Abstract
The Ras-related small GTP-binding proteins are involved in diverse cellular events, including cell signaling, proliferation, cytoskeletal organization, and secretion. The interconversion of the active, GTP-bound form of the protein to the inactive, GDP-bound form is influenced by two types of regulatory proteins, those that alter the intrinsic GTPase activity of the GTP-binding protein and those that affect the rate of GDP/GTP exchange. By utilizing a subtractive hybridization approach, we have isolated a human gene encoding Ly-GDI, a protein that has striking homology to the product of a previously cloned gene, Rho-GDI, which inhibits GDP/GTP exchange on the Rho family of GTPases. In contrast to Rho-GDI, which is ubiquitously expressed, Ly-GDI is expressed only in hematopoietic tissues and predominantly in B- and T-lymphocyte cell lines. The full-length Ly-GDI cDNA encodes a 27-kDa protein which binds to RhoA and inhibits GDP dissociation from RhoA. Stimulation of T lymphocytes with phorbol ester leads to phosphorylation of Ly-GDI, suggesting an involvement of Ly-GDI in lymphocyte activation pathways. Cell type-specific regulators of the Ras-like GTP-binding proteins may provide one mechanism by which different cell types respond uniquely to signals transduced through the same cell surface receptor or may provide a way by which the GTP-binding proteins can be uniquely engaged by tissue-restricted receptors.
Full text
PDF

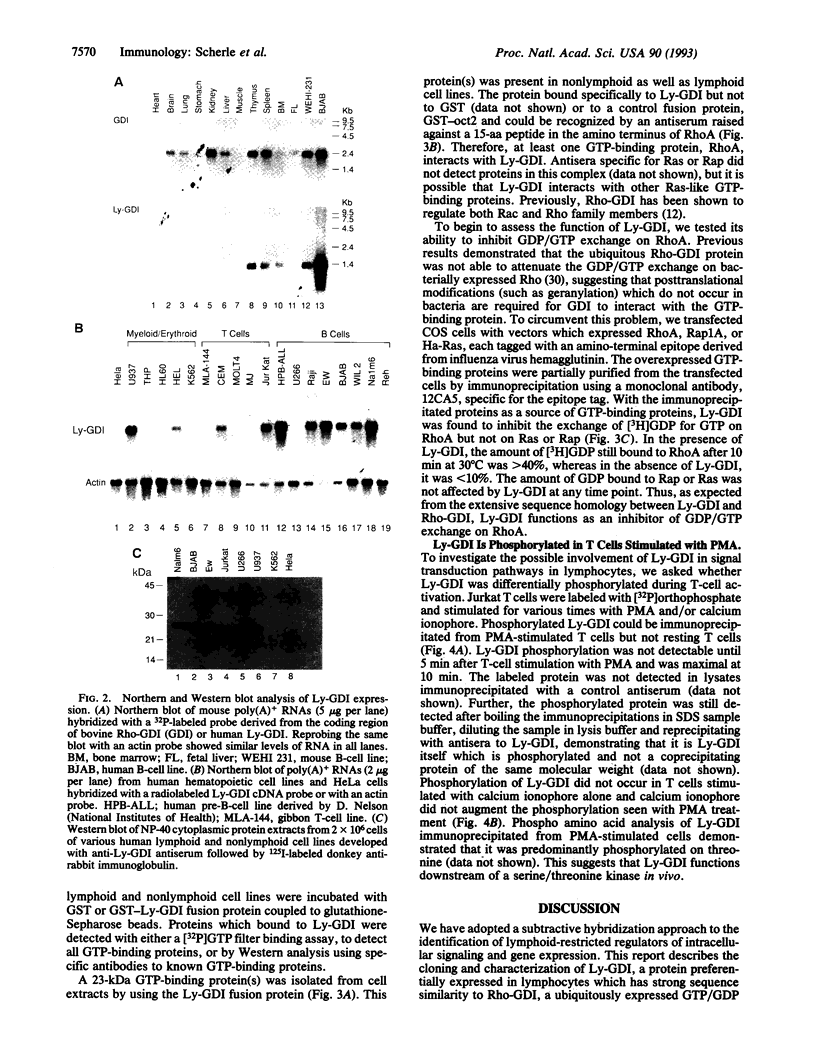
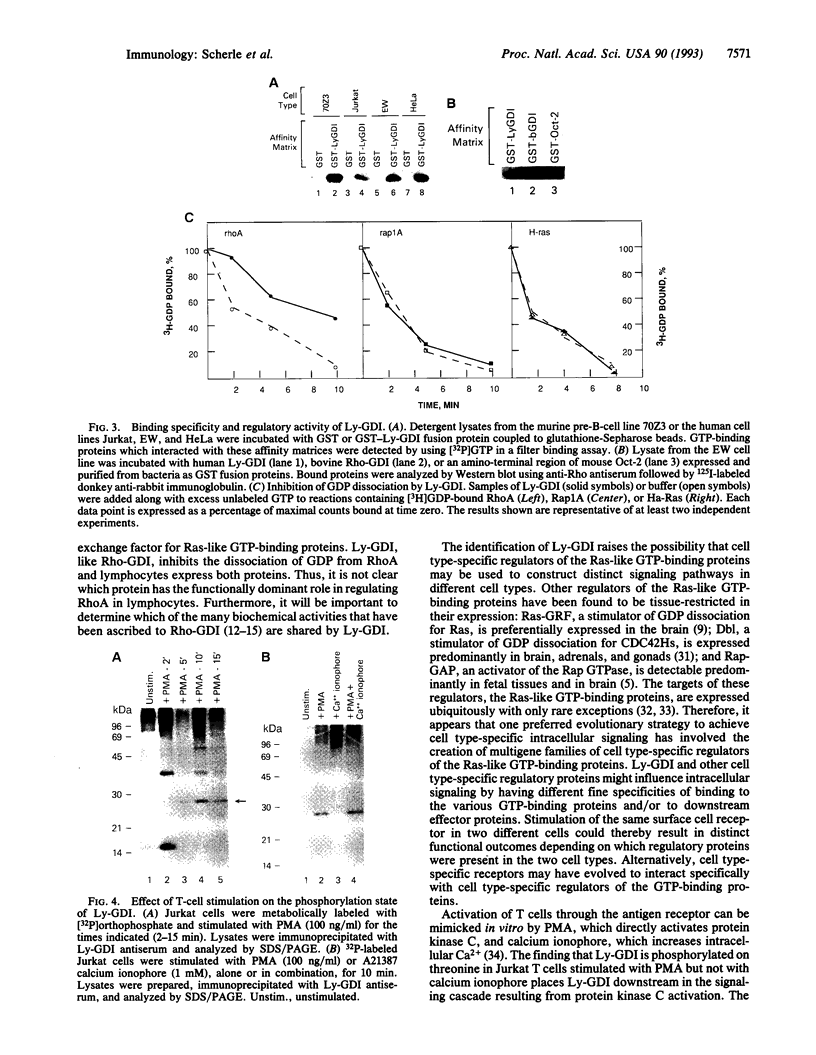

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo A., Pick E., Hall A., Totty N., Teahan C. G., Segal A. W. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):668–670. doi: 10.1038/353668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avraham H., Weinberg R. A. Characterization and expression of the human rhoH12 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2058–2066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldari C. T., Macchia G., Telford J. L. Interleukin-2 promoter activation in T-cells expressing activated Ha-ras. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4289–4291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R. Contingent genetic regulatory events in T lymphocyte activation. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):355–361. doi: 10.1126/science.2783497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBell K. E., Conti A., Alava M. A., Hoffman T., Bonvini E. Microfilament assembly modulates phospholipase C-mediated signal transduction by the TCR/CD3 in murine T helper lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2271–2280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J., Weber R. F., Bokoch G. M., Evans T., Snyderman R. rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16378–16382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Riehl R., Wu L., Weinberg R. A. Identification of a nucleotide exchange-promoting activity for p21ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5998–6002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto Y., Kaibuchi K., Hori Y., Fujioka H., Araki S., Ueda T., Kikuchi A., Takai Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for the rho proteins, ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1321–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett M. D., Major G. N., Totty N., Hall A. Purification and N-terminal sequence of the p21rho GTPase-activating protein, rho GAP. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 15;276(Pt 3):833–836. doi: 10.1042/bj2760833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Maru Y., Leonard D., Witte O. N., Evans T., Cerione R. A. A GDP dissociation inhibitor that serves as a GTPase inhibitor for the Ras-like protein CDC42Hs. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):812–815. doi: 10.1126/science.1439791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Sakai H., Gray L. S. Lymphocyte adhesion can be regulated by cytoskeleton-associated, PMA-induced capping of surface receptors. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C916–C926. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka K., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Takaishi K., Mizuno T., Asada M., Ménard L., Tomhave E., Didsbury J. Both stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins, smg GDS and rho GDI, are active on multiple small GTP-binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):921–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91820-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori Y., Kikuchi A., Isomura M., Katayama M., Miura Y., Fujioka H., Kaibuchi K., Takai Y. Post-translational modifications of the C-terminal region of the rho protein are important for its interaction with membranes and the stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. K., Kung H. F., Kamata T. Purification of a factor capable of stimulating the guanine nucleotide exchange reaction of ras proteins and its effect on ras-related small molecular mass G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8008–8012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomura M., Kikuchi A., Ohga N., Takai Y. Regulation of binding of rhoB p20 to membranes by its specific regulatory protein, GDP dissociation inhibitor. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelias J. M., Adra C. N., Wulf G. M., Guillemot J. C., Khagad M., Caput D., Lim B. cDNA cloning of a human mRNA preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and with homology to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for the rho GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1479–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Kikuchi A., Araki S., Hata Y., Kondo J., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4116–4122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed I., Downey G. P., Aktories K., Roifman C. M. Microfilament assembly is required for antigen-receptor-mediated activation of human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1139–1146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi R., Inverardi L., Rugarli C., Bender J. R. Antigen-receptor complex stimulation triggers protein kinase C-dependent CD11a/CD18-cytoskeleton association in T lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1211–1220. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizon V., Chardin P., Lerosey I., Olofsson B., Tavitian A. Human cDNAs rap1 and rap2 homologous to the Drosophila gene Dras3 encode proteins closely related to ras in the 'effector' region. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayter S. I., Woodrow M., Lucas S. C., Cantrell D. A., Downward J. p21ras mediates control of IL-2 gene promoter function in T cell activation. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4549–4556. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A., Eva A. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human dbl proto-oncogene: evidence that its overexpression is sufficient to transform NIH/3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2465–2473. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinfeld B., Munemitsu S., Clark R., Conroy L., Watt K., Crosier W. J., McCormick F., Polakis P. Molecular cloning of a GTPase activating protein specific for the Krev-1 protein p21rap1. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90555-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Albright C. F., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Association between GTPase activators for Rho and Ras families. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):153–154. doi: 10.1038/359153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Narasimhan V., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding the GAP-associated protein p190: implications for a signaling pathway from ras to the nucleus. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90454-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou C., Farnsworth C. L., Neel B. G., Feig L. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding a guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor for Ras p21. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):351–354. doi: 10.1038/358351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timblin C., Battey J., Kuehl W. M. Application for PCR technology to subtractive cDNA cloning: identification of genes expressed specifically in murine plasmacytoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1587–1593. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Kikuchi A., Ohga N., Yamamoto J., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a novel regulatory protein inhibiting the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to rhoB p20, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9373–9380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Macara I. G. A cytosolic protein catalyzes the release of GDP from p21ras. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2181667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeramian P., Chardin P., Madaule P., Tavitian A. Nucleotide sequence of human rho cDNA clone 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1869–1869. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. The human Rab genes encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast YPT1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12394–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]