Abstract
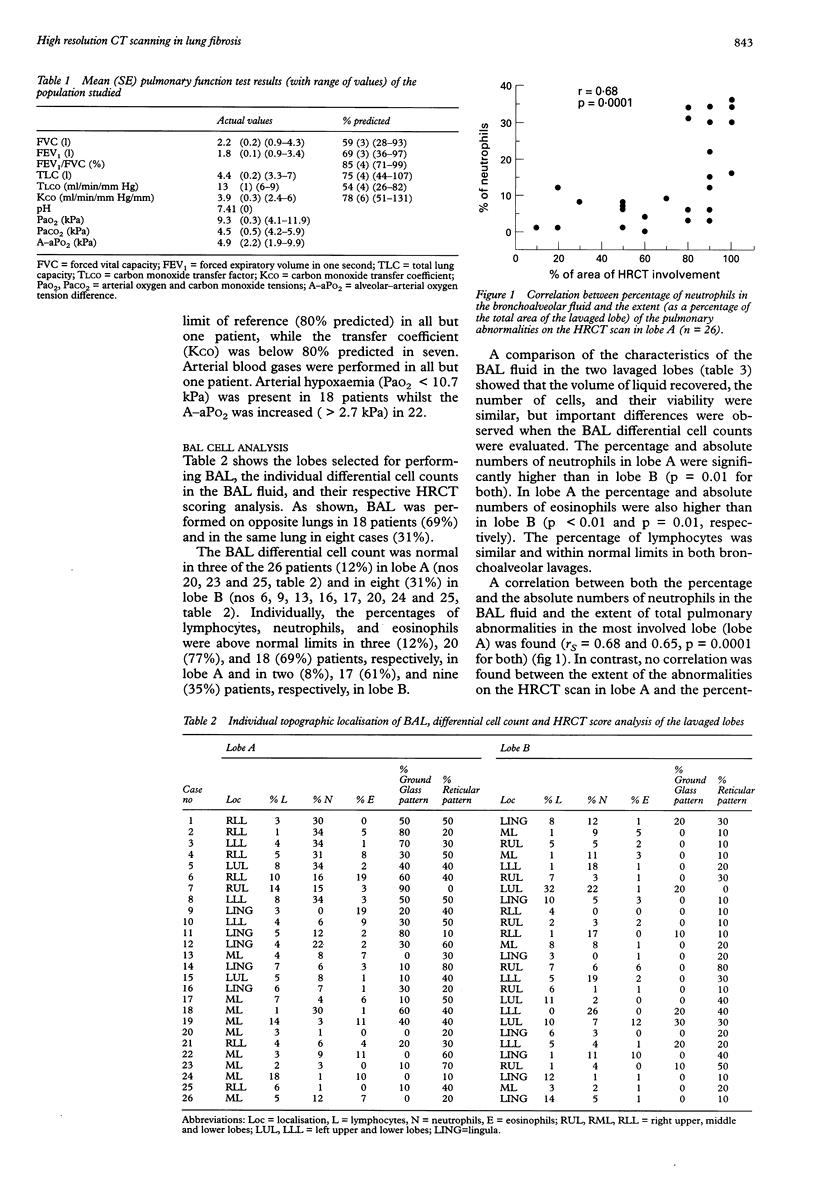
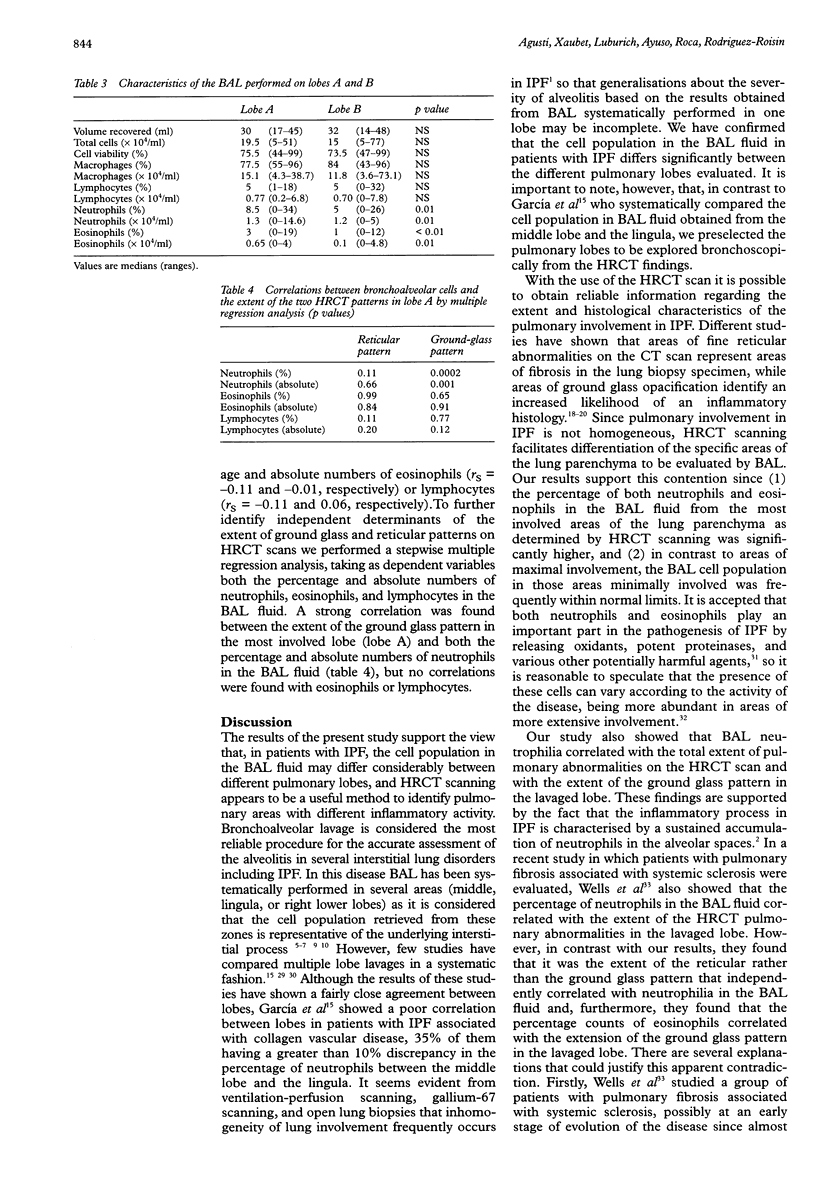
BACKGROUND: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is now recognised as a sensitive tool for predicting the histological characteristics of the lung parenchymal abnormalities in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). A reticular pattern on HRCT scanning is indicative of fibrotic histology while a ground glass pattern has been associated with inflammatory disease. The purpose of the present study was to investigate whether the cell population in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from different lobes differs according to HRCT characteristics in patients with IPF. METHODS: Twenty six patients with IPF (18 men) of mean (SE) age 67 (2) years were included in the study. A semiquantitative analysis of the extent of the abnormalities on the HRCT scan was applied by summing the proportion of both reticular and ground glass patterns in each lobe (expressed as percentage of total area evaluated) and 100 ml double BAL was then randomly performed in the lobe with the most extensive involvement (lobe A) and that with the least extensive involvement (lobe B). RESULTS: Twenty three of the 26 patients (88%) had an abnormal cell count in the BAL fluid from lobe A compared with 18 patients (69%) with abnormalities in the BAL fluid from lobe B. The median (range) percentage of 8.5% (0-34%) and the absolute numbers of neutrophils (1.3 x 10(4)/ml, 0-14.6 x 10(4)/ml) in lobe A were significantly higher than those in lobe B (5% (0-26%) and 1.2 x 10(4)/ml (0-5 x 10(4)/ml), respectively). The percentage (3%, 0-19%) and absolute numbers (0.65 x 10(4)/ml, 0-4 x 10(4)/ml (0-4.8 x 10(4)/ml), respectively). For the group as a whole a correlation was found between the percentage and absolute numbers of neutrophils in the BAL fluid and the total score of abnormalities on the HRCT scan in the most involved lobe (lobe A). Multiple regression analysis indicated that both the percentage and absolute numbers of neutrophils were significantly and independently related to the extent of ground glass pattern. CONCLUSIONS: In patients with IPF the cell population in the BAL fluid is not homogeneous and seems to be related to the characteristics of the abnormalities on the HRCT scan present in the lavaged lobe.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agustí C., Xaubet A., Agustí A. G., Roca J., Ramirez J., Rodriguez-Roisin R. Clinical and functional assessment of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: results of a 3 year follow-up. Eur Respir J. 1994 Apr;7(4):643–650. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07040643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agustí C., Xaubet A., Roca J., Agustí A. G., Rodriguez-Roisin R. Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis with and without associated collagen vascular disease: results of a two year follow up. Thorax. 1992 Dec;47(12):1035–1040. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.12.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington C. B., Gaensler E. A., Coutu R. E., FitzGerald M. X., Gupta R. G. Natural history and treated course of usual and desquamative interstitial pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 13;298(15):801–809. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804132981501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., Moss M. L., Line B. R., Reynolds H. Y. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical, histologic, radiographic, physiologic, scintigraphic, cytologic, and biochemical aspects. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Dec;85(6):769–788. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-6-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S., Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Analysis of airspace and interstitial mononuclear cell populations in human diffuse interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jul;118(1):7–15. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. G., Wolven R. G., Garcia P. L., Keogh B. A. Assessment of interlobar variation of bronchoalveolar lavage cellular differentials in interstitial lung diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Mar;133(3):444–449. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.3.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. A., Rohatgi P. K., Bergofsky E. H., Block E. R., Daniele R. P., Dantzker D. R., Davis G. S., Hunninghake G. W., King T. E., Jr, Metzger W. J. Clinical role of bronchoalveolar lavage in adults with pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Aug;142(2):481–486. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.2.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansell D. M., Kerr I. H. The role of high resolution computed tomography in the diagnosis of interstitial lung disease. Thorax. 1991 Feb;46(2):77–84. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.2.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: pathogenetic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Eur Respir J. 1990 Mar;3(3):355–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Turton C. W., Lukoszek A., Salsbury A. J., Dewar A., Collins J. V., Turner-Warwick M. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cell counts in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and their relation to therapy. Thorax. 1980 May;35(5):328–339. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.5.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Inflammatory and immune processes in the human lung in health and disease: evaluation by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):149–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Crystal R. G. Alveolitis: the key to the interstitial lung disorders. Thorax. 1982 Jan;37(1):1–10. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung A. N., Miller R. R., Müller N. L. Parenchymal opacification in chronic infiltrative lung diseases: CT-pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1993 Jul;188(1):209–214. doi: 10.1148/radiology.188.1.8511299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. S., Smith E. A., Kinsella M., Schabel S. I., Silver R. M. Lung disease associated with progressive systemic sclerosis. Assessment of interlobar variation by bronchoalveolar lavage and comparison with noninvasive evaluation of disease activity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Feb;141(2):301–306. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N. L., Miller R. R., Webb W. R., Evans K. G., Ostrow D. N. Fibrosing alveolitis: CT-pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1986 Sep;160(3):585–588. doi: 10.1148/radiology.160.3.3737898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N. L., Staples C. A., Miller R. R., Vedal S., Thurlbeck W. M., Ostrow D. N. Disease activity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: CT and pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1987 Dec;165(3):731–734. doi: 10.1148/radiology.165.3.3685351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura K., Kitaichi M., Izumi T., Nagai S., Kanaoka M., Itoh H. Usual interstitial pneumonia: histologic correlation with high-resolution CT. Radiology. 1992 Feb;182(2):337–342. doi: 10.1148/radiology.182.2.1732946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. W., Monick M., Hunninghake G. W. Prognostic role of eosinophils in pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 1987 Jul;92(1):51–56. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. W., Nugent K. M., Jolles H., Monick M., Hunninghake G. W. Uniformity of bronchoalveolar lavage in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jan;137(1):79–84. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Rodriguez-Roisin R., Cobo E., Burgos F., Perez J., Clausen J. L. Single-breath carbon monoxide diffusing capacity prediction equations from a Mediterranean population. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Apr;141(4 Pt 1):1026–1032. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.4_Pt_1.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Sanchis J., Agusti-Vidal A., Segarra F., Navajas D., Rodriguez-Roisin R., Casan P., Sans S. Spirometric reference values from a Mediterranean population. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 May-Jun;22(3):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd R. M., Haslam P. L., Turner-Warwick M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Relationships of pulmonary physiology and bronchoalveolar lavage to response to treatment and prognosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):1–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Helmers R. A., Dayton C. S., Merchant R. K., Hunninghake G. W. Determinants of bronchoalveolar lavage cellularity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Nov;71(5):1688–1693. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.71.5.1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Helmers R. A., Galvin J. R., Van Fossen D. S., Frees K. L., Dayton C. S., Burmeister L. F., Hunninghake G. W. Determinants of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Feb;149(2 Pt 1):450–454. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.2.8306044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Van Fossen D. S., Davis C. S., Helmers R. A., Dayton C. S., Burmeister L. F., Hunninghake G. W. Determinants of progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Feb;149(2 Pt 1):444–449. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.2.8306043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Burrows B., Johnson A. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: clinical features and their influence on survival. Thorax. 1980 Mar;35(3):171–180. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Haslam P. L. The value of serial bronchoalveolar lavages in assessing the clinical progress of patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):26–34. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watters L. C., Schwarz M. I., Cherniack R. M., Waldron J. A., Dunn T. L., Stanford R. E., King T. E. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pretreatment bronchoalveolar lavage cellular constituents and their relationships with lung histopathology and clinical response to therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Mar;135(3):696–704. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.3.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A. U., Hansell D. M., Rubens M. B., Cullinan P., Black C. M., du Bois R. M. The predictive value of appearances on thin-section computed tomography in fibrosing alveolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Oct;148(4 Pt 1):1076–1082. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.4_Pt_1.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A. U., Hansell D. M., Rubens M. B., Cullinan P., Haslam P. L., Black C. M., Du Bois R. M. Fibrosing alveolitis in systemic sclerosis. Bronchoalveolar lavage findings in relation to computed tomographic appearance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Aug;150(2):462–468. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.2.8049830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xaubet A., Agustí C., Roca J., Picado C., Rodriguez-Roisin R. BAL lymphocyte activation antigens and diffusing capacity are related in mild to moderate pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 1993 May;6(5):715–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xaubet A., Rodriguez-Roisín R., Bombí J. A., Marín A., Roca J., Agustí-Vidal A. Correlation of bronchoalveolar lavage and clinical and functional findings in asbestosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):848–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


