Abstract
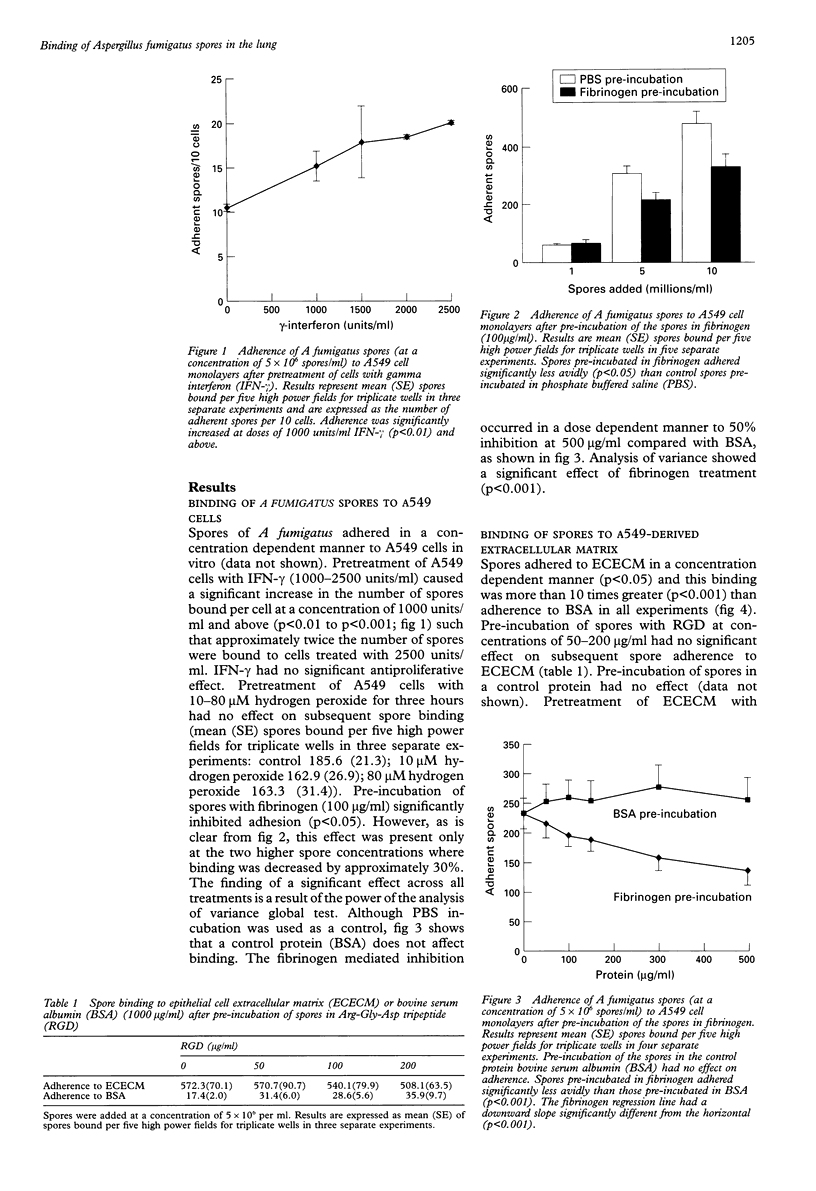
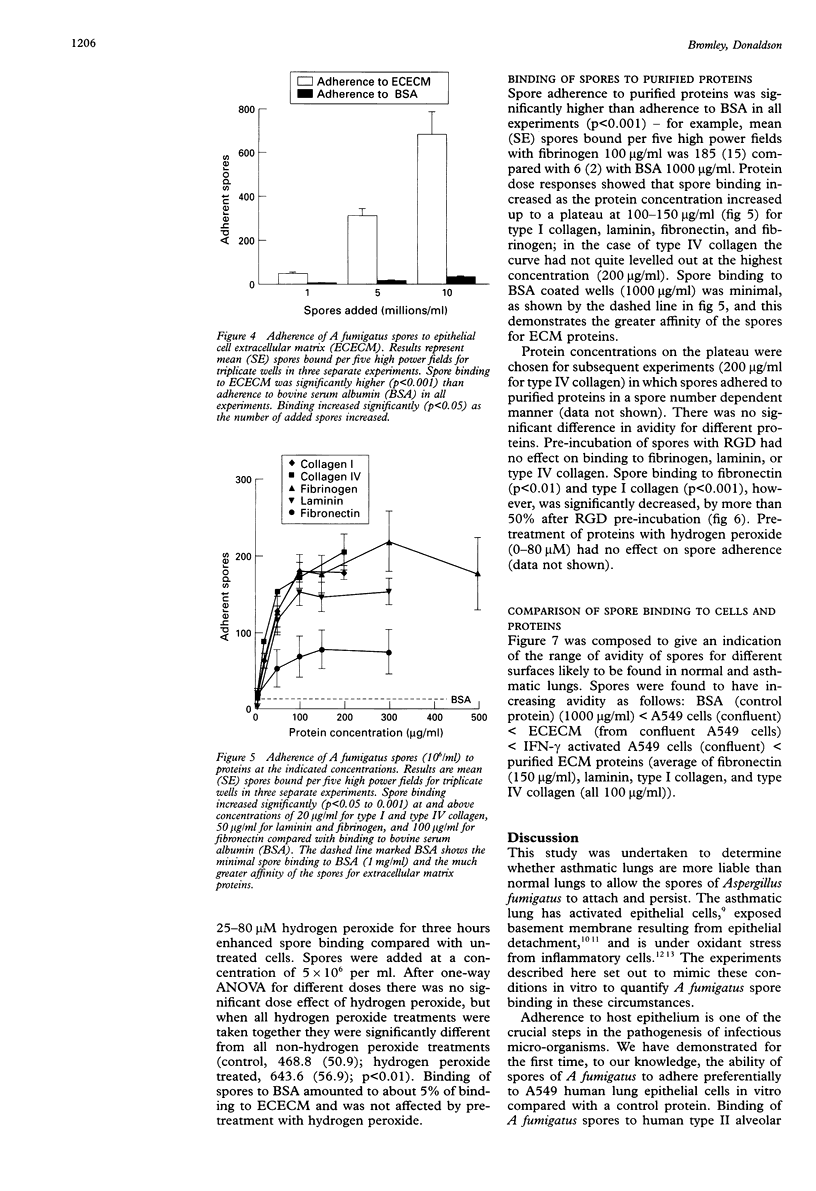
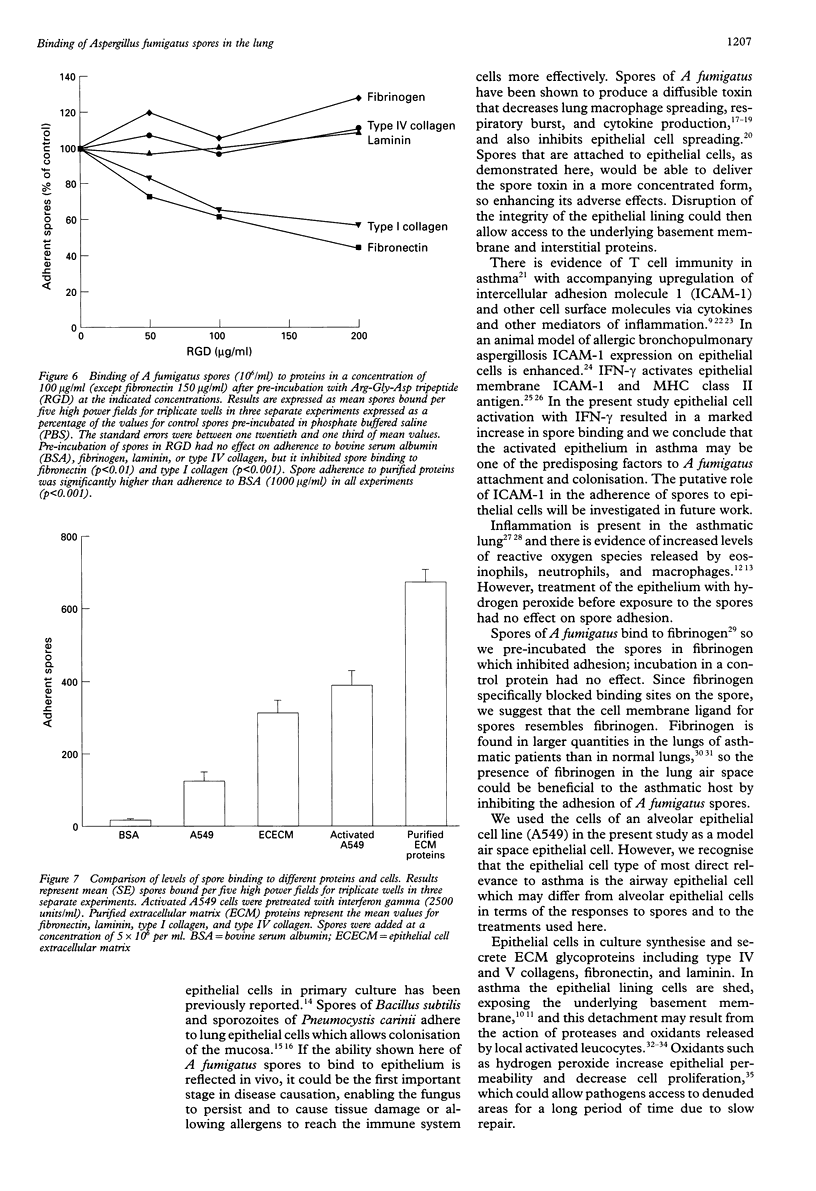
BACKGROUND: Aspergillus fumigatus is an opportunistic pathogen to which asthmatic subjects are particularly susceptible. The ability of spores of A fumigatus to bind to pulmonary cells and basement membrane proteins was investigated to determine the mechanisms involved in this susceptibility. METHODS: Cells of the A549 pulmonary epithelial cell line or purified basement membrane proteins were immobilised on the wells of microtitre plates. They were then exposed to spores of A fumigatus in suspension, with or without various pretreatments of the spores, cells, and proteins. Adherent spores were counted by light microscopy. RESULTS: Spores of A fumigatus bound in a concentration dependent manner to A549 epithelial cells and pretreatment of cells with interferon gamma (2500 units/ml) caused a significant doubling of spore binding. Binding of spores to A549 cells was inhibited by about a third by pre-incubation of the spores with fibrinogen (100 micrograms/ml). Spores bound specifically to extracellular matrix (ECM) components laid down by A549 cells, and pretreatment of the ECM components with hydrogen peroxide (25-80 microM) enhanced spore binding by approximately one third. They also bound specifically and in a saturable manner to purified fibrinogen, fibronectin, laminin, type I collagen, and type IV collagen. Pre-incubation of spores with Arg-Gly-Asp tripeptide (RGD; 50-200 micrograms/ ml) inhibited binding to fibronectin and type I collagen by 50%. CONCLUSIONS: This study suggests that the presence of activated epithelial cells and the exposure of basement membrane that occurs in asthma, together with oxidant stress, may facilitate the colonisation of the asthmatic lung by A fumigatus. The RGD sequence may be involved in spore binding to some ECM proteins. Free fibrinogen may protect against binding of A fumigatus spores to the pulmonary epithelium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annaix V., Bouchara J. P., Larcher G., Chabasse D., Tronchin G. Specific binding of human fibrinogen fragment D to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1747–1755. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1747-1755.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S., Tyring S. K., Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Coppenhaver D. H., Niesel D. W., Klimpel G. R., Stanton G. J., Hughes T. K. The interferons. Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. JAMA. 1991 Sep 11;266(10):1375–1383. doi: 10.1001/jama.266.10.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman E. D. A new look at the natural history of Aspergillus hypersensitivity in asthmatics. Respir Med. 1994 May;88(5):325–327. doi: 10.1016/0954-6111(94)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R., Roche W. R., Roberts J. A., Holgate S. T. Cellular events in the bronchi in mild asthma and after bronchial provocation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):806–817. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H. W., Wang J. M., Boutet M., Boulet L. P., Laviolette M. Increased expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in a murine model of pulmonary eosinophilia and high IgE level. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 May;100(2):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03671.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluzel M., Damon M., Chanez P., Bousquet J., Crastes de Paulet A., Michel F. B., Godard P. Enhanced alveolar cell luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987 Aug;80(2):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(87)90129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulot P., Bouchara J. P., Renier G., Annaix V., Planchenault C., Tronchin G., Chabasse D. Specific interaction of Aspergillus fumigatus with fibrinogen and its role in cell adhesion. Infect Immun. 1994 Jun;62(6):2169–2177. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.6.2169-2177.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson K., Slight J., Brown G. M., Bolton R. E. The ability of inflammatory bronchoalveolar leucocyte populations elicited with microbes or mineral dust to injure alveolar epithelial cells and degrade extracellular matrix in vitro. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Jun;69(3):327–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahy J. V., Liu J., Wong H., Boushey H. A. Cellular and biochemical analysis of induced sputum from asthmatic and from healthy subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 May;147(5):1126–1131. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.5.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelder C. M., Thomas P. S., Yates D. H., Adcock I. M., Morrison J. F., Barnes P. J. Cytokine expression in normal, atopic, and asthmatic subjects using the combination of sputum induction and the polymerase chain reaction. Thorax. 1995 Oct;50(10):1033–1037. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.10.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick D. J., Davies R. J., D'Souza M. F., Pepys J. An analysis of skin prick test reactions in 656 asthmatic patients. Thorax. 1975 Feb;30(1):2–8. doi: 10.1136/thx.30.1.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery P. K., Wardlaw A. J., Nelson F. C., Collins J. V., Kay A. B. Bronchial biopsies in asthma. An ultrastructural, quantitative study and correlation with hyperreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1745–1753. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman H. F., Tomee J. F., van der Werf T. S., de Monchy J. G., Koëter G. K. Review of fungus-induced asthmatic reactions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Jun;151(6):2109–2116. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.6.7767565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C., Ward C., Stenton C. S., Bird G., Hendrick D. J., Walters E. H. Number and activity of inflammatory cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in asthma and their relation to airway responsiveness. Thorax. 1988 Sep;43(9):684–692. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.9.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Smith R. L. Gelatin fragments block adherence of Candida albicans to extracellular matrix proteins. Microbiology. 1995 Oct;141(Pt 10):2681–2684. doi: 10.1099/13500872-141-10-2681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen L. A., Heino M., Laitinen A., Kava T., Haahtela T. Damage of the airway epithelium and bronchial reactivity in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):599–606. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Timpl R. Laminin and other basement membrane components. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:57–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J., Seaton A. Fungal spores in lung and sputum. Clin Allergy. 1978 Sep;8(5):525–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1978.tb01506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. J., Slight J., Donaldson K. Inhibition of the transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1 underlies loss of cytokine gene expression in rat alveolar macrophages treated with a diffusible product from the spores of Aspergillus fumigatus. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1996 Jul;15(1):88–96. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.15.1.8679226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPYS J., RIDDELL R. W., CITRON K. M., CLAYTON Y. M., SHORT E. I. Clinical and immunologic significance of Aspergillus fumigatus in the sputum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Aug;80:167–180. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pottratz S. T., Weir A. L., Wisniowski P. E. Pneumocystis carinii attachment increases expression of fibronectin-binding integrins on cultured lung cells. Infect Immun. 1994 Dec;62(12):5464–5469. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.12.5464-5469.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. D., Seaton A., Milne L. J., Raeburn J. A. Resistance of spores of Aspergillus fumigatus to ingestion by phagocytic cells. Thorax. 1987 Jun;42(6):466–472. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.6.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Czajkowski M., O'Neill M. M., Marlin S. D., Mainolfi E., Merluzzi V. J. Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on primary and continuous cell lines by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulation by pharmacologic agents and neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomonsson P., Grönneberg R., Gilljam H., Andersson O., Billing B., Enander I., Alkner U., Persson C. G. Bronchial exudation of bulk plasma at allergen challenge in allergic asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Dec;146(6):1535–1542. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.6.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoni G., Gismondi A., Liu J. H., Punturieri A., Santoni A., Frati L., Piccoli M., Djeu J. Y. Candida albicans expresses a fibronectin receptor antigenically related to alpha 5 beta 1 integrin. Microbiology. 1994 Nov;140(Pt 11):2971–2979. doi: 10.1099/13500872-140-11-2971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slight J., Nicholson W. J., Mitchell C. G., Pouilly N., Beswick P. H., Seaton A., Donaldson K. Inhibition of the alveolar macrophage oxidative burst by a diffusible component from the surface of the spores of the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Thorax. 1996 Apr;51(4):389–396. doi: 10.1136/thx.51.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Deshazo R. D. Bronchoalveolar lavage in asthma. An update and perspective. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Aug;148(2):523–532. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.2.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Sato A., Sugiura W., Chida K. Induction of MHC class II antigens on rat bronchial epithelial cells by interferon-gamma and its effect on antigen presentation. Lung. 1995;173(2):127–137. doi: 10.1007/BF02981472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thau N., Monod M., Crestani B., Rolland C., Tronchin G., Latgé J. P., Paris S. rodletless mutants of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 1994 Oct;62(10):4380–4388. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.10.4380-4388.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Bouchara J. P., Larcher G., Lissitzky J. C., Chabasse D. Interaction between Aspergillus fumigatus and basement membrane laminin: binding and substrate degradation. Biol Cell. 1993;77(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/s0248-4900(05)80189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venaille T. J., Mendis A. H., Phillips M. J., Thompson P. J., Robinson B. W. Role of neutrophils in mediating human epithelial cell detachment from native basement membrane. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Feb;95(2):597–606. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70322-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignola A. M., Campbell A. M., Chanez P., Bousquet J., Paul-Lacoste P., Michel F. B., Godard P. HLA-DR and ICAM-1 expression on bronchial epithelial cells in asthma and chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Sep;148(3):689–694. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.3.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignola A. M., Campbell A. M., Chanez P., Lacoste P., Michel F. B., Godard P., Bousquet J. Activation by histamine of bronchial epithelial cells from nonasthmatic subjects. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;9(4):411–417. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/9.4.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Virchow J. C., Jr, Bruijnzeel P. L., Blaser K. T cell subsets and their soluble products regulate eosinophilia in allergic and nonallergic asthma. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1829–1835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Yamato M., Aoyagi M., Yamamoto K. Identification of integrins involved in cell adhesion to native and denatured type I collagens and the phenotypic transition of rabbit arterial smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1995 Jul;219(1):249–256. doi: 10.1006/excr.1995.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaya M., Sekizawa K., Masuda T., Morikawa M., Sawai T., Sasaki H. Oxidants affect permeability and repair of the cultured human tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):L284–L293. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1995.268.2.L284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa T., Read R. C., Kroegel C., Rutman A., Chung K. F., Wilson R., Cole P. J., Barnes P. J. The effects of activated eosinophils and neutrophils on guinea pig airway epithelium in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):341–353. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.4.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


