Abstract
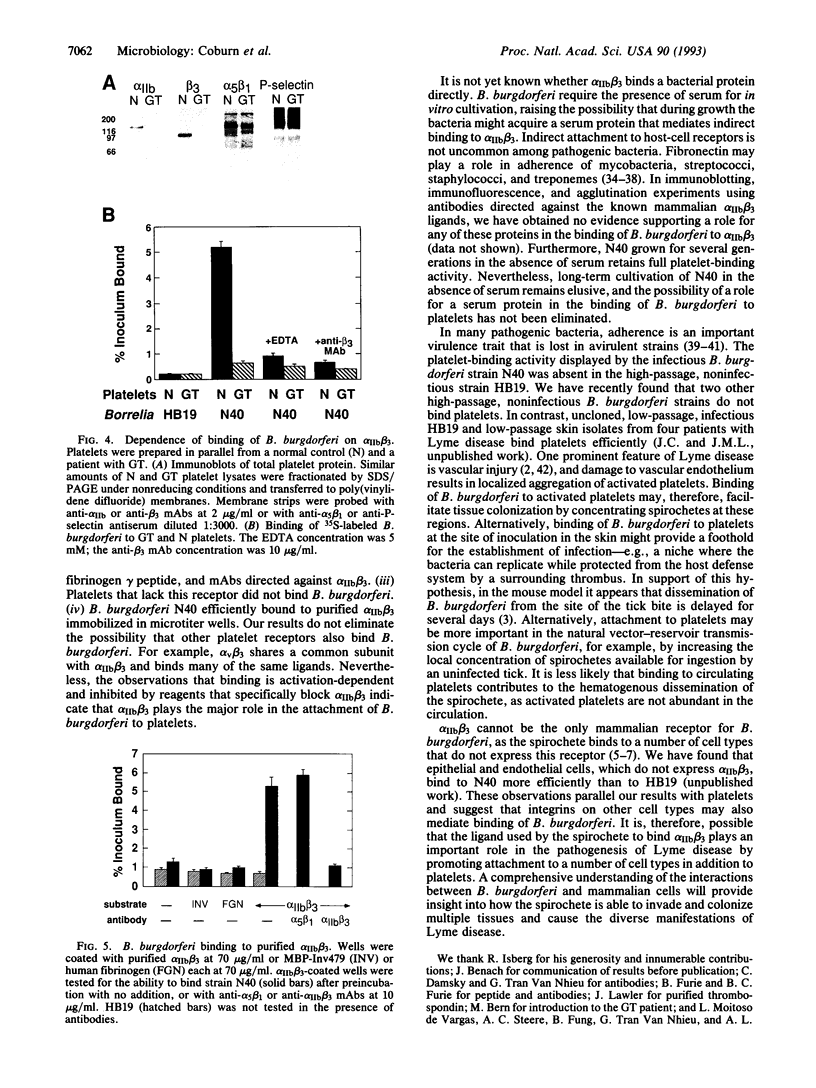
Lyme disease is a chronic, multisystemic infection caused by the tick-borne spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Attachment of the spirochete to host cells via specific receptors is likely to be important in the establishment of infection. B. burgdorferi have previously been shown to bind to a variety of mammalian cells in vitro. Here we demonstrate that binding of B. burgdorferi to human platelets is mediated by the integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (glycoprotein IIb-IIIa), a critical receptor in thrombosis and hemostasis. Functional expression of this receptor requires platelet activation, and binding of the spirochete was observed only to activated platelets. Binding was inhibited by a synthetic Arg-Gly-Asp peptide that blocks ligand interaction with many integrins and by a synthetic peptide based on the gamma chain of fibrinogen that blocks binding to alpha IIb beta 3. In addition, attachment of the spirochete to platelets was inhibited by monoclonal antibodies directed against alpha IIb beta 3 that are known to block ligand-receptor interaction. No inhibition was seen with control peptides or with antibodies directed against other platelet receptors. B. burgdorferi bound efficiently to purified alpha IIb beta 3 but did not bind to platelets deficient in this integrin. Efficient platelet binding was displayed by a cloned, infectious B. burgdorferi strain, whereas a cloned noninfectious strain did not bind to platelets. Binding to integrins may be important for the ability of B. burgdorferi to establish infection in the diverse tissues affected by Lyme disease.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid C., Garbe T., Lathigra R., Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Rook G. A., Young D. B. Genetic and immunological analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis fibronectin-binding proteins. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2712–2718. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2712-2718.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrieux A., Hudry-Clergeon G., Ryckewaert J. J., Chapel A., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F., Marguerie G. Amino acid sequences in fibrinogen mediating its interaction with its platelet receptor, GPIIbIIIa. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9258–9265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Successful cultivation of spirochetes from skin lesions of patients with erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Apr;93(2):161–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Armstrong A. L., Peeples R. A. Kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi dissemination and evolution of disease after intradermal inoculation of mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):263–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E. Role of fibronectin in the pathogenesis of syphilis. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9 (Suppl 4):S372–S385. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_4.s372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. S., Vilaire G. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1393–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI109597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chugh T. D., Burns G. J., Shuhaiber H. J., Bahr G. M. Adherence of Staphylococcus epidermidis to fibrin-platelet clots in vitro mediated by lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):315–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.315-319.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson P. R., Herzberg M. C. Purification and partial characterization of a 65-kDa platelet aggregation-associated protein antigen from the surface of Streptococcus sanguis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14080–14087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Phillips D. R. Calcium regulation of the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11366–11374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Speziale P., Hök M. Isolation and characterization of a fibronectin receptor from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6564–6571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Kloczewiak M., Bednarek M. A., Timmons S. Platelet receptor recognition domains on the alpha chain of human fibrinogen: structure-function analysis. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2909–2914. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Samsonoff W. A., Harris H. L., McKee M. Adherence and entry of Borrelia burgdorferi in Vero cells. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Apr;36(4):229–238. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-4-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg M. C., MacFarlane G. D., Gong K., Armstrong N. N., Witt A. R., Erickson P. R., Meyer M. W. The platelet interactivity phenotype of Streptococcus sanguis influences the course of experimental endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4809–4818. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4809-4818.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu-Lin S., Berman C. L., Furie B. C., August D., Furie B. A platelet membrane protein expressed during platelet activation and secretion. Studies using a monoclonal antibody specific for thrombin-activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9121–9126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston Y. E., Duray P. H., Steere A. C., Kashgarian M., Buza J., Malawista S. E., Askenase P. W. Lyme arthritis. Spirochetes found in synovial microangiopathic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jan;118(1):26–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J. Platelet membrane glycoproteins and their function: an overview. Blut. 1989 Jul;59(1):30–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00320245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtti T. J., Munderloh U. G., Ahlstrand G. G., Johnson R. C. Borrelia burgdorferi in tick cell culture: growth and cellular adherence. J Med Entomol. 1988 Jul;25(4):256–261. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/25.4.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtti T. J., Munderloh U. G., Johnson R. C., Ahlstrand G. G. Colony formation and morphology in Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2054–2058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2054-2058.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Fournier R. S., Isberg R. R. Identification of the integrin binding domain of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1979–1989. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Fournier R. S., Isberg R. R. Mapping and topographic localization of epitopes of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3424–3433. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3424-3433.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Moitoso de Vargas L., Isberg R. R. Binding of cultured mammalian cells to immobilized bacteria. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):683–686. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.683-686.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance J. H., Baddour L. M., Simpson W. A. The role of fibronectin binding in the rat model of experimental endocarditis caused by Streptococcus sanguis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):7–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI114717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P., Martin M. N. A monoclonal antibody to a membrane glycoprotein binds only to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9799–9804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. An abnormal platelet glycoprotein pattern in three cases of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1974 Oct;28(2):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Evidence for the presence of nonequivalent disulfide bonds using nonreduced-reduced two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M., Hayman E. G., Ruoslahti E. Synthetic peptide with cell attachment activity of fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1224–1227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Specific and saturable binding of plasma fibronectin to thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9477–9482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Schierz G. European Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from humans and ticks culture conditions and antibiotic susceptibility. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):112–118. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Argraves S., Suzuki S., Ruoslahti E. Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid adhesion receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1987;144:475–489. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)44196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratliff T. L., McGarr J. A., Abou-Zeid C., Rook G. A., Stanford J. L., Aslanzadeh J., Brown E. J. Attachment of mycobacteria to fibronectin-coated surfaces. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1307–1313. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. M., Pollack R. J., Telford S. R., 3rd, Spielman A. Delayed dissemination of Lyme disease spirochetes from the site of deposition in the skin of mice. J Infect Dis. 1992 Oct;166(4):827–831. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.4.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Furie M. B., Benach J. L., Lane B. P., Fleit H. B. Interaction between Borrelia burgdorferi and endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1637–1647. doi: 10.1172/JCI114615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Comstock L. E. Interaction of Lyme disease spirochetes with cultured eucaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1324–1326. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1324-1326.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Hawiger J. Isolation of human platelets by albumin gradient and gel filtration. Methods Enzymol. 1989;169:11–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)69046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]