Abstract
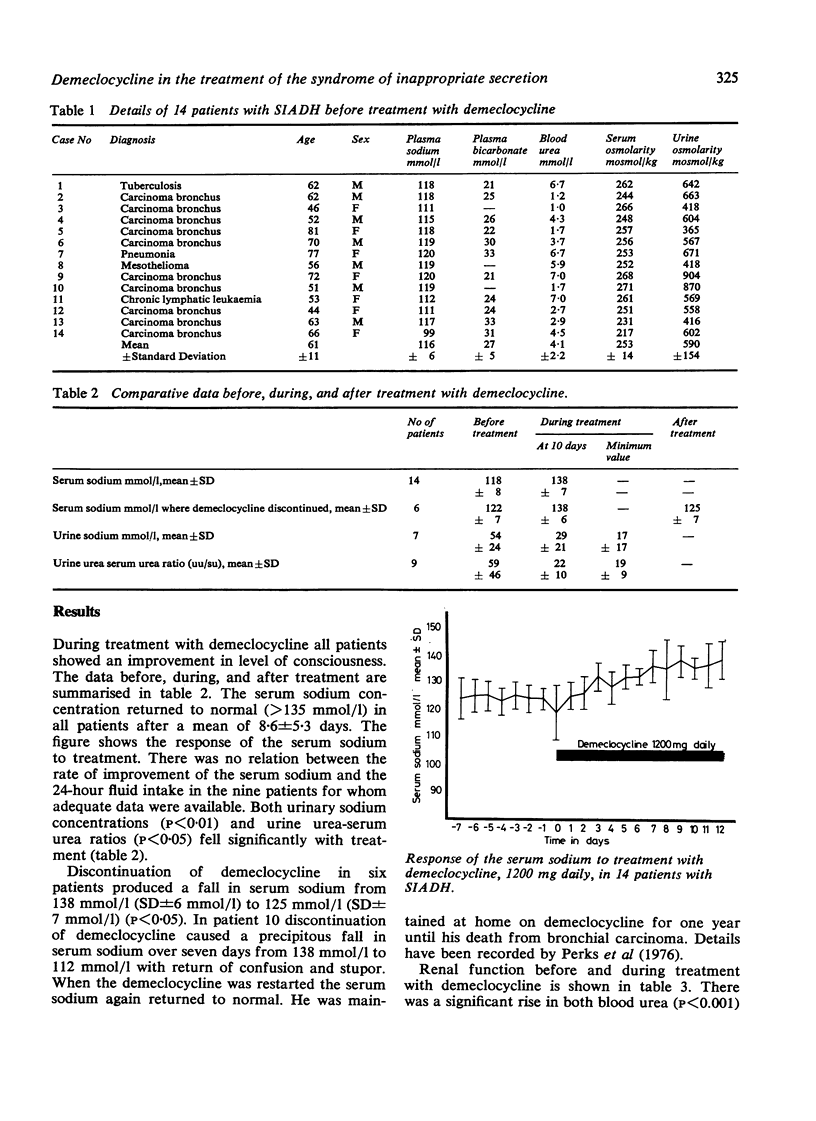
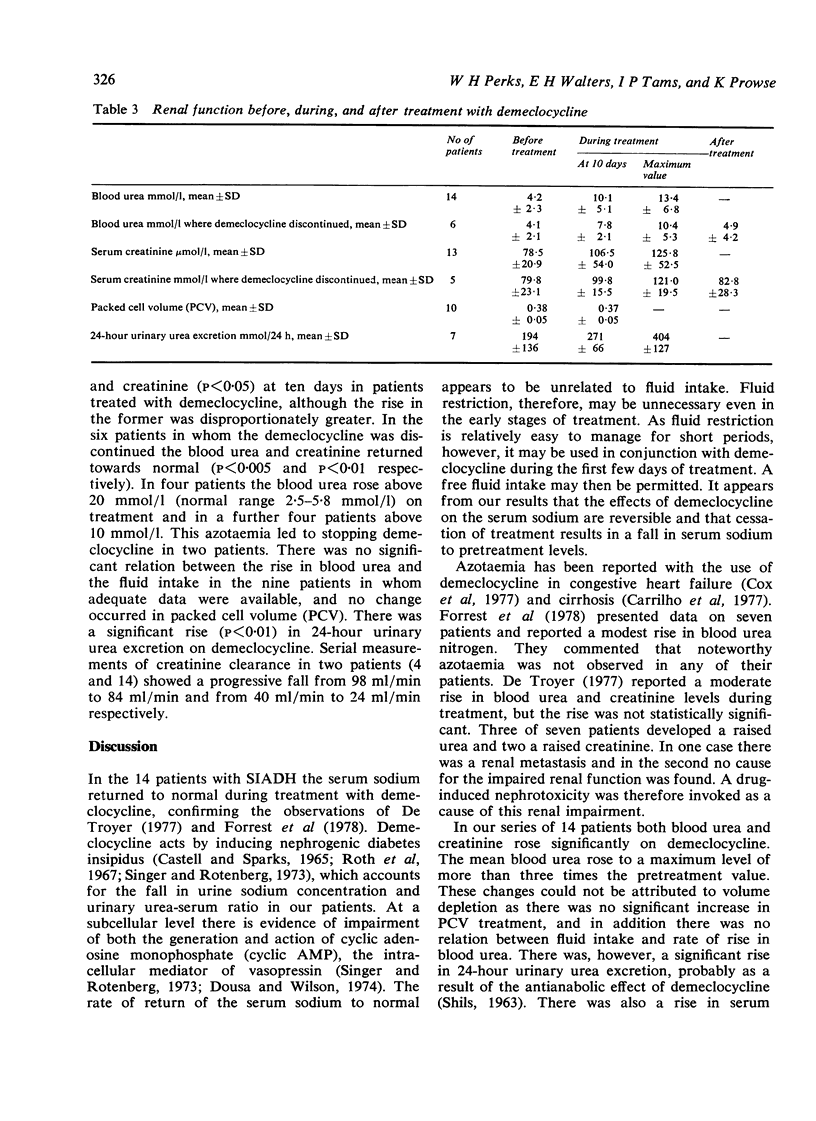
Fourteen patients with the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) have been treated with demethylchlortetracycline (demeclocycline) 1200 mg daily. In 12 patients the underlying lesion was malignant. The serum sodium returned to normal (greater than 135 mmol/l) in all patients after a mean of 8.6 days (SD +/- 5.3 days). Blood urea rose significantly from the pretreatment level of 4.2 +/- 2.3 mmol/l to 10.1 +/- 5.1 mmol/l at ten days (P less than 0.001). The average maximum blood urea was 13.4 +/- 6.8 mmol/l. In four patients the urea rose above 20 mmol/l, and in two of these demecyocycline was discontinued because of thie rise. The azotaemia could be attributed to a combination of increased urea producation and a mild specific drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Discontinuation of demeclocycline in six patients led to a fall in serum sodium, in one case precipitously, and return of the urea towards normal levels. Demeclocycline appears therefore to be an effective maintenance treatment of SIADH, and the azotaemia that occurs is reversible and probably dose dependent.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CASTELL D. O., SPARKS H. A. NEPHROGENIC DIABETES INSIPIDUS DUE TO DEMETHYLCHLORTETRACYCLINE HYDROCHLORIDE. JAMA. 1965 Jul 19;193:237–239. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090030059024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrilho F., Bosch J., Arroyo V., Mas A., Viver J., Rodes J. Renal failure associated with demeclocycline in cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Aug;87(2):195–197. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrill D. A., Stote R. M., Birge J. R., Singer I. Demeclocycline treatment in the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Nov;83(5):654–656. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-5-654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M., Guzzo J., Morrison G., Singer I. Demeclocycline and therapy of hyponatremia. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jan;86(1):113–114. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Demanet J. C. Clinical, biological and pathogenic features of the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. A review of 26 cases with marked hyponatraemia. Q J Med. 1976 Oct;45(180):521–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Demanet J. C. Correction of antidiuresis by demeclocycline. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):915–918. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A. Demeclocycline. Treatment for syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. JAMA. 1977 Jun 20;237(25):2723–2726. doi: 10.1001/jama.237.25.2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dousa T. P., Wilson D. M. Effects of demethylchlortetracycline on cellular action of antidiuretic hormone in vitro. Kidney Int. 1974 Apr;5(4):279–284. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest J. N., Jr, Cox M., Hong C., Morrison G., Bia M., Singer I. Superiority of demeclocycline over lithium in the treatment of chronic syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 26;298(4):173–177. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801262980401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perks W. H., Crow J. C., Green M. Mesothelioma associated with the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Apr;117(4):789–794. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.4.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perks W. H., Mohr P., Liversedge L. A. Demeclocycline in inappropriate A.D.H. syndrome. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1414–1414. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91958-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth H., Becker K. L., Shalhoub R. J., Katz S. Nephrotoxicity of demethylchlortetracycline hydrochloride. A prospective study. Arch Intern Med. 1967 Oct;120(4):433–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHILS M. E. Renal disease and the metabolic effects of tetracycline. Ann Intern Med. 1963 Mar;58:389–408. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-58-3-389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I., Rotenberg D. Demeclocycline-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. In-vivo and in-vitro studies. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):679–683. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


