Abstract
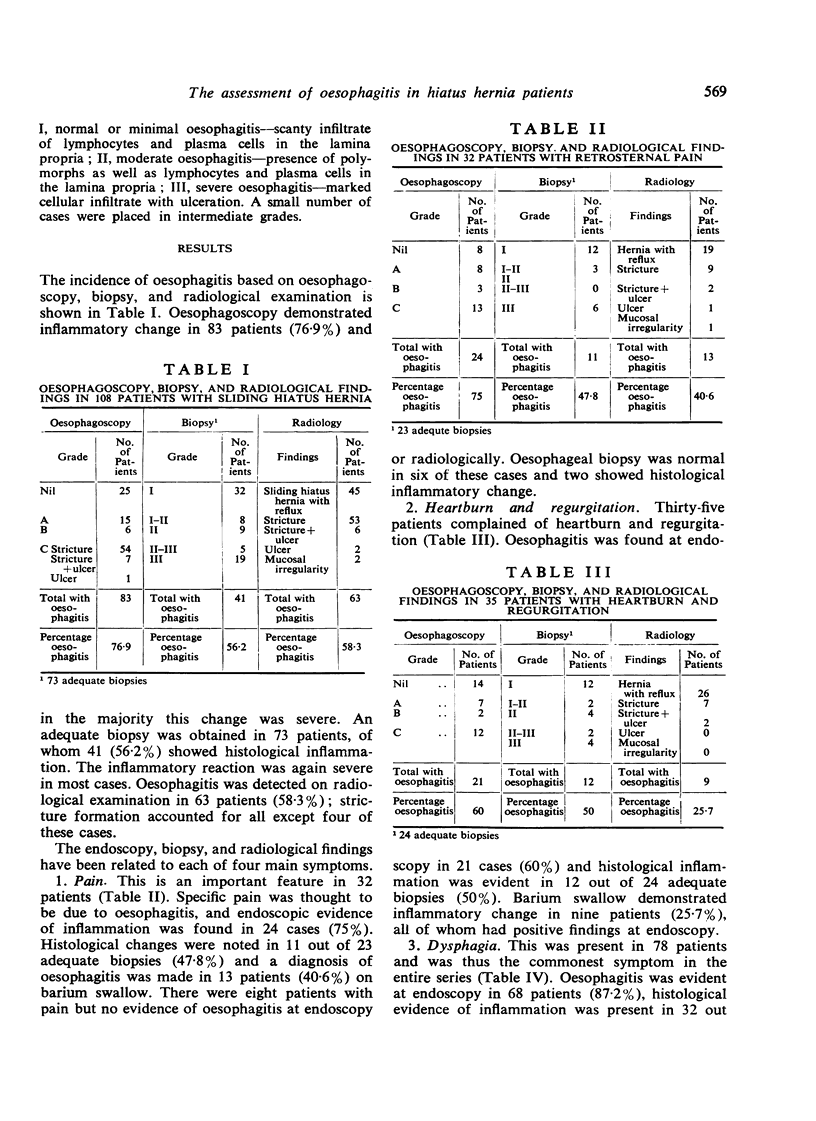
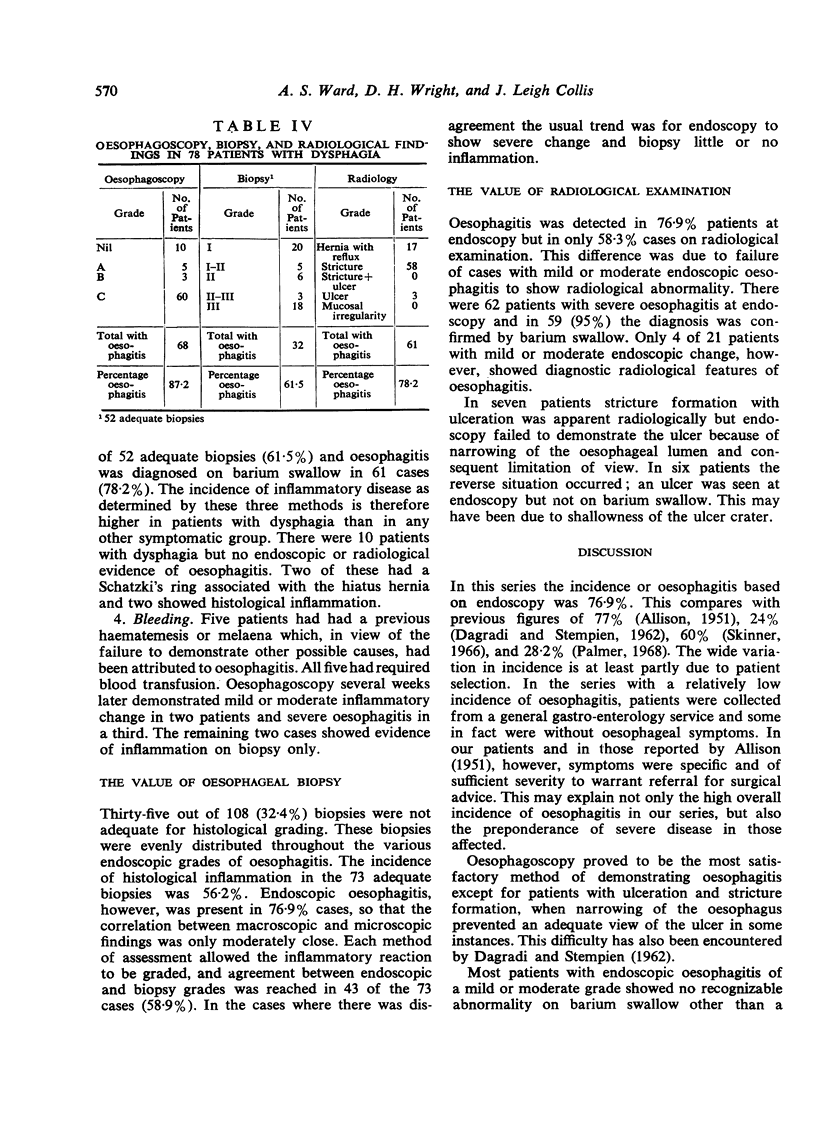
The incidence of oesophagitis has been determined in 108 patients with sliding hiatus hernias using endoscopic, histological, and radiological criteria. Particular consideration has been given to the relationship between inflammatory disease and clinical symptoms. All the patients were attending a thoracic surgical clinic and the spectrum of disease encountered was fairly severe; over half of the cases had established strictures when first seen. The incidence of oesophagitis based on endoscopic evidence was 76·9%, while inflammatory change was noted on biopsy in 56·2% and at barium swallow in 58·3% of the patients. Oesophagoscopy proved to be the most satisfactory method of assessment; biopsy specimens were either inadequate or correlated poorly with other criteria while barium swallow was of diagnostic value only in severe oesophagitis. The main symptoms were pain, heartburn with regurgitation, dysphagia, and bleeding. Dysphagia was common due to the preponderance of patients with strictures, while obvious bleeding was very uncommon. Endoscopic oesophagitis was found in 75% of the patients with specific retrosternal pain and in 60% of those with heartburn and regurgitation. The inability to equate heartburn with oesophagitis is emphasized. The incidence of inflammatory change in patients with dysphagia was 87·2%; nearly all the cases in this group showed stricture formation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON P. R. Reflux esophagitis, sliding hiatal hernia, and the anatomy of repair. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1951 Apr;92(4):419–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSTEIN L. M., BAKER L. A. A clinical test for esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1958 May;34(5):760–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARVER G. M., Jr, SEALY W. C. Peptic esophagitis. AMA Arch Surg. 1954 Mar;68(3):286–295. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1954.01260050288004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCCO A. E. ENDOSCOPIC AND BIOPSY CORRELATION OF ESOPHAGITIS: A REVIEW OF EIGHTY-FOUR CASES. Bull Gastrointest Endosc. 1965 Feb;11:29–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGRADI A. E., STEMPIEN S. J. Symptomatic esophageal hiatus sliding hernia. Clinical, radiologic, and endoscopic study of 100 cases. Am J Dig Dis. 1962 Jul;7:613–633. doi: 10.1007/BF02232777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMUNDS V. Hiatus hernia; a clinical study of 200 cases. Q J Med. 1957 Oct;26(104):445–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOD R. H., McCHESNEY J. A. Hiatus hernia with esophagitis and acute hemorrhage. JAMA. 1962 Oct 20;182:243–246. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050420019005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTONE A. S. Oesophagitis and peptic ulcer of the oesophagus. Br J Radiol. 1955 May;28(329):229–240. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-28-329-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAMER P., HOLLANDER W. Comparison of experimental esophageal pain with clinical pain of angina pectoris and esophageal disease. Gastroenterology. 1955 Nov;29(5):719–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LODGE K. V. The pathology of non-specific oesophagitis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):17–24. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHAND P. Hiatus hernia: a cause of gastro-intestinal haemorrhage. Br J Surg. 1960 Mar;47:515–526. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004720511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER E. D. Subacute erosive (peptic) esophagitis; histopathologic study. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Jan;59(1):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL C. I., HENDRIX T. R. Esophageal motor abnormalities induced by acid perfusion in patients with heartburn. J Clin Invest. 1963 May;42:686–695. doi: 10.1172/JCI104760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuman B. M., Rinaldo J. A. Relative frequency of esophagitis and gastritis in patients with symptomatic hiatus hernia. Gastrointest Endosc. 1966 Feb;12(3):14–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B. Symptomatic esophageal reflux. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Oct;11(10):771–779. doi: 10.1007/BF02233837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor C. W., Collis J. L. Anaemia and hiatus hernia: experience in 450 patients. Thorax. 1967 Jan;22(1):73–78. doi: 10.1136/thx.22.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


