Abstract
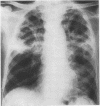
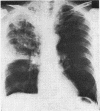
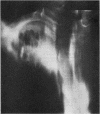
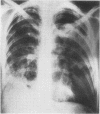
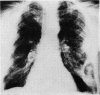
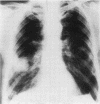
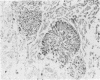
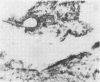
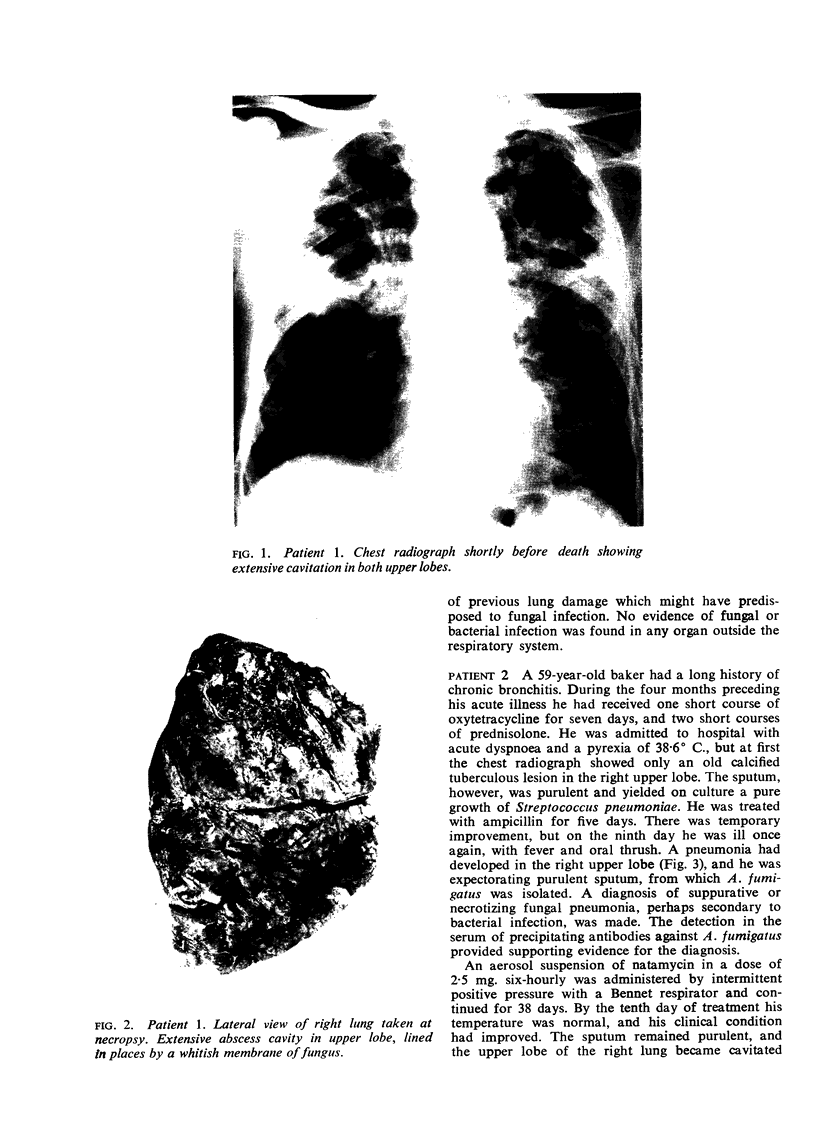
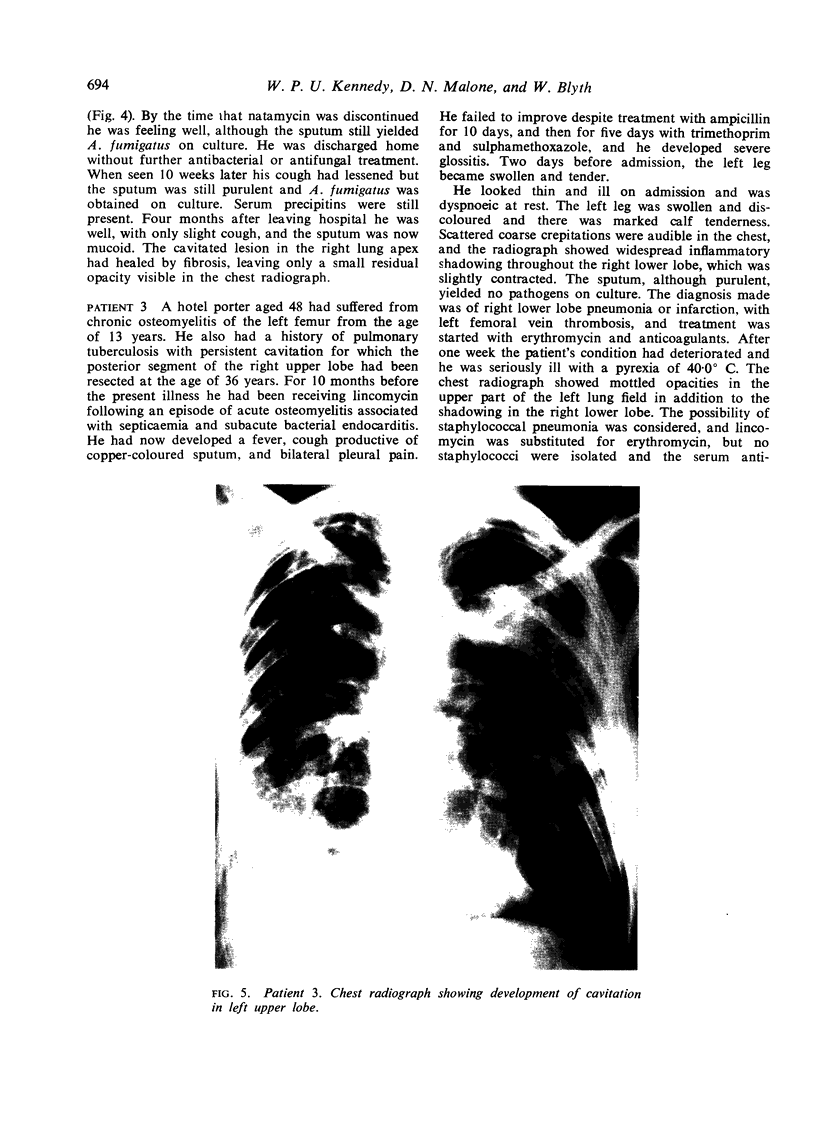
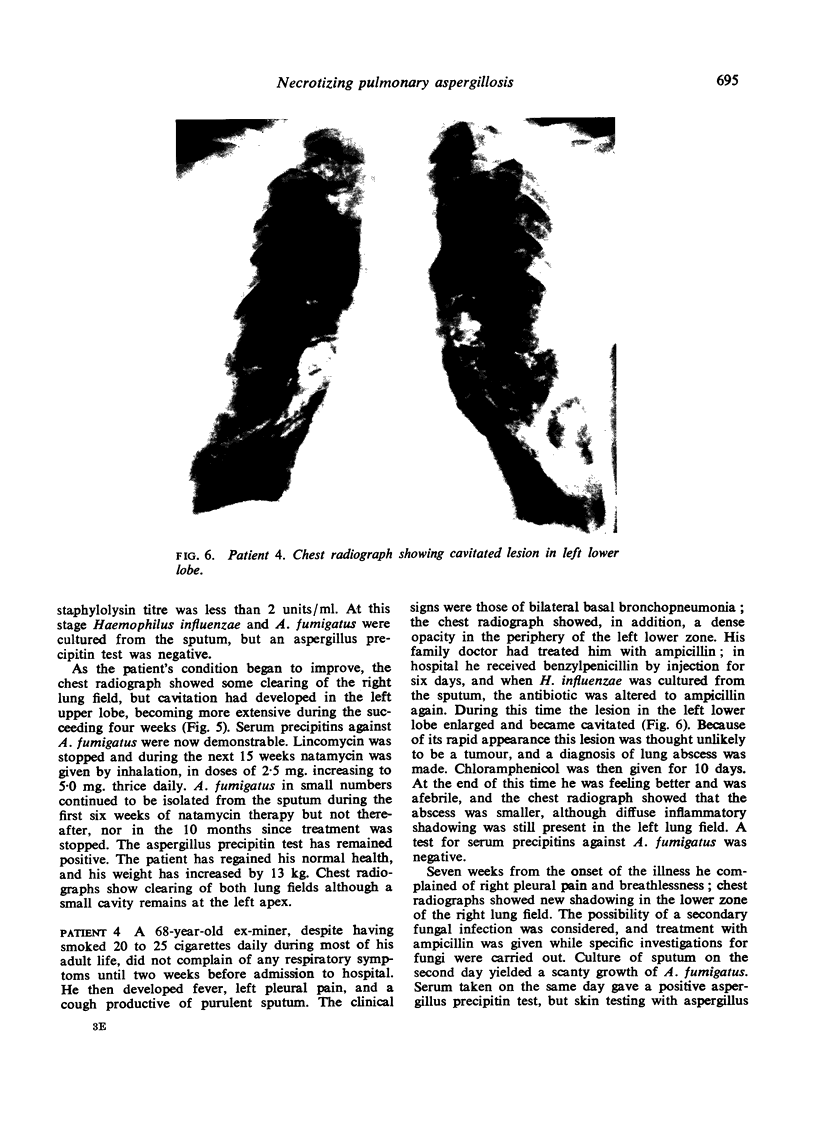
Necrotizing or invasive aspergillary infection of the lungs has previously been considered a rare condition affecting only the debilitated or seriously ill. Four patients with necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis are described, and the mycological and histopathological findings are discussed. The diagnosis in the first patient was not made until necropsy, following death from fulminating pulmonary infection. Of three patients treated with natamycin, two made a satisfactory recovery; the other died later from bronchial carcinoma. Previous multiple antibiotic therapy in each case may have been a contributory factor to infection with Aspergillus fumigatus. We suggest that fungal infection of the lungs should be actively sought in patients with pulmonary disease, especially in those receiving multiple antibiotic or corticosteroid therapy.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECH A. O. Diffuse bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax. 1961 Jun;16:144–152. doi: 10.1136/thx.16.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL M. J., CLAYTON Y. M. BRONCHOPULMONARY ASPERGILLOSIS. A CORRELATION OF THE CLINICAL AND LABORATORY FINDINGS IN 272 PATIENTS INVESTIGATED FOR BRONCHOPULMONARY ASPERGILLOSIS. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Feb;89:186–196. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.89.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONEN P. E., WALKER G. R., TURNER J. A., FIELD P. Invasive primary aspergillosis of the lung with cerebral metastasis and complete recovery. Dis Chest. 1962 Jul;42:88–94. doi: 10.1378/chest.42.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREWTHER W. G., LENNOX F. G. Preparation of crystals containing protease from aspergillus oryzae. Nature. 1950 Apr 29;165(4200):680–680. doi: 10.1038/165680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P., SMITH I. W., DEMPSTER G., EDMUNDS P. N. Non-flagellar filamentous appendages (fimbriae) and haemagglutinating activity in Bacterium coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(2):335–348. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS G., LATOUCHE C. J. THE TREATMENT OF BRONCHOPULMONARY MYCOSES WITH A NEW ANTIBIOTIC--PIMARICIN. Lancet. 1964 Jun 20;1(7347):1349–1353. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English M. P., Henderson A. H. Significance and interpretation of laboratory tests in pulmonary aspergillosis. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Nov;20(6):832–834. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.6.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWING N. F., HAMLIN I. M. Tissue reactions to Aspergillus in cases of Hodgkin's disease and leukaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Sep;13:396–413. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.5.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROCOTT R. G. A stain for fungi in tissue sections and smears using Gomori's methenamine-silver nitrate technic. Am J Clin Pathol. 1955 Aug;25(8):975–979. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/25.8_ts.0975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINSON K. F. W., MOON A. J., PLUMMER N. S. Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis; a review and a report of eight new cases. Thorax. 1952 Dec;7(4):317–333. doi: 10.1136/thx.7.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONGBOTTOM J. L., PEPYS J. PULMONARY ASPERGILLOSIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND IMMUNOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF ANTIGENS AND C-SUBSTANCE IN ASPERGILLUS FUMIGATUS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:141–151. doi: 10.1002/path.1700880119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan A. Interactions between some aural aspergillus species and bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Oct;58(2):261–266. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUDAIRA M., SCHWARTZ J. Tracheobronchopulmonary mycoses caused by opportunistic fungi, with particular reference to aspergillosis. Lab Invest. 1962 Nov;11:1053–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORIE N. G., DE VRIES G. A., KIKSTRA A. Growth of Aspergillus in the human lung. Aspergilloma and aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Nov;82:649–662. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.82.5.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Antigen-antibody reactions in gels. IV. Types of reactions in coordinated systems of diffusion. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;32(2):230–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce A. K., Edmonson E. B., McGee G., Ketchersid J., Loudon R. G., Sanford J. P. An analysis of factors predisposing to gram-negative bacillary necrotizing pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Sep;94(3):309–315. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.94.3.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIDDELL R. W. The role of fungi as human pathogens. Proc R Soc Med. 1958 Jul;51(7):491–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDRANSKY H., FRIEDMAN L. The effect of cortisone and antibiotic agents on experimental pulmonary aspergillosis. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jan-Feb;35(1):169–183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEFANINI M., MARIN H. M., SOARDI F., MOSSA A. Fibrinolysis. IX. The comparative activity in vivo of trypsin and aspergillin O (moldfibrinolysin). Angiology. 1962 Jun;13:254–259. doi: 10.1177/000331976201300603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEFANINI M., MARIN H. Fibrinolysis. I. Fibrinolytic activity of extracts from non-pathogenic fungi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Nov;99(2):504–507. doi: 10.3181/00379727-99-24398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRUYK A. P., HOETTE I., DROST G., WAISVISZ J. M., VAN EEK T., HOOGERHEIDE J. C. Pimaricin, a new antifungal antibiotic. Antibiot Annu. 1957;5:878–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYMMERS W. C. Histopathologic aspects of the pathogenesis of some opportunistic fungal infections, as exemplified in the pathology of aspergillosis and the phycomycetoses. Lab Invest. 1962 Nov;11:1073–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedder J. S., Schorr W. F. Primary disseminated pulmonary aspergillosis with metastatic skin nodules. Successful treatment with inhalation nystatin therapy. JAMA. 1969 Aug 25;209(8):1191–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]