Abstract
For many tRNAs, the discriminator base preceding the CCA sequence at the 3' end is important for aminoacylation. We show that the discriminator base influences the stability of the 1.72 base pair onto which it is stacked. Mutations of the discriminator base from adenosine to cytidine or uridine make the cytidine residue in the C1-G72 base pair of mutant Escherichia coli initiator tRNAs more reactive toward sodium bisulfite, the single-strand-specific reagent. The activity of the enzyme Met-tRNA transformylase toward these and other mutant initiator tRNAs is also consistent with destabilization of the 1.72 base pair in vitro and in vivo. By influencing the strength of the 1.72 base pair, the discriminator base could affect the energetic cost of opening the base pair and modulate the structure of the tRNA near the site of aminoacylation. For some aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and other proteins that interact with tRNA, these factors could be important for specific recognition and/or formation of the transition state during catalysis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhanot O. S., Chambers R. W. Bisulfite-induced C changed to U transitions in yeast alanine tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2551–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Seno T., Söll G. Is there a discriminator site in transfer RNA? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3063–3067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frugier M., Florentz C., Giegé R. Anticodon-independent aminoacylation of an RNA minihelix with valine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3990–3994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon J. M., Meinnel T., Mechulam Y., Lazennec C., Blanquet S., Fayat G. Nucleotides of tRNA governing the specificity of Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA(fMet) formyltransferase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91000-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper M. L., Russell R. L., Smith J. D. Mischarging in mutant tyrosine transfer RNAs. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 15;22(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn M., Rogers M. J., Söll D. Anticodon and acceptor stem nucleotides in tRNA(Gln) are major recognition elements for E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):258–260. doi: 10.1038/352258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Yarus M. Discrimination between aminoacyl groups on su+ 7 tRNA by elongation factor Tu. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 5;139(4):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komine Y., Adachi T., Inokuchi H., Ozeki H. Genomic organization and physical mapping of the transfer RNA genes in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):579–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90224-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kössel H., RajBhandary U. L. Studies on polynucleotides. LXXXVI. Enzymic hydrolysis of N-acylaminoacyl-transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 14;35(3):539–560. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. P., Dyson M. R., Mandal N., Varshney U., Bahramian B., RajBhandary U. L. Striking effects of coupling mutations in the acceptor stem on recognition of tRNAs by Escherichia coli Met-tRNA synthetase and Met-tRNA transformylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9262–9266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. P., Seong B. L., RajBhandary U. L. Structural and sequence elements important for recognition of Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA by methionyl-tRNA transformylase are clustered in the acceptor stem. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18012–18017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal N., RajBhandary U. L. Escherichia coli B lacks one of the two initiator tRNA species present in E. coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7827–7830. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7827-7830.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K., Jenkins R. A., Schneider J. Nucleotides that determine Escherichia coli tRNA(Arg) and tRNA(Lys) acceptor identities revealed by analyses of mutant opal and amber suppressor tRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9260–9264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K., Jenkins R. A., Schneider J. Rapid determination of nucleotides that define tRNA(Gly) acceptor identity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menninger J. R. The accumulation as peptidyl-transfer RNA of isoaccepting transfer RNA families in Escherichia coli with temperature-sensitive peptidyl-transfer RNA hydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6808–6813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moras D. Structural and functional relationships between aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90326-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Abelson J. tRNA identity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:1029–1049. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.005121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallanck L., Li S., Schulman L. H. The anticodon and discriminator base are major determinants of cysteine tRNA identity in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7221–7223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pütz J., Puglisi J. D., Florentz C., Giegé R. Identity elements for specific aminoacylation of yeast tRNA(Asp) by cognate aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1696–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2047878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould M. A., Perona J. J., Söll D., Steitz T. A. Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1135–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2479982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M., Krishnaswamy S., Boeglin M., Poterszman A., Mitschler A., Podjarny A., Rees B., Thierry J. C., Moras D. Class II aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetases: crystal structure of yeast aspartyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Asp). Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1682–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.2047877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., DiRenzo A. B., Behlen L. S., Uhlenbeck O. C. Nucleotides in yeast tRNAPhe required for the specific recognition by its cognate synthetase. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1363–1366. doi: 10.1126/science.2646717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Goddard J. P. Loss of methionine acceptor activity resulting from a base change in the anticodon of Escherichia coli formylmethionine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1341–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Pelka H. The structural basis for the resistance of Escherichia coli formylmethionyl transfer ribonucleic acid to cleavage by Escherichia coli peptidyl transfer ribonucleic acid hydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):542–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H. Recognition of tRNAs by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:23–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong B. L., Lee C. P., RajBhandary U. L. Suppression of amber codons in vivo as evidence that mutants derived from Escherichia coli initiator tRNA can act at the step of elongation in protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6504–6508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong B. L., RajBhandary U. L. Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA: mutations in GGGCCC sequence conserved in anticodon stem of initiator tRNAs affect initiation of protein synthesis and conformation of anticodon loop. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):334–338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong B. L., RajBhandary U. L. Mutants of Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA: a single base change enables initiator tRNA to act as an elongator in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8859–8863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
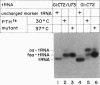
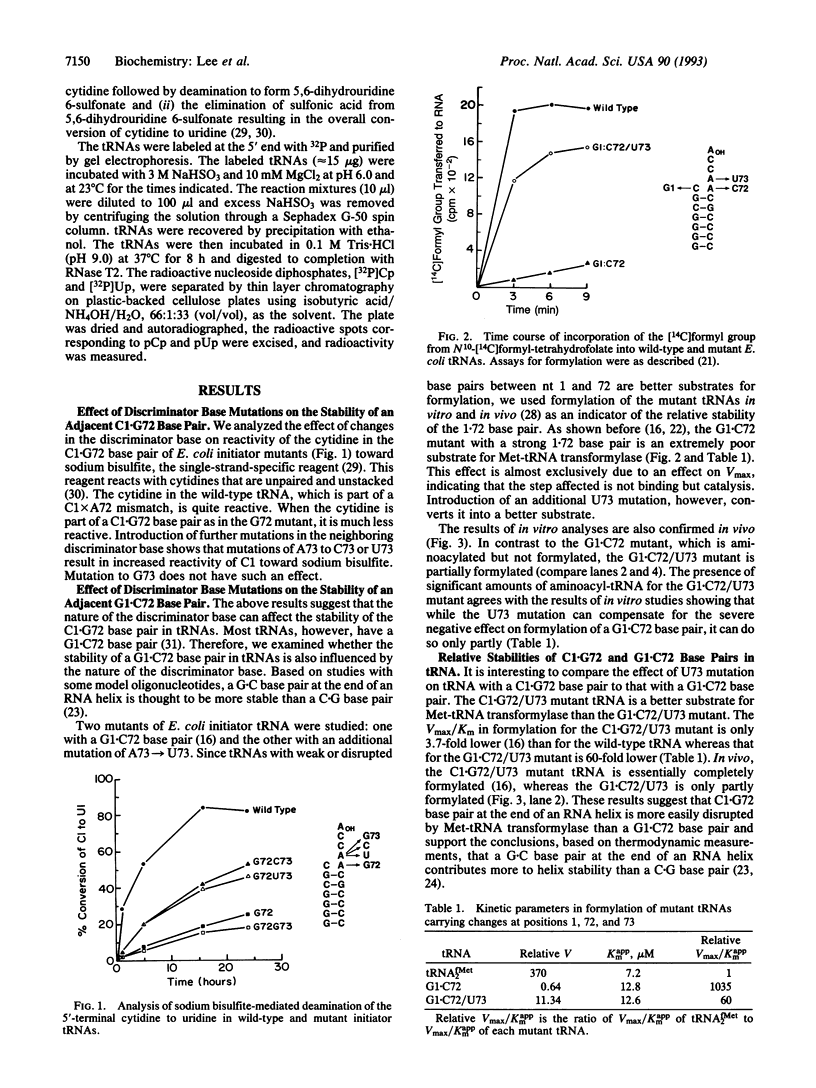
- Sherman J. M., Rogers K., Rogers M. J., Söll D. Synthetase competition and tRNA context determine the in vivo identify of tRNA discriminator mutants. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1055–1062. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90314-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi J. P., Francklyn C., Hill K., Schimmel P. A nucleotide that enhances the charging of RNA minihelix sequence variants with alanine. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 17;29(15):3621–3626. doi: 10.1021/bi00467a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi J. P., Schimmel P. Aminoacylation of alanine minihelices. "Discriminator" base modulates transition state of single turnover reaction. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2705–2708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Asahara H., Tamura K., Hasegawa T., Himeno H. The role of anticodon bases and the discriminator nucleotide in the recognition of some E. coli tRNAs by their aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. J Mol Evol. 1992 Nov;35(5):436–443. doi: 10.1007/BF00171822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura Y., Aono H., Ozeki H., Sarabhai A., Lamfrom H., Abelson J. Mutant tyrosine tRNA of altered amino acid specificity. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 15;22(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Hartmann T., Weber J., Blank J., Zeidler R. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17 (Suppl):r1–172. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto N., Kierzek R., Turner D. H. Sequence dependence for the energetics of dangling ends and terminal base pairs in ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4554–4558. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. H., Sugimoto N., Freier S. M. RNA structure prediction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:167–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney U., Lee C. P., RajBhandary U. L. Direct analysis of aminoacylation levels of tRNAs in vivo. Application to studying recognition of Escherichia coli initiator tRNA mutants by glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24712–24718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo N. H., Roe B. A., Rich A. Three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli initiator tRNAfMet. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):346–351. doi: 10.1038/286346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]