Abstract
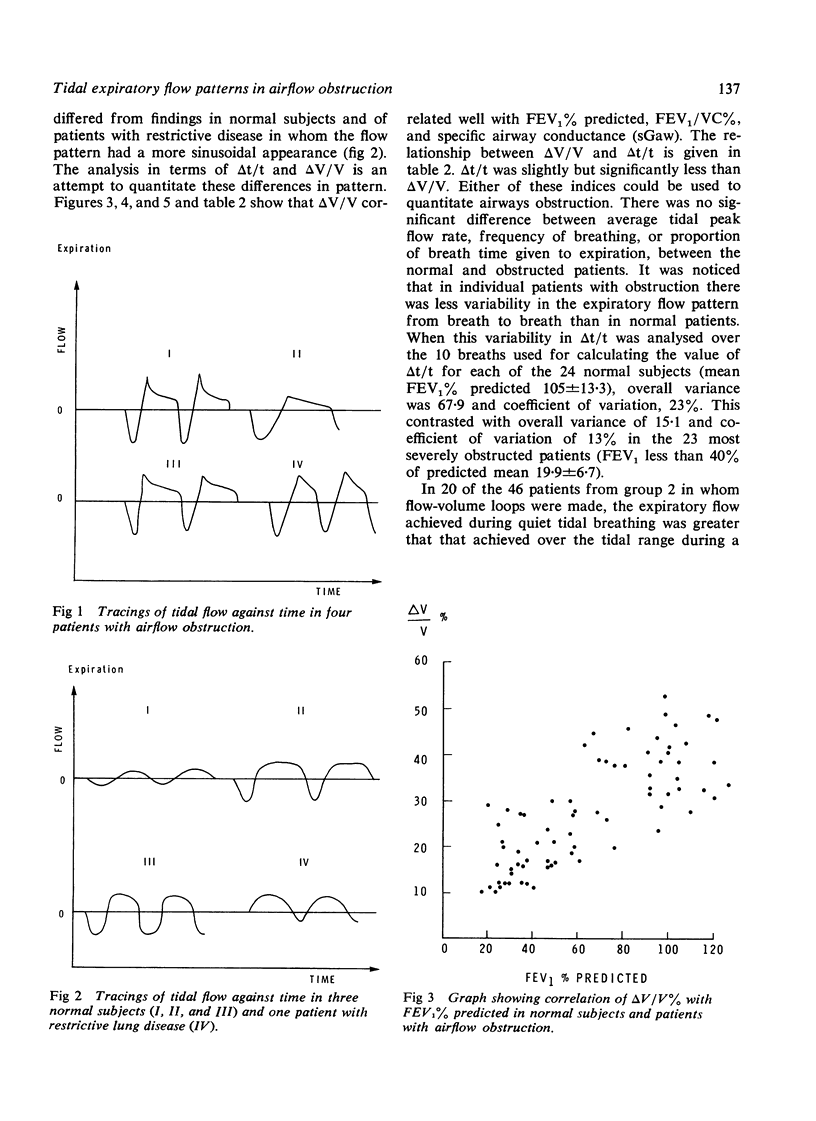
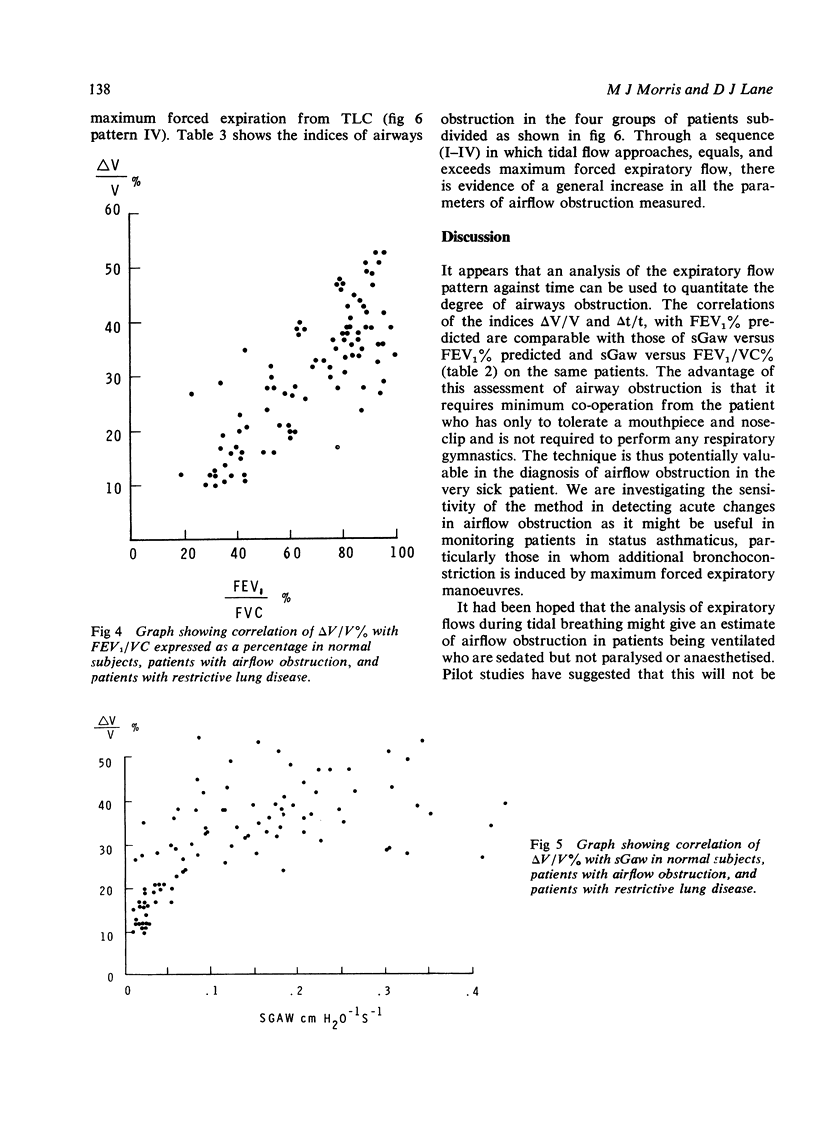
Tidal expiratory flow pattern was analysed in 99 subjects with a view to assessing it as a quantitative measurement of airflow obstruction. Fifteen normal volunteers, nine patients with dyspnoea referred for investigation in whom airway resistance was within normal limits, 24 patients with restrictive lung disorders, and 51 patients with airway obstruction were studied. The expiratory flow pattern against time had a quadrilateral configuration in airway obstruction, which differed from the more sinusoidal form that is seen in subjects without airflow obstruction. The rapid rise to tidal peak flow was analysed in two ways, percentage of volume expired at tidal peak flow (delta V/V) and percentage of expiratory time to tidal peak flow (delta t/t). Both these indices correlated significantly with conventional measurements of airway obstruction. The pattern of expiratory flow in airflow obstruction during quiet breathing resembles that of a forced expiratory maneuver at similar lung volumes. In some cases this may be caused by dynamic compression occurring during tidal breathing. In others, the pattern may result from the static recoil of the lung being permitted to drive flow freely in expiration, rather than being braked by postinspiratory contraction of inspiratory musculature.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGOSTONI E., SANT'AMBROGIO G., DEL PORTILLO CARRASCO H. Electromyography of the diaphragm in man and transdiaphragmatic pressure. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Nov;15:1093–1097. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.6.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett D., Jr, Remmers J. E., Gautier H. Laryngeal regulation of respiratory airflow. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jul;18(2):194–204. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., COMROE J. H., Jr A new method for measuring airway resistance in man using a body plethysmograph: values in normal subjects and in patients with respiratory disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):327–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI103282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. H., HOWELL J. B. The correlation of intercostal muscle activity with respiratory air flow in concious human subjects. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:471–476. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier H., Remmers J. E., Bartlett D., Jr Control of the duration of expiration. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jul;18(2):205–221. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayrard P., Orehek J., Grimaud C., CHarpin J. Bronchoconstrictor effects of a deep inspiration in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Apr;111(4):433–439. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço R. V., Mueller E. P. Quantification of electrical activity in the human diaphragm. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Mar;22(3):598–600. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.3.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILIC-EMILI J., MEAD J., TURNER J. M., GLAUSER E. M. IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR ESTIMATING PLEURAL PRESSURE FROM ESOPHAGEAL BALLOONS. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Mar;19:207–211. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J., Turner J. M., Macklem P. T., Little J. B. Significance of the relationship between lung recoil and maximum expiratory flow. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jan;22(1):95–108. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETIT J. M., MILIC-EMILI G., DELHEZ L. Role of the diaphragm in breathing in conscious normal man: an electromyographic study. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Nov;15:1101–1106. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.6.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIERCE J. A. Studies of free collapse in the intact human lung. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Jul;54(1):96–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers J. E., Bartlett D., Jr Reflex control of expiratory airflow and duration. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Jan;42(1):80–87. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.42.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent N. J., Knudson R., Leith D. E., Macklem P. T., Mead J. Factors influencing pulmonary resistance. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Aug;29(2):236–243. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.29.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


