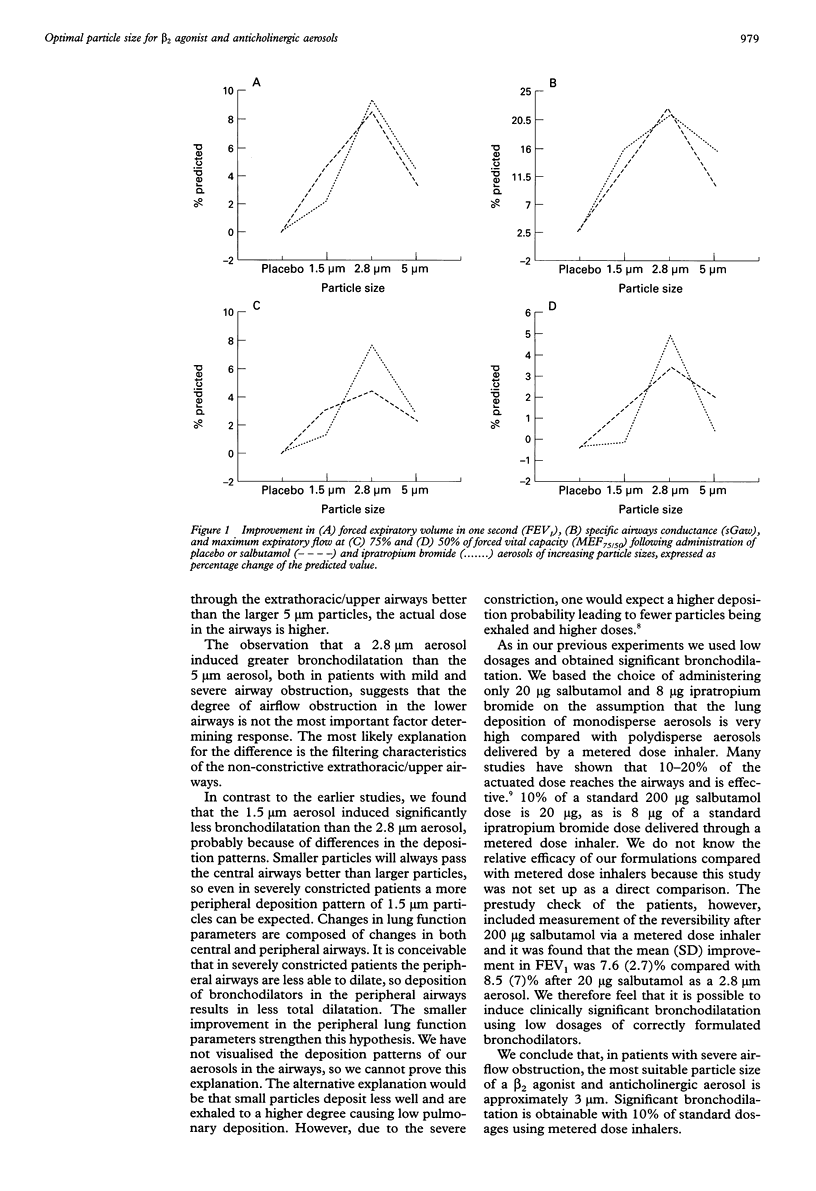
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The optimal particle size of a beta 2 agonist or anticholinergic aerosol in patients with severe airflow obstruction is unknown. METHODS: Seven stable patients with a mean forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) of 37.9% of the predicted value inhaled three types of monodisperse salbutamol and ipratropium bromide aerosols with particle sizes of 1.5 microns, 2.8 microns, and 5 microns, respectively, and a placebo aerosol. The volunteers inhaled 20 micrograms salbutamol and 8 micrograms ipratropium bromide, after which lung function changes were determined and analysed with repeated measurements analysis of variance (ANOVA). RESULTS: Greater improvements in FEV1, specific airway conductance (sGaw) and maximum expiratory flow at 75%/50% of the forced vital capacity (MEF75/50) were induced by the 2.8 microns aerosol than by the other particle sizes. CONCLUSIONS: In patients with severe airflow obstruction the particle size of choice for a beta 2 agonist or anticholinergic aerosol should be approximately 3 microns.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. J., Wilson J. D., Hiller F. C. Respiratory tract deposition of ultrafine particles in subjects with obstructive or restrictive lung disease. Chest. 1990 May;97(5):1115–1120. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.5.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann M., Yeates D. B., Albert R. E. Deposition, retention, and clearance of inhaled particles. Br J Ind Med. 1980 Nov;37(4):337–362. doi: 10.1136/oem.37.4.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zainudin B. M., Biddiscombe M., Tolfree S. E., Short M., Spiro S. G. Comparison of bronchodilator responses and deposition patterns of salbutamol inhaled from a pressurised metered dose inhaler, as a dry powder, and as a nebulised solution. Thorax. 1990 Jun;45(6):469–473. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.6.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


