Abstract
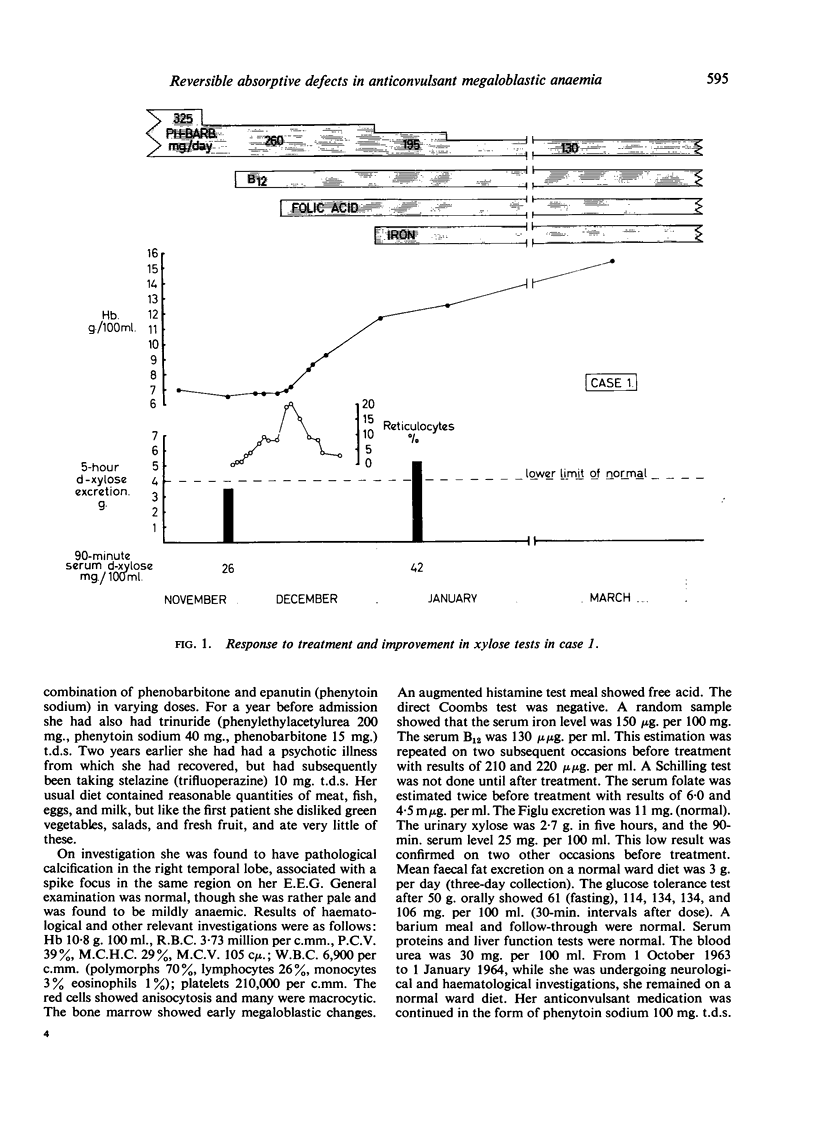
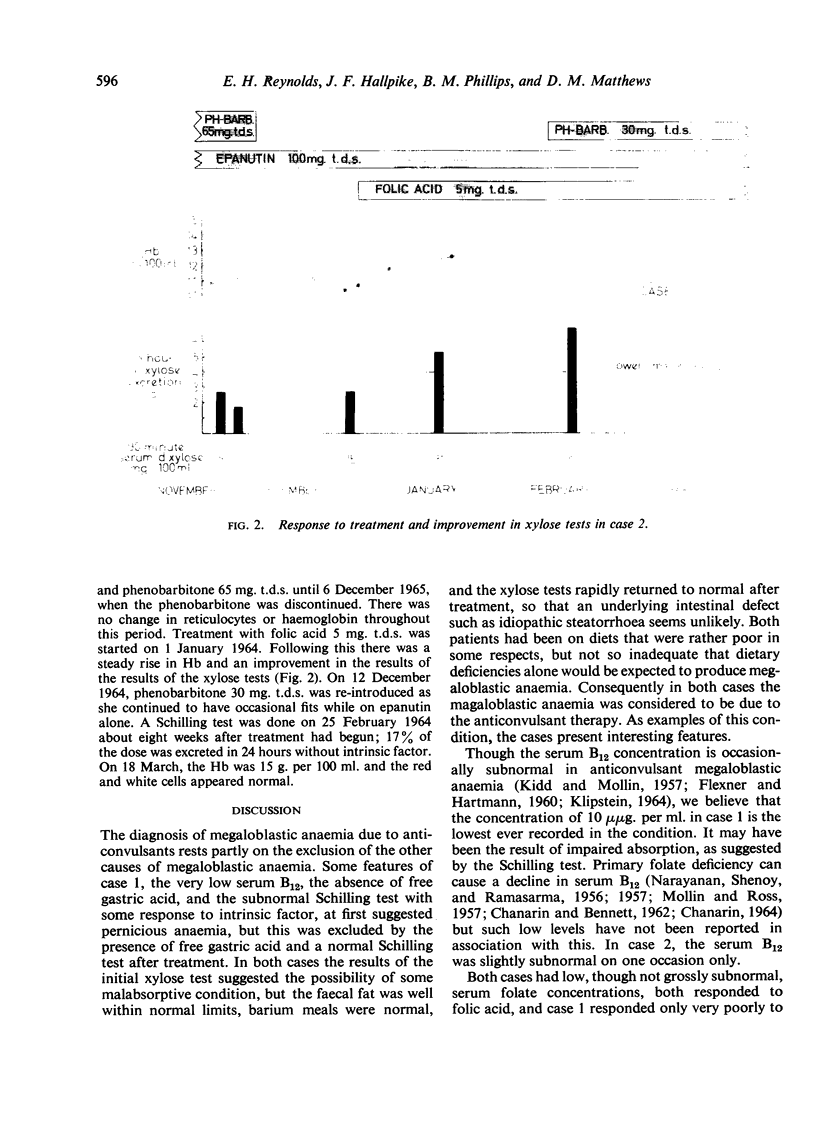
Two cases of anticonvulsant megaloblastic anaemia are described, showing features of unusual interest. Though both cases were apparently deficient in folic acid, the Figlu tests were negative. One patient had an extremely low serum B12 concentration apparently associated with defective B12 absorption due to deficiency of intrinsic factor, and both showed impaired intestinal absorption of D-xylose. There was, however, no evidence of permanent gastro-intestinal dysfunction, and the absorptive defects disappeared completely after treatment with folic acid.
Possible reasons for the findings are discussed. It is suggested that absorptive defects produced by the drugs may play some part in initiating anticonvulsant megaloblastic anaemia, and that once deficiencies of haemopoietic factors are established, a vicious circle may be set up owing to the effects of these deficiencies on the gastro-intestinal tract.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BADENOCH J. The use of labelled vitamin B12 and gastric biopsy in the investigation of anaemia. Proc R Soc Med. 1954 Jun;47(6):426–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSON J. A., Jr, CULVER P. J., RAGLAND S., JONES C. M., DRUMMEY G. D., BOUGAS E. The d-xylose absorption test in malabsorption syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1957 Feb 21;256(8):335–339. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195702212560802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEZMAN A., KINNEAR D. G., ZAMCHECK N. D-xylose and potassium iodide absorption and serum carotene in pernicious anemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Feb;53(2):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANARIN I., LAIDLAW J., LOUGHRIDGE L. W., MOLLIN D. L. Megaloblastic anaemia due to phenobarbitone; the convulsant action of therapeutic doses of folic acid. Br Med J. 1960 Apr 9;1(5179):1099–1102. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5179.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANARIN I., MOLLIN D. L., ANDERSON B. B. Folic acid deficiency and the megaloblastic anaemias. Proc R Soc Med. 1958 Sep;51(9):757–763. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSON W. N., ULTMANN J. E., ROSEMAN D. M. Megaloblastic anemia during primidone (mysoline) therapy. J Am Med Assoc. 1957 Mar 16;163(11):940–942. doi: 10.1001/jama.1957.82970460003008a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKE W. T., FONE D. J., COX E. V., MEYNELL M. J., GADDIE R. ACUTE FOLIC ACID DEFICIENCY OF UNKNOWN AETIOLOGY: TEMPERATE SPRUE. Gut. 1963 Sep;4:292–298. doi: 10.1136/gut.4.3.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRUSKIN M. S., WALLEN M. H., BONAGURA L. Anticonvulsant-associated megaloblastic anemia. Response to 25 microgm. of folic acid administered by mouth daily. N Engl J Med. 1962 Sep 6;267:483–485. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196209062671004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erf L. A., Rhoads C. P. THE GLYCINE TOLERANCE TEST IN SPRUE AND PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. J Clin Invest. 1940 Mar;19(2):409–421. doi: 10.1172/JCI101143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEXNER J. M., HARTMANN R. C. Megaloblastic anemia associated with anticonvulsant drugs. Am J Med. 1960 Mar;28:386–396. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRDWOOD R. H. Folic acid, its analogs and antagonists. Adv Clin Chem. 1960;3:235–297. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRDWOOD R. H., LENMAN J. A. Megaloblastic anaemia occurring during primidone therapy. Br Med J. 1956 Jan 21;1(4959):146–147. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4959.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GYDELL K. Megaloblastic anaemia in patients treated with diphenylhydantoin and primidone. Acta Haematol. 1957 Jan;17(1):1–15. doi: 10.1159/000205202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWKINS C. F., MEYNELL M. J. Macrocytosis and macrocytic anaemia caused by anticonvulsant drugs. Q J Med. 1958 Jan;27(105):45–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORSFIELD G. I., CHALMERS J. N. MEGALOBLASTIC ANAEMIA ASSOCIATED WITH ANTICONVULSANT THERAPY. Practitioner. 1963 Sep;191:316–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath C. W., Fullerton H. W. THE RATE OF ABSORPTION OF IODIDE AND GLYCINE FROM THE GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT IN NORMAL PERSONS AND IN DISEASE CONDITIONS. J Clin Invest. 1935 Jul;14(4):475–481. doi: 10.1172/JCI100698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmer O. M., Fouts P. J. GASTRO-INTESTINAL STUDIES. VII. THE EXCRETION OF XYLOSE IN PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. J Clin Invest. 1937 May;16(3):343–349. doi: 10.1172/JCI100862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON W. The mode of action of folic acid antagonists on cells. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):603–617. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD P., MOLLIN D. L. Megaloblastic anaemia and vitamin-B12 deficiency after anticonvulsant therapy; report of two cases. Br Med J. 1957 Oct 26;2(5051):974–976. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5051.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIPSTEIN F. A. SUBNORMAL SERUM FOLATE AND MACROCYTOSIS ASSOCIATED WITH ANTICONVULSANT DRUG THERAPY. Blood. 1964 Jan;23:68–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBERT H. P., PRANKERD T. A., SMELLIE J. M. Pernicious anaemia in childhood. A report of two cases in one family and their relationship to the aetiology of pernicious anaemia. Q J Med. 1961 Jan;30:71–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEES F. Radioactive vitamin B12 absorption in the megaloblastic anaemia caused by anticonvulsant drugs. Q J Med. 1961 Jul;30:231–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANNHEIMER E., PAKESCH F., REIMER E. E., VETTER H. Die hämatologischen Komplikationen der Epilepsiebehandlung mit Hydantoinkörpern. Med Klin. 1952 Oct 17;47(42):1397–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLIN D. L., BOOTH C. C., BAKER S. J. The absorption of vitamin B12 in control subjects, in Addisonian pernicious anaemia and in the malabsorption syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1957 Oct;3(4):412–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAYANAN M. S., RAMASARMA G. B., SHENOY K. G. Rise of serum folic acid-levels after injection of vitamin B12 in nutritional macrocytic anaemia. Nature. 1956 Dec 15;178(4546):1347–1348. doi: 10.1038/1781347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWMAN M. J., SUMNER D. W. Megaloblastic anemia following the use of primidone. Blood. 1957 Feb;12(2):183–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIKLIS E., QUASTEL J. H. Effects of metabolic inhibitors on potassium-stimulated glucose absorption by isolated surviving guinea pig intestine. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Mar;36(3):363–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATERS A. H., MOLLIN D. L. Studies on the folic acid activity of human serum. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Jul;14:335–344. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.4.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORMSLEY K. G. USE OF LABELLED TRIOLEIN, VITAMIN A, AND D-XYLOSE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALABSORPTION. Gut. 1963 Sep;4:261–272. doi: 10.1136/gut.4.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAMCHECK N. Dynamic interaction among body nutrition, gut mucosal metabolism and morphology and transport across the mucosa. Fed Proc. 1960 Dec;19:855–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




