Abstract
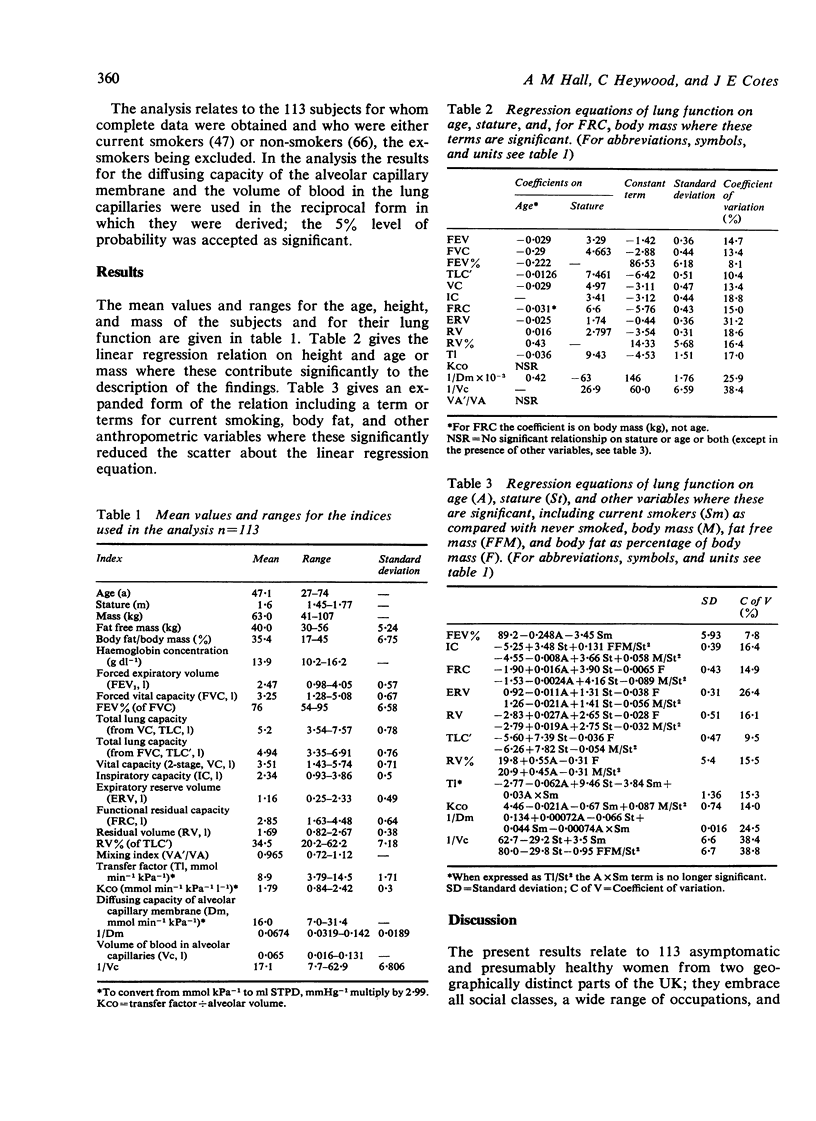
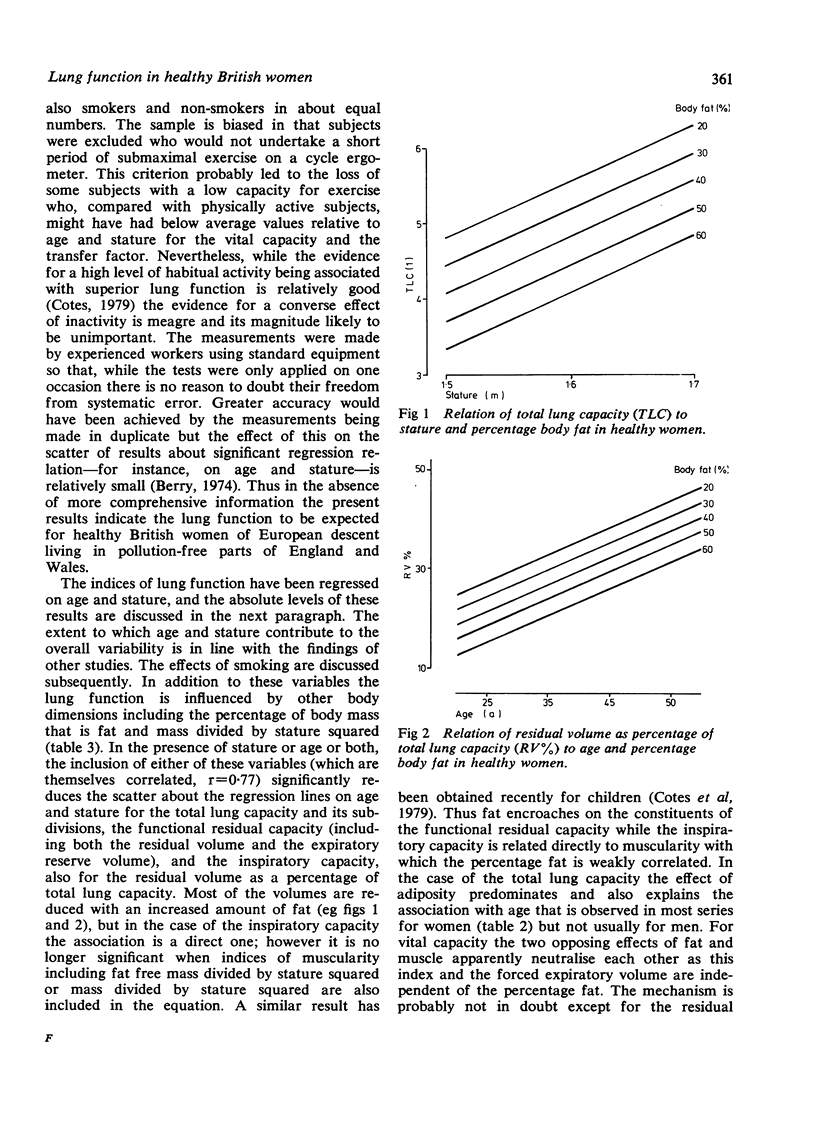
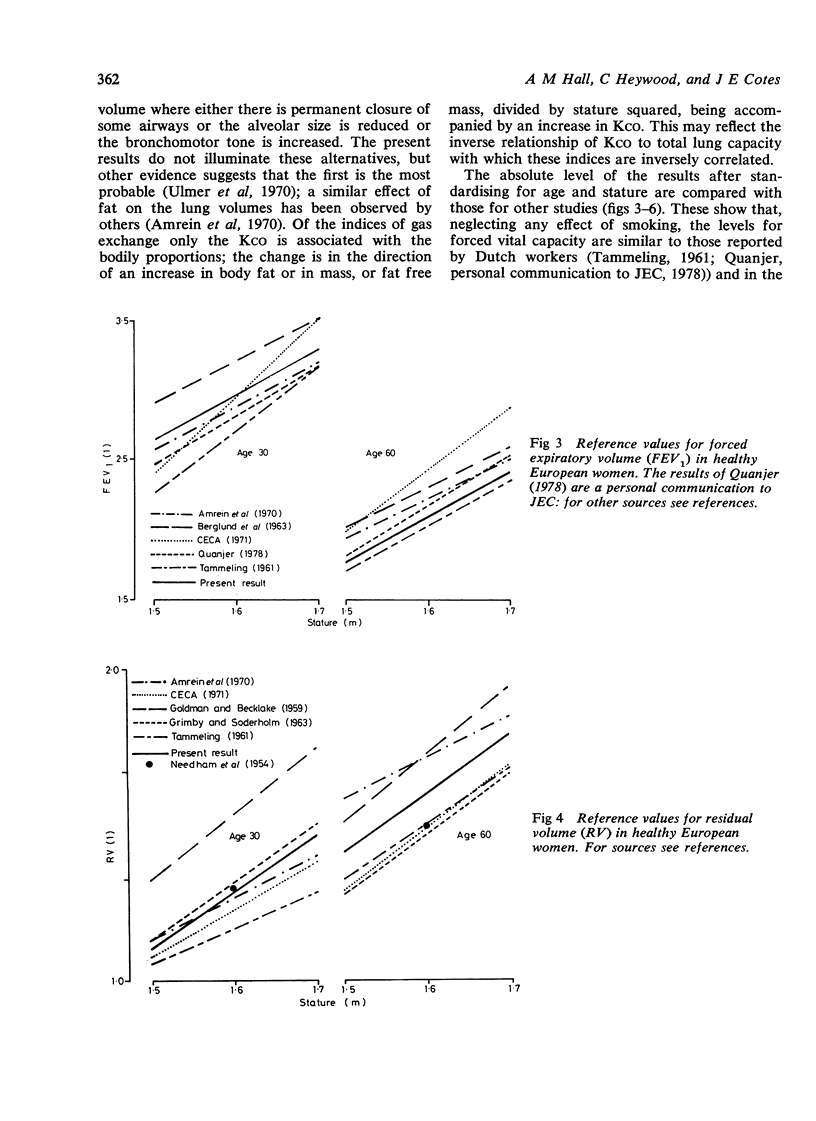
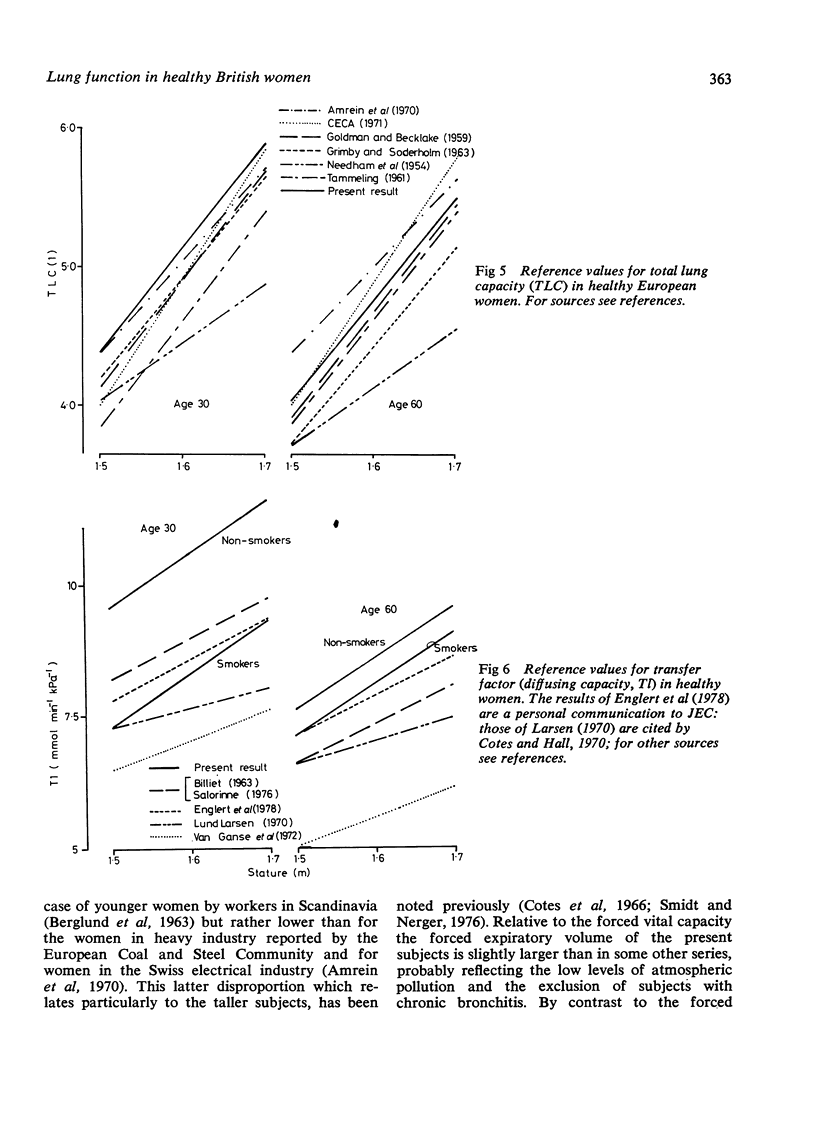
The forces expiratory volume, total lung capacity, transfer factor (diffusing capacity), and their subdivisions have been measured in 113 healthy British women aged 27 to 74 years of whom 47 were current smokers and 66 were lifetime non-smokers. The results have been analysed in terms of age, stature, mass, body fat, and smoking. In addition to their relation to stature and to age, the inspiratory capacity was positively correlated with indices of body muscle while the residual volume, expiratory reserve volume, and total lung capacity were inversely correlated with the percentage of body mass that is fat or with mass divided by the square of stature. The inverse correlation between total lung capacity and age was apparently due to the quantity of body fat increasing with age. The transfer factor and its subdivisions were inversely correlated with smoking. In this study the forced expiratory volume and vital capacity were independent of both fat and smoking; the transfer factor was independent of the physiological response to exercise. The results provide reference values for lung function in British women.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein R., Keller R., Joos H., Herzog H. Valeurs théoriques nouvelles de l'exploration de la fonction ventilatoire du poumon. Bull Physiopathol Respir (Nancy) 1970 Apr-Jun;6(2):317–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGLUND E., BIRATH G., BJURE J., GRIMBY G., KJELLMER I., SANDQVIST L., SODERHOLM B. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. I. Forced expirograms in subjects between 7 and 70 years of age. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Feb;173:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLIET L., BAISIER W., NAEDTS J. P. [Effect of size, sex and age on the pulmonary diffusion capacity of the normal adult]. J Physiol (Paris) 1963;55:199–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry G. Longitudinal observations. Their usefulness and limitations with special reference to the forced expiratory volume. Bull Physiopathol Respir (Nancy) 1974 Sep-Oct;10(5):643–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Berry G., Burkinshaw L., Davies C. T., Hall A. M., Jones P. R., Knibbs A. V. Cardiac frequency during submaximal exercise in young adults; relation to lean body mass, total body potassium and amount of leg muscle. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1973 Jul;58(3):239–250. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1973.sp002212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Dabbs J. M., Hall A. M., Axford A. T., Laurence K. M. Lung volumes, ventilatory capacity, and transfer factor in healthy British boy and girl twins. Thorax. 1973 Nov;28(6):709–715. doi: 10.1136/thx.28.6.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Hall A. M., Johnson G. R., Jones P. R., Knibbs A. V. Proceedings: Decline with age of cardiac frequency during submaximal exercise in healthy women. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):24P–25P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Rossiter C. E., Higgins I. T., Gilson J. C. Average normal values for the forced expiratory volume in white Caucasian males. Br Med J. 1966 Apr 23;1(5494):1016–1019. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5494.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. I., BECKLAKE M. R. Respiratory function tests; normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Apr;79(4):457–467. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salorinne Y. Single-breath pulmonary diffusing capacity. Reference values and application in connective tissue diseases and in various lung diseases. Scand J Respir Dis Suppl. 1976;96:1–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ganse W. F., Ferris B. G., Jr, Cotes J. E. Cigarette smoking and pulmonary diffusing capacity. (Transfer factor). Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Jan;105(1):30–41. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.105.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


