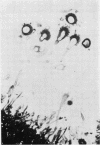
Abstract
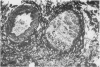
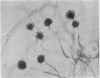
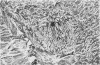
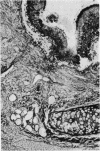
The history and the clinical and necropsy findings are presented of a patient who died from Aspergillus fumigatus pyaemia occurring as an opportunistic infection complicating a dissecting aortic aneurysm. The diagnosis was made (and treatment instituted) during life: it rested upon repeated isolation of the organism from tracheal aspirations, a positive blood culture and positive serum precipitin reactions to A. fumigatus. Debilitating disease along with large doses of antibiotics and corticosteroids provided the conditions necessary for the normally saphrophytic fungi to become pathogenic. As the therapy for aspergillosis is still ineffective, the danger of prescribing large doses of antibiotics together with corticosteroids is stressed.
Full text
PDF
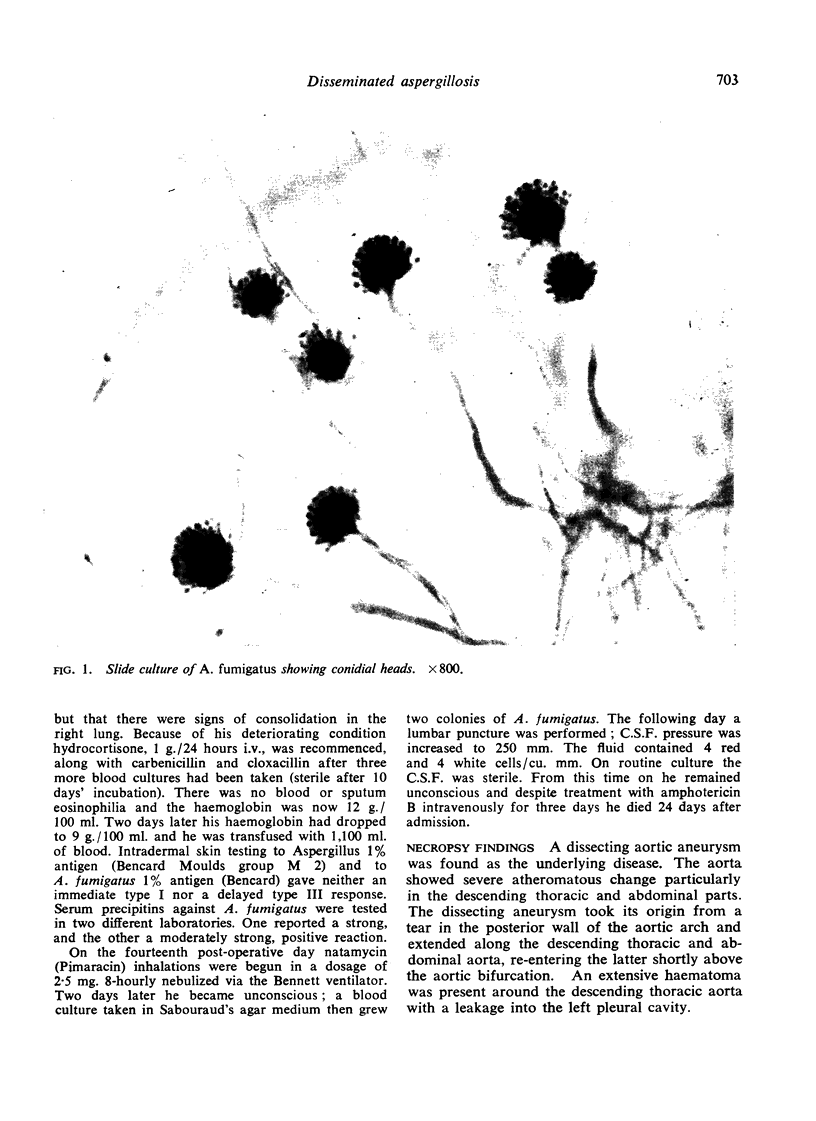


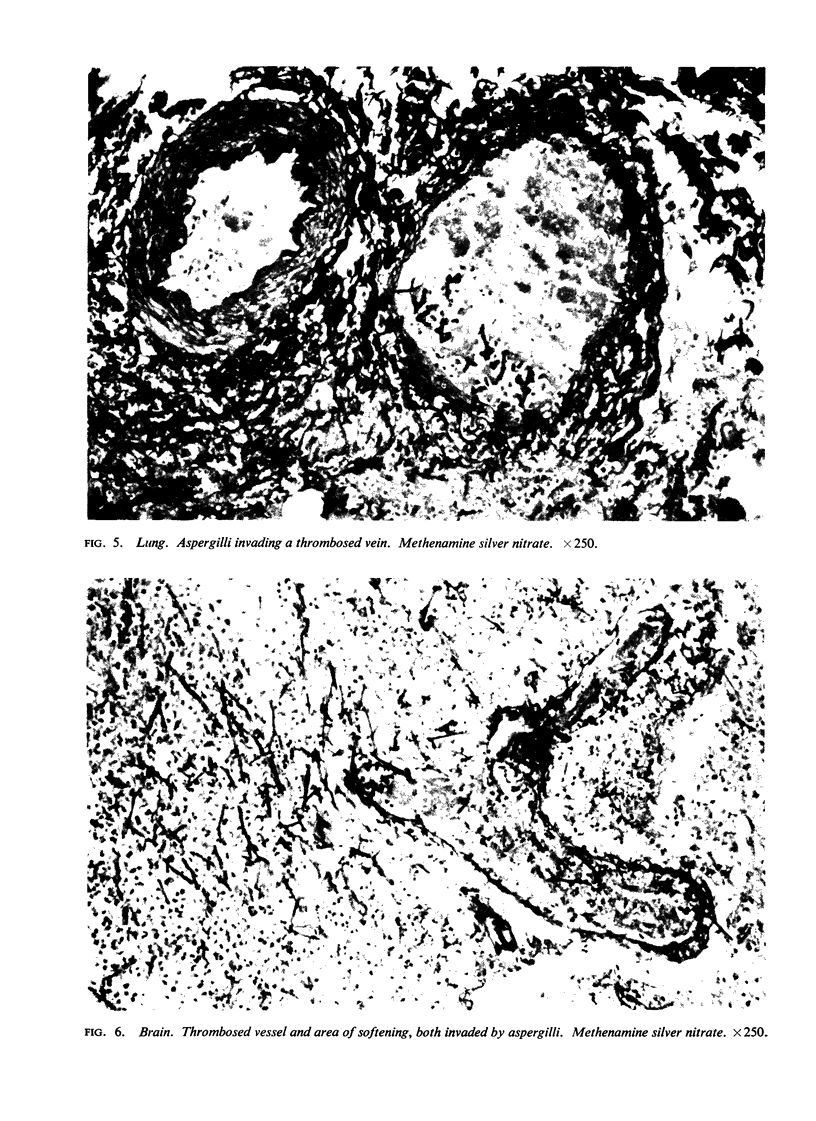

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila R. Immunological study of pulmonary aspergilloma. Thorax. 1968 Mar;23(2):144–152. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan H. I., Frisch E., Houghton J. D., Climo M. S., Natsios G. A. Aspergillus fumigatus endocarditis. Report of a case diagnosed during life. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Feb;68(2):378–385. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-2-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRCEVIC N., MATTHEWS W. F. Pathologic changes in acute disseminated aspergillosis, particularly involvement of the central nervous system. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Dec;32:536–551. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/32.5.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. H. Allergic aspergillosis: review of 32 cases. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):501–512. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. H., English M. P., Vecht R. J. Pulmonary aspergillosis. A survey of its occurrence in patients with chronic lung disease and a discussion of the significance of diagnostic tests. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):513–518. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. H., Pearson J. E. Treatment of bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with observations on the use of natamycin. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):519–523. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo T. K., Sugai K., Leong T. K. Disseminated aspergillosis. Case report and review of the world literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jun;45(6):697–703. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/45.6.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPYS J., RIDDELL R. W., CITRON K. M., CLAYTON Y. M., SHORT E. I. Clinical and immunologic significance of Aspergillus fumigatus in the sputum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Aug;80:167–180. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Marchioro T. L., Schneck S. A., Hill R. B., Jr Systemic fungal infections complicating renal transplantation and immunosuppressive therapy. Clinical, microbiologic, neurologic and pathologic features. Am J Med. 1967 Jul;43(1):28–38. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]