Abstract
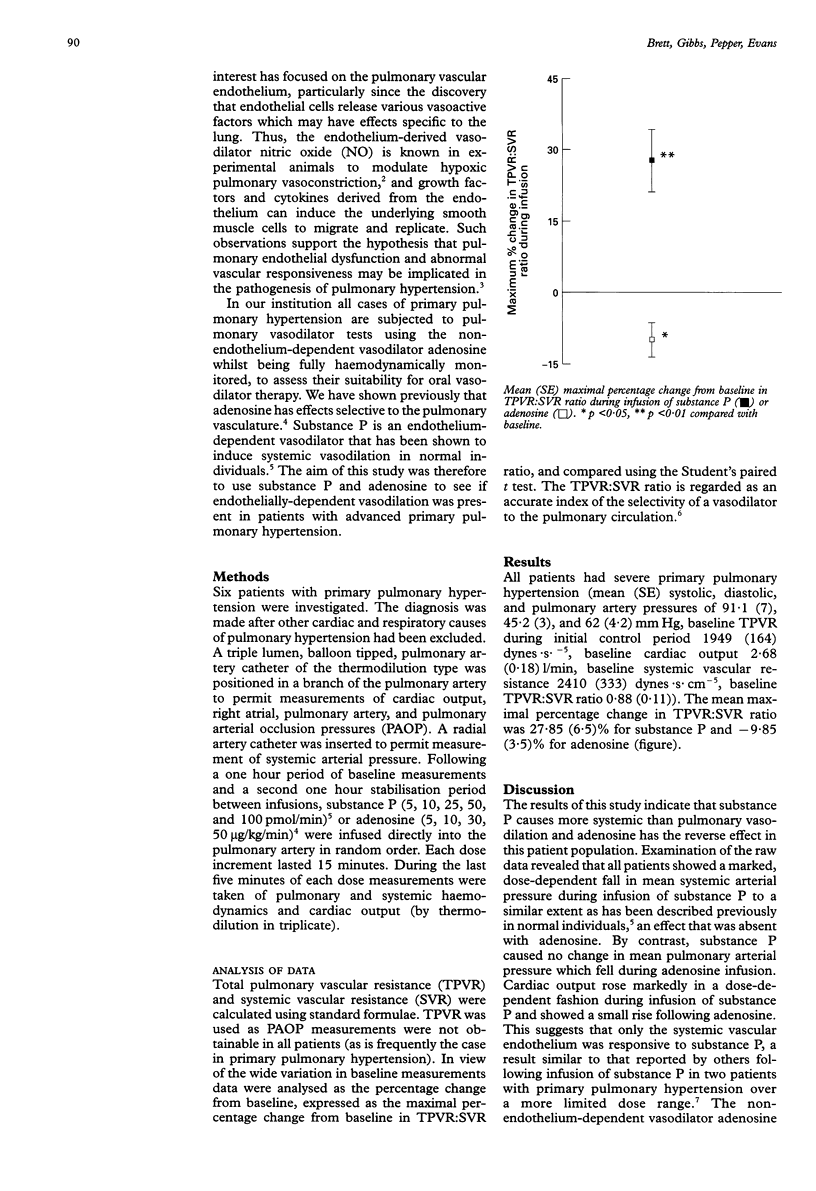
BACKGROUND: Pulmonary vascular tone may be modulated by endothelium-derived vasoactive mediators. Endothelial dysfunction is thought to occur in primary pulmonary hypertension. The aim of this study was to evaluate the vascular responses of patients with severe primary pulmonary hypertension to endothelium-dependent vasodilators (for example, substance P) and non-endothelium-dependent vaasodilators (for example, adenosine). METHODS: Six patients with primary pulmonary hypertension (mean (SE) systolic, diastolic, and pulmonary artery pressures 91.1 (7), 45.2 (3), and 62 (4.2) mm Hg, respectively, and baseline total pulmonary vascular resistance (TPVR) 1949 (164) dynes.s.cm-5) underwent sequential infusions of substance P (5-100 pmol/min) and adenosine (5-50 micrograms/kg/min) in random order. Pulmonary and systemic haemodynamics were monitored by indwelling radial and pulmonary arterial catheters. RESULTS: Substance P caused a marked fall in systemic vascular resistance (SVR) but minimal pulmonary vasodilation (mean maximal percentage change from baseline in TPVR:SVR ratio 27.85 (6.5)%, p < 0.01). Adenosine caused TPVR to fall, but resulted in no change in SVR (mean maximum percentage change from baseline in TPVR:SVR ratio -9.85 (3.5)%, p < 0.05). CONCLUSION: Endothelium-dependent vasodilation is deficient in the pulmonary circulation of patients with primary pulmonary hypertension and may contribute to the abnormalities of pulmonary vascular tone and reactivity seen in that condition.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christman B. W., McPherson C. D., Newman J. H., King G. A., Bernard G. R., Groves B. M., Loyd J. E. An imbalance between the excretion of thromboxane and prostacyclin metabolites in pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 9;327(2):70–75. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207093270202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T. W., Dixon C. M., Clarke B., Conradson T. B., Barnes P. J. Comparison of neurokinin A and substance P on cardiovascular and airway function in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;25(2):273–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03302.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J. Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 9;327(2):117–119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207093270209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. M., McCormack D. G., Griffiths M. J., Morgan C. J., Barnes P. J., Evans T. W. Adenosine as a vasodilator in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1991 Sep;84(3):1145–1149. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.3.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepke-Zaba J., Higenbottam T. W., Dinh-Xuan A. T., Stone D., Wallwork J. Inhaled nitric oxide as a cause of selective pulmonary vasodilatation in pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 1991 Nov 9;338(8776):1173–1174. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. T., Groves B. M., Weir E. K. Adenosine and selective reduction of pulmonary vascular resistance in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1991 Sep;84(3):1437–1439. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.3.1437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Kaufmann E., Levy P. S. The effect of high doses of calcium-channel blockers on survival in primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 9;327(2):76–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207093270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S. Primary pulmonary hypertension. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1988 Nov-Dec;31(3):205–238. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(88)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uren N. G., Ludman P. F., Crake T., Oakley C. M. Response of the pulmonary circulation to acetylcholine, calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P and oral nicardipine in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992 Mar 15;19(4):835–841. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(92)90528-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


