Abstract
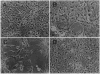
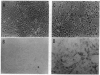
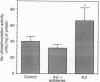
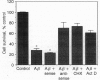
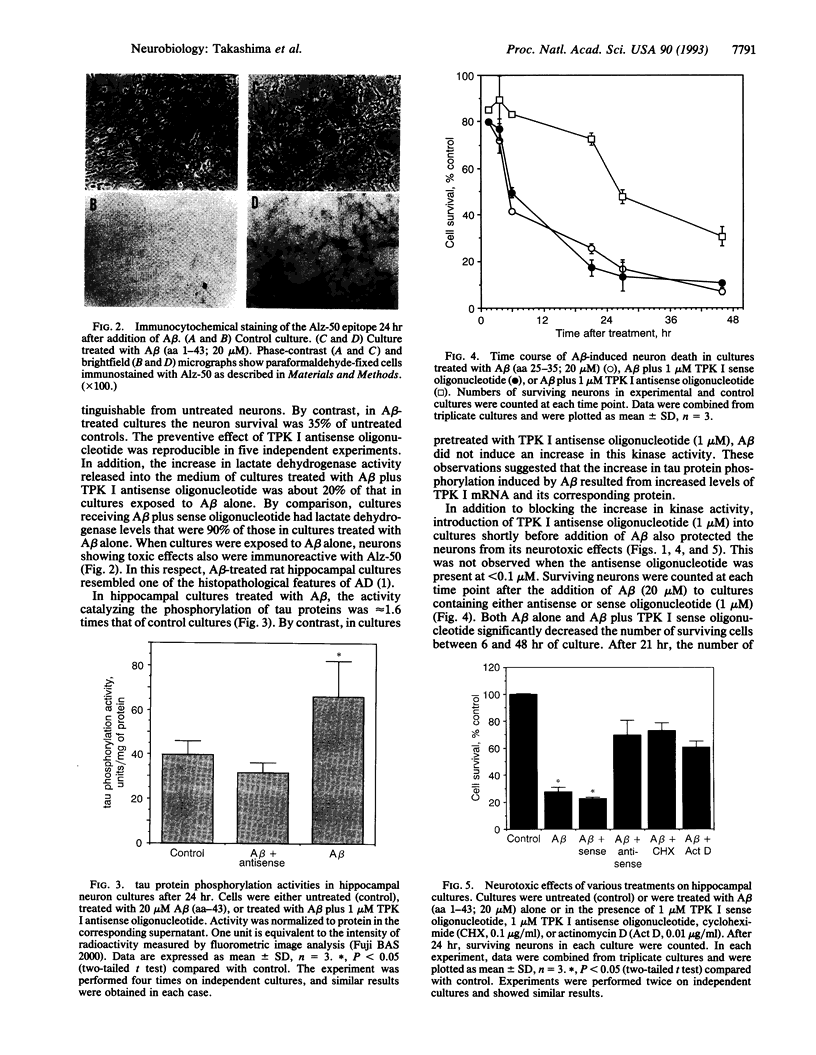
Pathological changes of Alzheimer disease are characterized by cerebral cortical atrophy as a result of degeneration and loss of neurons. Typical histological lesions include numerous senile plaques composed of deposits of amyloid beta-protein and neurofibrillary tangles consisting predominantly of ubiquitin and highly phosphorylated tau proteins. Previously, tau protein kinase I (TPK I) was purified and its cDNA was cloned. To examine the biological role of this enzyme in neurons, we have studied the induction of its kinase activity in primary cultures of embryonic rat hippocampal neurons. Treatment of cultures with amyloid beta-protein significantly increased TPK I activity and induced the appearance of tau proteins recognized by the Alz-50 monoclonal antibody. In addition, though amyloid beta-protein was neurotoxic, either cycloheximide or actinomycin D prevented neuronal death. Death was also prevented by TPK I antisense oligonucleotides but not by sense oligonucleotides. These observations suggest that rat hippocampal neurons undergo programmed cell death in response to amyloid beta-protein and that TPK I is a key enzyme in this process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arispe N., Rojas E., Pollard H. B. Alzheimer disease amyloid beta protein forms calcium channels in bilayer membranes: blockade by tromethamine and aluminum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):567–571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker G. A., Cowan W. M. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977 May 13;126(3):397–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90594-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busciglio J., Lorenzo A., Yankner B. A. Methodological variables in the assessment of beta amyloid neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Aging. 1992 Sep-Oct;13(5):609–612. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(92)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Pike C. J., Copani A. beta-Amyloid neurotoxicity: a discussion of in vitro findings. Neurobiol Aging. 1992 Sep-Oct;13(5):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(92)90060-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidani L., Goate A. Mutations in APP and their role in beta-amyloid deposition. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1992;379:195–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone G., Tagliavini F., Linoli G., Bouras C., Frigerio L., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Down patients: extracellular preamyloid deposits precede neuritic degeneration and senile plaques. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Feb 13;97(1-2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanger D. P., Hughes K., Woodgett J. R., Brion J. P., Anderton B. H. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 induces Alzheimer's disease-like phosphorylation of tau: generation of paired helical filament epitopes and neuronal localisation of the kinase. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Nov 23;147(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90774-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. A., Higgins G. A. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):184–185. doi: 10.1126/science.1566067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Ihara Y., Uchida T., Imahori K. A novel tubulin-dependent protein kinase forming a paired helical filament epitope on tau. J Biochem. 1988 Sep;104(3):319–321. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Omori A., Sato K., Tomizawa K., Imahori K., Uchida T. A serine/threonine proline kinase activity is included in the tau protein kinase fraction forming a paired helical filament epitope. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jul 22;128(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90259-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Omori A., Takamatsu M., Sato K., Arioka M., Uchida T., Imahori K. Phosphorylation sites on tau by tau protein kinase I, a bovine derived kinase generating an epitope of paired helical filaments. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Dec 14;148(1-2):202–206. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90839-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Takamatsu M., Tomizawa K., Omori A., Takahashi M., Arioka M., Uchida T., Imahori K. Tau protein kinase I converts normal tau protein into A68-like component of paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10897–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J. Y., Yang L. L., Cotman C. W. Beta-amyloid protein increases the vulnerability of cultured cortical neurons to excitotoxic damage. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 19;533(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91355-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Takashima A. Cell cycle-dependent modulation of biosynthesis and stimulus-evoked release of catecholamines in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Neurochem. 1986 May;46(5):1493–1500. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb01767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Binder L., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Lee G. Epitopes that span the tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowall N. W., Beal M. F., Busciglio J., Duffy L. K., Yankner B. A. An in vivo model for the neurodegenerative effects of beta amyloid and protection by substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7247–7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love S., Saitoh T., Quijada S., Cole G. M., Terry R. D. Alz-50, ubiquitin and tau immunoreactivity of neurofibrillary tangles, Pick bodies and Lewy bodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Jul;47(4):393–405. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198807000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. P., Schmidt R. E., DiStefano P. S., Lowry O. H., Carter J. G., Johnson E. M., Jr Inhibitors of protein synthesis and RNA synthesis prevent neuronal death caused by nerve growth factor deprivation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):829–844. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P., Cheng B., Davis D., Bryant K., Lieberburg I., Rydel R. E. beta-Amyloid peptides destabilize calcium homeostasis and render human cortical neurons vulnerable to excitotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1992 Feb;12(2):376–389. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00376.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kondo J., Ihara Y. Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1641–1644. doi: 10.1126/science.3029875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukina N., Kosik K. S., Selkoe D. J. Recognition of Alzheimer paired helical filaments by monoclonal neurofilament antibodies is due to crossreaction with tau protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3415–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Friedman R., Shaw G., Chau V. Ubiquitin is detected in neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites of Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3033–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roher A. E., Ball M. J., Bhave S. V., Wakade A. R. Beta-amyloid from Alzheimer disease brains inhibits sprouting and survival of sympathetic neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):572–579. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91455-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. Biochemistry of altered brain proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:463–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillantini M. G., Goedert M., Jakes R., Klug A. Different configurational states of beta-amyloid and their distributions relative to plaques and tangles in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3947–3951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillantini M. G., Goedert M., Jakes R., Klug A. Topographical relationship between beta-amyloid and tau protein epitopes in tangle-bearing cells in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B. L., Pruchnicki A., Dickson D. W., Davies P. A neuronal antigen in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):648–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3083509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R. Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2431–2438. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07419.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Caceres A., Duffy L. K. Nerve growth factor potentiates the neurotoxicity of beta amyloid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9020–9023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Dawes L. R., Fisher S., Villa-Komaroff L., Oster-Granite M. L., Neve R. L. Neurotoxicity of a fragment of the amyloid precursor associated with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):417–420. doi: 10.1126/science.2474201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Duffy L. K., Kirschner D. A. Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2218531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]