2005;437:1043–7. doi: 10.1038/nature04217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shepard JL, Amatruda JF, Finkelstein D, Ziai J, Finley KR, Stern HM, et al. A mutation in separase causes genome instability and increased susceptibility to epithelial cancer. Genes Dev. 2007;21:55–9. doi: 10.1101/gad.1470407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ganem NJ, Cornils H, Chiu SY, O'Rourke KP, Arnaud J, Yimlamai D, et al. Cytokinesis failure triggers hippo tumor suppressor pathway activation. Cell. 2014;158:833–48. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Choudhary A, Lera RF, Martowicz ML, Oxendine K, Laffin JJ, Weaver BA, et al. Interphase cytofission maintains genomic integrity of human cells after failed cytokinesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:13026–31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1308203110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Uetake Y, Sluder G. Cell cycle progression after cleavage failure: mammalian somatic cells do not possess a “tetraploidy checkpoint”. J Cell Biol. 2004;165:609–15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200403014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Davoli T, de Lange T. The causes and consequences of polyploidy in normal development and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:585–610. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wong C, Stearns T. Mammalian cells lack checkpoints for tetraploidy, aberrant centrosome number, and cytokinesis failure. BMC Cell Biol. 2005;6:6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-6-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang L, Zhao Z, Meyer MB, Saha S, Yu M, Guo A, et al. CARM1 methylates chromatin remodeling factor BAF155 to enhance tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer cell. 2014;25:21–36. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Roschke AV, Tonon G, Gehlhaus KS, McTyre N, Bussey KJ, Lababidi S, et al. Karyotypic complexity of the NCI-60 drug-screening panel. Cancer Res. 2003;63:8634–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15545–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mitelman F, Johansson B, Mertens F. Mitelman Database of Chromosome Aberrations and Gene Fusions in Cancer. 2012 Available from: http://cgap.nci.nih.gov/Chromosomes/Mitelman.
- 24.Castedo M, Coquelle A, Vivet S, Vitale I, Kauffmann A, Dessen P, et al. Apoptosis regulation in tetraploid cancer cells. The EMBO journal. 2006;25:2584–95. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Storchova Z, Breneman A, Cande J, Dunn J, Burbank K, O'Toole E, et al. Genome-wide genetic analysis of polyploidy in yeast. Nature. 2006;443:541–7. doi: 10.1038/nature05178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Soule HD, Maloney TM, Wolman SR, Peterson WD, Jr, Brenz R, McGrath CM, et al. Isolation and characterization of a spontaneously immortalized human breast epithelial cell line, MCF-10. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6075–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Epstein CJ. Cell size, nuclear content, and the development of polyploidy in the Mammalian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967;57:327–34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Galitski T, Saldanha AJ, Styles CA, Lander ES, Fink GR. Ploidy regulation of gene expression. Science. 1999;285:251–4. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5425.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Senovilla L, Vitale I, Galluzzi L, Vivet S, Joza N, Younes AB, et al. p53 represses the polyploidization of primary mammary epithelial cells by activating apoptosis. Cell cycle. 2009;8:1380–5. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.9.8305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shoemaker RH. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:813–23. doi: 10.1038/nrc1951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Monkhorst K, Jonkers I, Rentmeester E, Grosveld F, Gribnau J. X inactivation counting and choice is a stochastic process: evidence for involvement of an X-linked activator. Cell. 2008;132:410–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Anzali S, Barnickel G, Cezanne B, Krug M, Filimonov D, Poroikov V. Discriminating between drugs and nondrugs by prediction of activity spectra for substances (PASS) J Med Chem. 2001;44:2432–7. doi: 10.1021/jm0010670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T, Housman DE. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993;74:957–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Berglind H, Pawitan Y, Kato S, Ishioka C, Soussi T. Analysis of p53 mutation status in human cancer cell lines: a paradigm for cell line cross-contamination. Cancer biology & therapy. 2008;7:699–708. doi: 10.4161/cbt.7.5.5712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, Modell JW, Blat IC, Wrobel MJ, et al. The Connectivity Map: using gene-expression signatures to connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science. 2006;313:1929–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1132939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sermeus A, Michiels C. Reciprocal influence of the p53 and the hypoxic pathways. Cell death & disease. 2011;2:e164. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Barrett MT, Pritchard D, Palanca-Wessels C, Anderson J, Reid BJ, Rabinovitch PS. Molecular phenotype of spontaneously arising 4N (G2-tetraploid) intermediates of neoplastic progression in Barrett's esophagus. Cancer Res. 2003;63:4211–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Olaharski AJ, Sotelo R, Solorza-Luna G, Gonsebatt ME, Guzman P, Mohar A, et al. Tetraploidy and chromosomal instability are early events during cervical carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:337–43. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Daniels MJ, Wang Y, Lee M, Venkitaraman AR. Abnormal cytokinesis in cells deficient in the breast cancer susceptibility protein BRCA2. Science. 2004;306:876–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1102574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jonsdottir AB, Stefansson OA, Bjornsson J, Jonasson JG, Ogmundsdottir HM, Eyfjord JE. Tetraploidy in BRCA2 breast tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:305–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Caldwell CM, Green RA, Kaplan KB. APC mutations lead to cytokinetic failures in vitro and tetraploid genotypes in Min mice. J Cell Biol. 2007;178:1109–20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200703186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Danes BS. Increased tetraploidy: cell-specific for the Gardner gene in the cultured cell. Cancer. 1976;38:1983–8. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197611)38:5<1983::aid-cncr2820380520>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dikovskaya D, Schiffmann D, Newton IP, Oakley A, Kroboth K, Sansom O, et al. Loss of APC induces polyploidy as a result of a combination of defects in mitosis and apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 2007;176:183–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200610099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Adamson PC, Poplack DG, Balis FM. The cytotoxicity of thioguanine vs mercaptopurine in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia research. 1994;18:805–10. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(94)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Roh M, van der Meer R, Abdulkadir SA. Tumorigenic polyploid cells contain elevated ROS and ARE selectively targeted by antioxidant treatment. Journal of cellular physiology. 2012;227:801–12. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Godinho SA, Picone R, Burute M, Dagher R, Su Y, Leung CT, et al. Oncogene-like induction of cellular invasion from centrosome amplification. Nature. 2014;510:167–71. doi: 10.1038/nature13277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.