Abstract
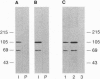
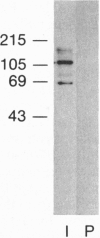
Murine neuroblastoma N1E-115 cells are a useful system in which to study neuronal angiotensin II (AngII) receptors. N1E-115 cells possess both type 1 (AT1) and type 2 (AT2) AngII receptor subtypes, as does mammalian brain. AT2 receptors in brain or N1E-115 cells can be solubilized in 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate. In the present study, heparin-Sepharose chromatography was used to partially purify solubilized N1E-115 membranes to produce an enriched population of AT2 receptors. Subsequently, an eluted peak, containing the majority of AT2 binding activity, was used as an immunogen in the development of protein-directed polyclonal antibodies. The antibodies specifically detected immunoreactive proteins of approximately 110 and 66 kDa in both solubilized N1E-115 cells, as well as the original protein material that eluted from the heparin-Sepharose column, whereas no such immunoreactivity was detected in a kidney epithelial cell line that lacks any specific 125I-labeled AngII (125I-AngII) binding activity. Moreover, the antibodies immunoreacted with affinity-purified AT2 receptors. These antibodies were also able to immunoprecipitate AT2 receptors from solubilized N1E-115 cells, as revealed by the pharmacologic profile of 125I-AngII binding to the precipitated protein. Similarly, the antibodies were able to immunoprecipitate a 66-kDa protein that had been covalently crosslinked with 125I-AngII by use of the homobifunctional crosslinker dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate). Collectively, these results demonstrate the development of a specific AT2 receptor antibody that may be used to further characterize this receptor subtype at both the cellular and molecular levels.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottari S. P., Taylor V., King I. N., Bogdal Y., Whitebread S., de Gasparo M. Angiotensin II AT2 receptors do not interact with guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 19;207(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90091-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumpus F. M., Catt K. J., Chiu A. T., DeGasparo M., Goodfriend T., Husain A., Peach M. J., Taylor D. G., Jr, Timmermans P. B. Nomenclature for angiotensin receptors. A report of the Nomenclature Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 1991 May;17(5):720–721. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.5.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluharty S. J., Reagan L. P. Characterization of binding sites for the angiotensin II antagonist 125I-[Sarc1,Ile8]-angiotensin II on murine neuroblastoma N1E-115 cells. J Neurochem. 1989 May;52(5):1393–1400. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakar S. S., Sellers J. C., Devor D. C., Musgrove L. C., Neill J. D. Angiotensin II type-1 receptor subtype cDNAs: differential tissue expression and hormonal regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 31;183(3):1090–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80302-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Sumners C., Posner P. Modulation of net outward current in cultured neurons by angiotensin II: involvement of AT1 and AT2 receptors. Brain Res. 1992 May 15;580(1-2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90960-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mah S. J., Ades A. M., Mir R., Siemens I. R., Williamson J. R., Fluharty S. J. Association of solubilized angiotensin II receptors with phospholipase C-alpha in murine neuroblastoma NIE-115 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;42(2):217–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauzy C. A., Hwang O., Egloff A. M., Wu L. H., Chung F. Z. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a gene encoding the human angiotensin II type 1A receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):277–284. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80804-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Williamson R. E., Rogulja I., Fluharty S. J., Williamson J. R. Angiotensin II effects on the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells: kinetic properties of the Ca2+ transient measured in single fura-2-loaded cells. J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):278–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. J., Alexander R. W., Griendling K. K., Runge M. S., Bernstein K. E. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the vascular type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):233–236. doi: 10.1038/351233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach M. J. Renin-angiotensin system: biochemistry and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev. 1977 Apr;57(2):313–370. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. I. Functions of angiotensin in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:413–435. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reagan L. P., Ye X. H., Mir R., DePalo L. R., Fluharty S. J. Up-regulation of angiotensin II receptors by in vitro differentiation of murine N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;38(6):878–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg K., Ji H., Clark A. J., Shapira H., Catt K. J. Cloning and expression of a novel angiotensin II receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9455–9458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Yamano Y., Bardhan S., Iwai N., Murray J. J., Hasegawa M., Matsuda Y., Inagami T. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a bovine adrenal angiotensin II type-1 receptor. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):230–233. doi: 10.1038/351230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
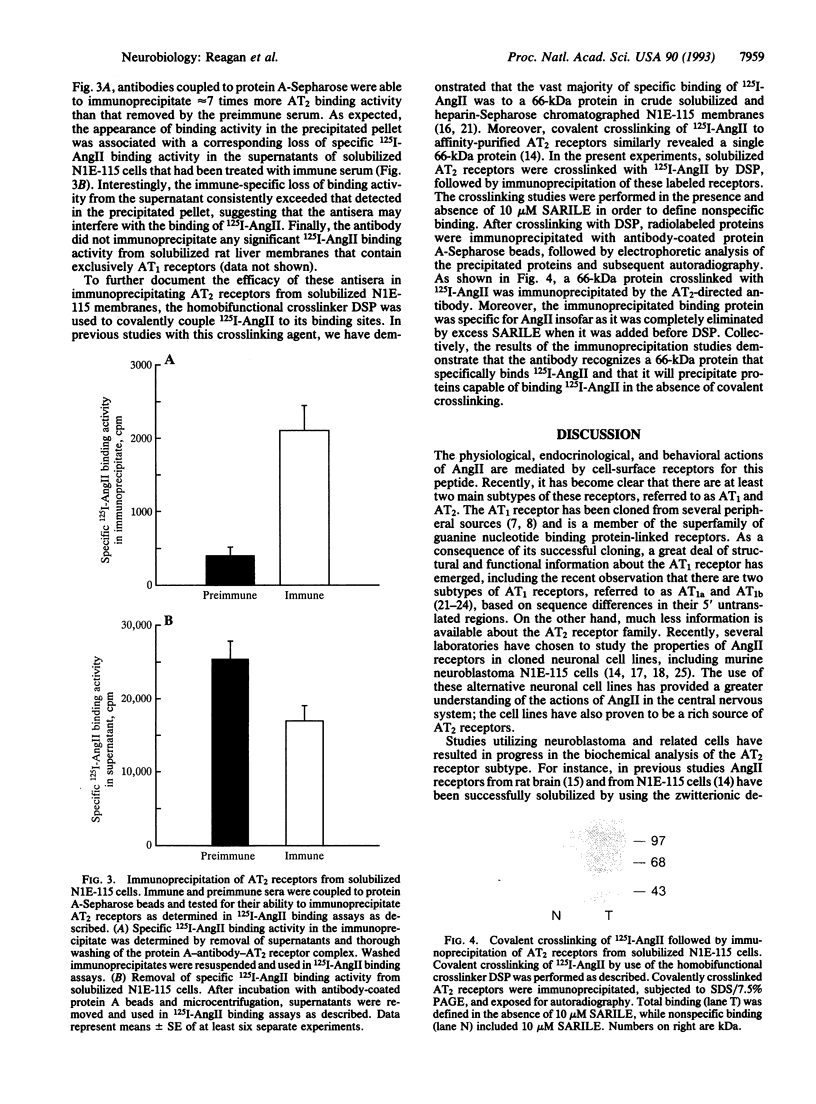
- Siemens I. R., Adler H. J., Addya K., Mah S. J., Fluharty S. J. Biochemical analysis of solubilized angiotensin II receptors from murine neuroblastoma N1E-115 cells by covalent cross-linking and affinity purification. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):717–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemens I. R., Swanson G. N., Fluharty S. J., Harding J. W. Solubilization and partial characterization of angiotensin II receptors from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1991 Aug;57(2):690–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb03801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Chiu A. T., Wong P. C., Herblin W. F., Timmermans P. B. Pharmacology of nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:135–165. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumners C., Myers L. M. Angiotensin II decreases cGMP levels in neuronal cultures from rat brain. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jan;260(1 Pt 1):C79–C87. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.1.C79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumners C., Myers L. M., Kalberg C. J., Raizada M. K. Physiological and pharmacological comparisons of angiotensin II receptors in neuronal and astrocyte glial cultures. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;34(5):355–385. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90032-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallant E. A., Diz D. I., Khosla M. C., Ferrario C. M. Identification and regulation of angiotensin II receptor subtypes on NG108-15 cells. Hypertension. 1991 Jun;17(6 Pt 2):1135–1143. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.6.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Saavedra J. M. Heterogeneity of angiotensin II AT2 receptors in the rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;41(2):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Saavedra J. M. Quantitative autoradiography reveals different angiotensin II receptor subtypes in selected rat brain nuclei. J Neurochem. 1991 Jan;56(1):348–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarahn E. D., Ye X., Ades A. M., Reagan L. P., Fluharty S. J. Angiotensin-induced cyclic GMP production is mediated by multiple receptor subtypes and nitric oxide in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1960–1963. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gasparo M., Whitebread S., Mele M., Motani A. S., Whitcombe P. J., Ramjoué H. P., Kamber B. Biochemical characterization of two angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;16 (Suppl 4):S31–S35. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199016004-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]