Abstract
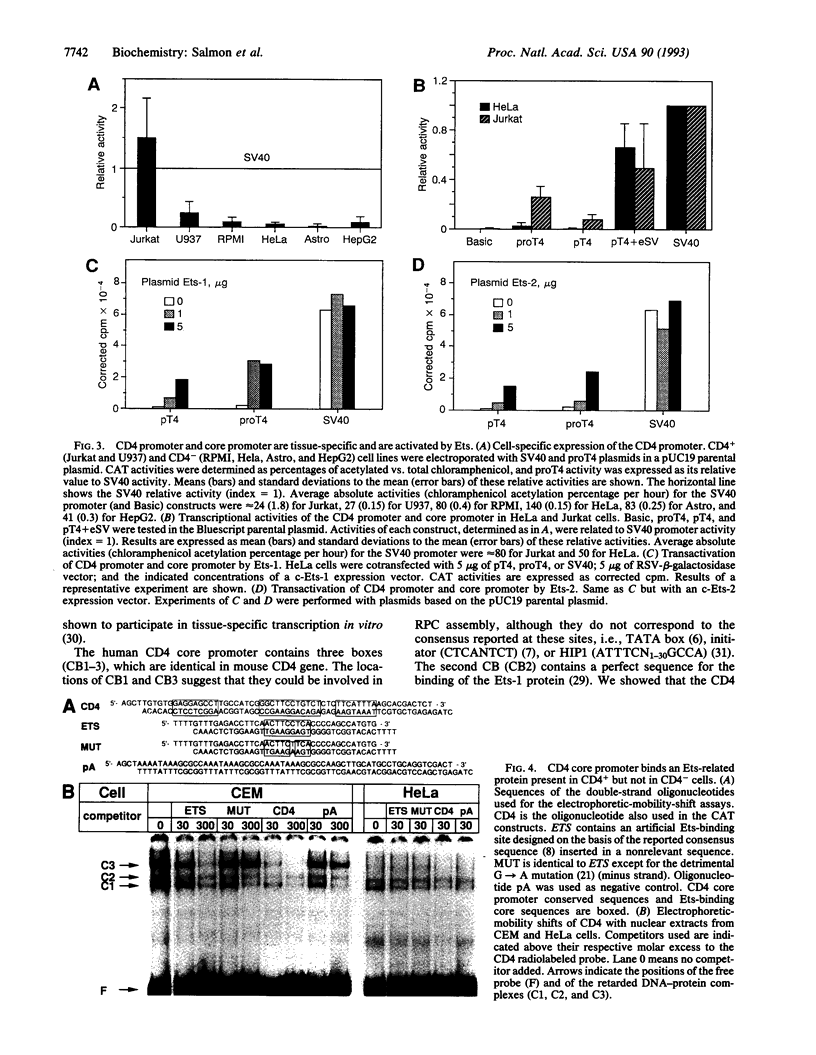
We analyzed the 5' transcription control sequences of the human CD4 gene. We located the transcription initiation site and showed that the CD4 core promoter (positions -40 to +16) lacks a classical "TATA" or initiator positioning consensus sequence but directs precise and efficient transcription when coupled to the ubiquitously active simian virus 40 enhancer. The transcriptional activity of the CD4 gene promoter correlated with CD4 expression in various cell types. Interestingly, the CD4 core promoter also displayed a tissue-specific transcriptional activity. Within this fragment, three nucleic acid sequences are completely conserved in the murine CD4 gene. One of these sequences contains a perfect ETS consensus sequence. Another ETS consensus sequence is located 1060 nt upstream. Electrophoretic-mobility-shift assays showed that the core promoter ETS motif binds an Ets-related protein specifically expressed at high levels in CD4+ cells. Moreover, in CD4- cells, overexpression of Ets-1 or Ets-2 efficiently and specifically activated transcription from the CD4 promoter and core promoter. These data indicate that Ets transcription factors play a central role in controlling CD4 gene expression, by binding to both a classical remote site and an unusual proximal activator sequence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Letwin K., Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):908–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat N. K., Komschlies K. L., Fujiwara S., Fisher R. J., Mathieson B. J., Gregorio T. A., Young H. A., Kasik J. W., Ozato K., Papas T. S. Expression of ets genes in mouse thymocyte subsets and T cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):672–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek H., Tantravahi R. V., Rao V. N., Reddy E. S., Reddy E. P. Myb and Ets proteins cooperate in transcriptional activation of the mim-1 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1291–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettehadieh E., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L., Hess-Bienz D., Watts J., Shastri N., Aebersold R. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and activation of MAP kinases by p56lck. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.1311128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman S. D., Tourvieille B., Parnes J. R. Structure of the mouse gene encoding CD4 and an unusual transcript in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7644–7648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Bhat N. K., Gottschalk L. R., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B., Papas T. S., Leiden J. M. Sequence-specific binding of human Ets-1 to the T cell receptor alpha gene enhancer. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):814–818. doi: 10.1126/science.2237431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R., Gettner S. N. Unusual intron in the immunoglobulin domain of the newly isolated murine CD4 (L3T4) gene. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):453–455. doi: 10.1038/325453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R., Thomas Y., Maddon P. J., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and sequence of the gene encoding T8: a molecule defining functional classes of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Molineaux S. M., Maddon D. E., Zimmerman K. A., Godfrey M., Alt F. W., Chess L., Axel R. Structure and expression of the human and mouse T4 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9155–9159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić-Zugić J. Phenotypic and functional stages in the intrathymic development of alpha beta T cells. Immunol Today. 1991 Feb;12(2):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90160-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey E. A., Fowlkes B. J., Gordon J. W., Kioussis D., von Boehmer H., Ramsdell F., Axel R. Thymic selection in CD8 transgenic mice supports an instructive model for commitment to a CD4 or CD8 lineage. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90212-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong R. H., Chamberlain J. W., Parnes J. R. Signal for T-cell differentiation to a CD4 cell lineage is delivered by CD4 transmembrane region and/or cytoplasmic tail. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):718–720. doi: 10.1038/356718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. TATA-binding protein is a classless factor. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):819–821. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu G., Wurster A. L., Lipsick J. S., Hedrick S. M. Expression of the CD4 gene requires a Myb transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1592–1604. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Sumita K., Hirose S., Mikoshiba K. Core promoter of the mouse myelin basic protein gene governs brain-specific transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3101–3108. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Wang C. Y., Ho I. C., Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Miesfeldt S., Zhang L., Nabel G. J., Karpinski B. cis-acting sequences required for inducible interleukin-2 enhancer function bind a novel Ets-related protein, Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1043–1053. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourvieille B., Gorman S. D., Field E. H., Hunkapiller T., Parnes J. R. Isolation and sequence of L3T4 complementary DNA clones: expression in T cells and brain. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):610–614. doi: 10.1126/science.3094146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Hahn S. L., Giovane A. The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78757-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Flores P., Gutman A., Wasylyk B. PEA3 is a nuclear target for transcription activation by non-nuclear oncogenes. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3371–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Gutman A., Nicholson R., Wasylyk B. The c-Ets oncoprotein activates the stromelysin promoter through the same elements as several non-nuclear oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Kerckaert J. P., Wasylyk B. A novel modulator domain of Ets transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):965–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]