Abstract
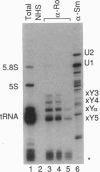
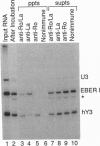
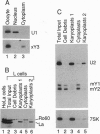
Ro small ribonucleoproteins consist of a 60-kDa protein and possibly additional proteins complexed with several small RNA molecules. The RNA components of these particles, designated Y RNAs, are about 100 nt long. Although these small ribonucleoproteins are abundant components of a variety of vertebrate species and cell types, their subcellular location is controversial, and their function is completely unknown. We have identified and characterized the Ro RNPs of Xenopus laevis. Three of the four distinct Xenopus Y RNAs appear to be related to the previously sequenced human hY3, hY4, and hY5 RNAs. The fourth Xenopus Y RNA, xY alpha, does not appear to be a homologue of any of the human Y RNAs. Each of the human and Xenopus Y RNAs possesses a conserved stem that contains the binding site for the 60-kDa Ro protein. Xenopus and human 60-kDa Ro proteins are 78% identical in amino acid sequence, with the conservation extending throughout the entire protein. When human hY3 RNA is mixed with Xenopus egg extracts, the human RNA assembles with the Xenopus Ro protein to form chimeric Ro ribonucleoproteins. By analyzing RNA extracted from manually enucleated oocytes and germinal vesicles, we have determined that Y RNAs are located in the oocyte cytoplasm. By examining the distribution of mouse Ro ribonucleoproteins in cytoplast and karyoplast fractions derived from L-929 cells, we have determined that Ro ribonucleoprotein particles also primarily reside in the cytoplasm of mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alspaugh M. A., Tan E. M. Antibodies to cellular antigens in Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1067–1073. doi: 10.1172/JCI108007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga S. J., Yang X. D., Steitz J. A. An intact Box C sequence in the U3 snRNA is required for binding of fibrillarin, the protein common to the major family of nucleolar snRNPs. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2645–2651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07807.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Chetrit E., Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M. A 52-kD protein is a novel component of the SS-A/Ro antigenic particle. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1560–1571. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Harley J. B., Keene J. D. Molecular analysis of the 60-kDa human Ro ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9479–9483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Phy M: an RNase activity specific for U and A residues useful in RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3133–3142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr, Eliceiri G. L. Intracellular distribution of low molecular weight RNA species in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):398–403. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon C. E., Deng J. S., Peebles C. L., Tan E. M. The importance of tissue substrate in the SS-A/Ro antigen-antibody system. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Feb;27(2):166–173. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wolin S. L., Rinke J., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins are a subclass of La ribonucleoproteins: further characterization of the Ro and La small ribonucleoproteins from uninfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1138–1149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Hoshino H., Harada F. Nucleotide sequence of 4.5S RNA (C8 or hY5) from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91875-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Dingwall C., Maier G., Franke W. W. Molecular characterization of a karyophilic, histone-binding protein: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and expression of nuclear protein N1/N2 of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3547–3552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G., Gross H. J. Rapid RNA sequencing: nucleases from Staphylococcus aureus and Neurospora crassa discriminate between uridine and cytidine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3481–3490. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R. RNA polymerase III transcription of genes that lack internal control regions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. In vitro synthesis of vertebrate U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):287–292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamula M. J., O'Brien C. A., Harley J. B., Hardin J. A. The Ro ribonucleoprotein particle: induction of autoantibodies and the detection of Ro RNAs among species. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Sep;52(3):435–446. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli M., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of RNA protein antigens reactive with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Description of a cytoplasmic nonribosomal antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jul-Aug;17(4):421–429. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroy G., Spencer E., Hurwitz J. Characteristics of reactions catalyzed by purified guanylyltransferase from vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4490–4498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien C. A., Harley J. B. A subset of hY RNAs is associated with erythrocyte Ro ribonucleoproteins. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3683–3689. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Gerber A. S., Hartl D. L. Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):621–623. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., Slobbe R. L., van Venrooij W. J. Analysis of protein--RNA interactions within Ro ribonucleoprotein complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5173–5180. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Tan E. M., Henning D., Nohga K., Busch H. Detection of a nucleolar 7-2 ribonucleoprotein and a cytoplasmic 8-2 ribonucleoprotein with autoantibodies from patients with scleroderma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1383–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter K., Grunz H., Dawid I. B. Gene expression in the embryonic nervous system of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8086–8090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E. Purified lupus antigen La recognizes an oligouridylate stretch common to the 3' termini of RNA polymerase III transcripts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toczyski D. P., Steitz J. A. The cellular RNA-binding protein EAP recognizes a conserved stem-loop in the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):703–710. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M. H., Weinstein I. B. A preparative method for obtaining enucleated mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):669–674. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Genes for two small cytoplasmic Ro RNAs are adjacent and appear to be single-copy in the human genome. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):735–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. The Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins: identification of the antigenic protein and its binding site on the Ro RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J. K., Melton D. A. Synthesis of long, capped transcripts in vitro by SP6 and T7 RNA polymerases. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:42–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Sauterer R. A., Feeney R. J. Newly synthesized small nuclear RNAs appear transiently in the cytoplasm. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]