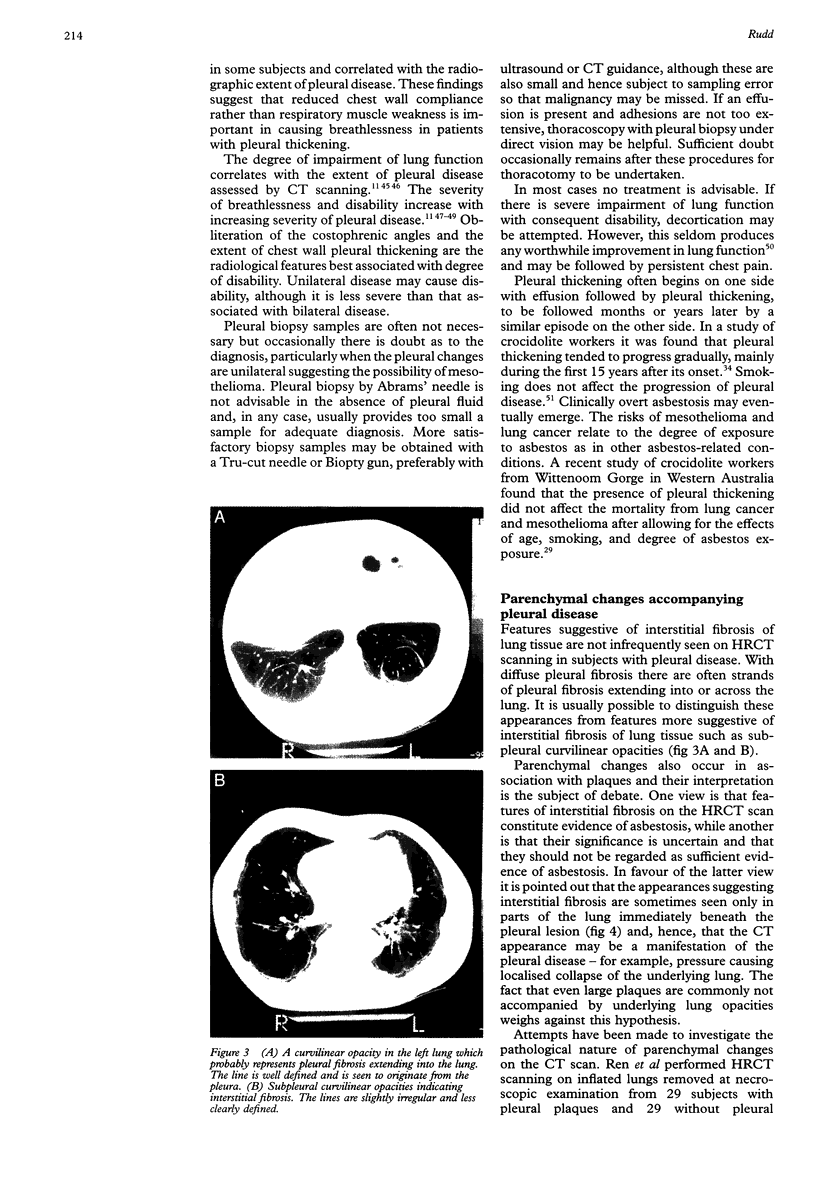
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira M., Yamamoto S., Yokoyama K., Kita N., Morinaga K., Higashihara T., Kozuka T. Asbestosis: high-resolution CT-pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1990 Aug;176(2):389–394. doi: 10.1148/radiology.176.2.2367652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira M., Yokoyama K., Yamamoto S., Higashihara T., Morinaga K., Kita N., Morimoto S., Ikezoe J., Kozuka T. Early asbestosis: evaluation with high-resolution CT. Radiology. 1991 Feb;178(2):409–416. doi: 10.1148/radiology.178.2.1987601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blesovsky A. The folded lung. Br J Dis Chest. 1966 Jan;60(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(66)80017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbeau J., Ernst P., Chrome J., Armstrong B., Becklake M. R. The relationship between respiratory impairment and asbestos-related pleural abnormality in an active work force. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Oct;142(4):837–842. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.4.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton M. G. Asbestos pleural disease. Br J Dis Chest. 1982 Jan;76(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churg A., Vedal S. Fiber burden and patterns of asbestos-related disease in workers with heavy mixed amosite and chrysotile exposure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Sep;150(3):663–669. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.3.8087335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson W. O., Musk A. W., Glancy J. J. Pleural thickening and gas transfer in asbestosis. Thorax. 1983 Sep;38(9):657–661. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.9.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D., Andrews M. I., Jones J. S. Asbestos induced pericardial effusion and constrictive pericarditis. Thorax. 1991 Jun;46(6):429–432. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.6.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dernevik L., Gatzinsky P. Long term results of operation for shrinking pleuritis with atelectasis. Thorax. 1985 Jun;40(6):448–452. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.6.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENSTADT H. B. BENIGN ASBESTOS PLEURISY. JAMA. 1965 May 3;192:419–421. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080180077029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epler G. R., McLoud T. C., Gaensler E. A. Prevalence and incidence of benign asbestos pleural effusion in a working population. JAMA. 1982 Feb 5;247(5):617–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein M. M. A study of dose-response relationships for asbestos associated disease. Br J Ind Med. 1985 May;42(5):319–325. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.5.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler E. A., Kaplan A. I. Asbestos pleural effusion. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Feb;74(2):178–191. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-2-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs A. R., Stephens M., Griffiths D. M., Blight B. J., Pooley F. D. Fibre distribution in the lungs and pleura of subjects with asbestos related diffuse pleural fibrosis. Br J Ind Med. 1991 Nov;48(11):762–770. doi: 10.1136/oem.48.11.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries P. G., Mackenzie F. A., Sheers G., Kemp J. H., Oliver T. P., Wright D. S. Radiological survey of men exposed to asbestos in naval dockyards. Br J Ind Med. 1972 Jul;29(3):274–279. doi: 10.1136/oem.29.3.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedenstierna G., Alexandersson R., Kolmodin-Hedman B., Szamosi A., Tollqvist J. Pleural plaques and lung function in construction workers exposed to asbestos. Eur J Respir Dis. 1981;62(2):111–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillerdal G. Asbestos related pleuropulmonary lesions and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Thorax. 1984 Oct;39(10):752–758. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.10.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillerdal G. Non-malignant asbestos pleural disease. Thorax. 1981 Sep;36(9):669–675. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.9.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillerdal G. Pleural and parenchymal fibrosis mainly affecting the upper lung lobes in persons exposed to asbestos. Respir Med. 1990 Mar;84(2):129–134. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(08)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjortsberg U., Orbaek P., Aborelius M., Jr, Ranstam J., Welinder H. Railroad workers with pleural plaques: II. Small airway dysfunction among asbestos-exposed workers. Am J Ind Med. 1988;14(6):643–647. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700140603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu H., Beckett L., Kelsey K., Christiani D. The left-sided predominance of asbestos-related pleural disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Oct;148(4 Pt 1):981–984. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.4_Pt_1.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Jones R. N., Glindmeyer H. W., Hammad Y. Y., Weill H. Follow up study of workers exposed to man made mineral fibres. Br J Ind Med. 1993 Jul;50(7):658–667. doi: 10.1136/oem.50.7.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarad N. A., Carroll M. P., Laroche C., Poulakis N., Moxham J., Green M., Rudd R. M. Respiratory muscle function in patients with asbestos-related pleural disease. Respir Med. 1994 Feb;88(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0954-6111(94)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarad N. A., Underwood S. R., Rudd R. M. Asbestos-related pericardial thickening detected by magnetic resonance imaging. Respir Med. 1993 May;87(4):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0954-6111(93)90029-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
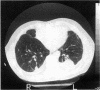
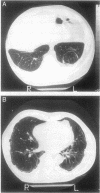
- Jarad N. A., Wilkinson P., Pearson M. C., Rudd R. M. A new high resolution computed tomography scoring system for pulmonary fibrosis, pleural disease, and emphysema in patients with asbestos related disease. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Feb;49(2):73–84. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Powers D., Warshaw R. H. Pulmonary effects of exposure to fine fibreglass: irregular opacities and small airways obstruction. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Oct;49(10):714–720. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.10.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Warshaw R. H. Abnormal lung function associated with asbestos disease of the pleura, the lung, and both: a comparative analysis. Thorax. 1991 Jan;46(1):33–38. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Warshaw R. H. Abnormal pulmonary function associated with diaphragmatic pleural plaques due to exposure to asbestos. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Sep;47(9):611–614. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.9.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Warshaw R. Pulmonary functional impairment associated with pleural asbestos disease. Circumscribed and diffuse thickening. Chest. 1990 Oct;98(4):965–972. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.4.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilis R., Lerman Y., Selikoff I. J. Symptomatic benign pleural effusions among asbestos insulation workers: residual radiographic abnormalities. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Jul;45(7):443–449. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.7.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilis R., Miller A., Godbold J., Chan E., Selikoff I. J. Pulmonary function and pleural fibrosis: quantitative relationships with an integrative index of pleural abnormalities. Am J Ind Med. 1991;20(2):145–161. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700200203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilis R., Ribak J., Suzuki Y., Penner L., Bernstein N., Selikoff I. J. Non-malignant chest x ray changes in patients with mesothelioma in a large cohort of asbestos insulation workers. Br J Ind Med. 1987 Jun;44(6):402–406. doi: 10.1136/oem.44.6.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin C. R., Sheers G. Diffuse pleural thickening in asbestos workers: disability and lung function abnormalities. Thorax. 1984 Aug;39(8):604–607. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.8.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan G. H., Rossiter C. E. Development of radiological and clinical evidence of parenchymal fibrosis in men with non-malignant asbestos-related pleural lesions. Br J Ind Med. 1982 Feb;39(1):54–59. doi: 10.1136/oem.39.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. Chronic pleuritic pain in four patients with asbestos induced pleural fibrosis. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Mar;47(3):147–153. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.3.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson G., Hagberg S., Pettersson K., Thiringer G. Asbestos pleural effusion: a clinical entity. Thorax. 1987 Sep;42(9):646–651. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.9.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver L. C., Eisen E. A., Greene R., Sprince N. L. Asbestos-related pleural plaques and lung function. Am J Ind Med. 1988;14(6):649–656. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700140604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver R. M., Neville E. Progressive apical pleural fibrosis: a 'constrictive' ventilatory defect. Br J Dis Chest. 1988 Oct;82(4):439–443. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(88)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren H., Lee D. R., Hruban R. H., Kuhlman J. E., Fishman E. K., Wheeler P. S., Hutchins G. M. Pleural plaques do not predict asbestosis: high-resolution computed tomography and pathology study. Mod Pathol. 1991 Mar;4(2):201–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggli V. L., Pratt P. C., Brody A. R. Asbestos content of lung tissue in asbestos associated diseases: a study of 110 cases. Br J Ind Med. 1986 Jan;43(1):18–28. doi: 10.1136/oem.43.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Galvin J. R., Dayton C. S., Stanford W., Merchant J. A., Hunninghake G. W. Determinants of restrictive lung function in asbestos-induced pleural fibrosis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 May;68(5):1932–1937. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.5.1932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Galvin J. R., Yagla S. J., Speakman S. B., Merchant J. A., Hunninghake G. W. Restrictive lung function and asbestos-induced pleural fibrosis. A quantitative approach. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2685–2692. doi: 10.1172/JCI116507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastien P., Janson X., Gaudichet A., Hirsch A., Bignon J. Asbestos retention in human respiratory tissues: comparative measurements in lung parenchyma and in parietal pleura. IARC Sci Publ. 1980;(30):237–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selikoff I. J. The occurrence of pleural calcification among asbestos insulation workers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):351–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B. L., Daughaday C. C., Spilberg I. Benign asbestos pleurisy in the rabbit. A model for the study of pathogenesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Sep;128(3):481–485. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Kohyama N. Translocation of inhaled asbestos fibers from the lung to other tissues. Am J Ind Med. 1991;19(6):701–704. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen E., Ahlamn K., Wükeri M. A current hypothesis of the lymphatic transport of inspired dust to the parietal pleura. Chest. 1973 Aug;64(2):193–196. doi: 10.1378/chest.64.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. C., Moncrieff C. B., Coles R., Griffiths D. M., Munday D. E. Correlation between fibre content of the lungs and disease in naval dockyard workers. Br J Ind Med. 1986 Jun;43(6):391–395. doi: 10.1136/oem.43.6.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss W. Asbestos-related pleural plaques and lung cancer. Chest. 1993 Jun;103(6):1854–1859. doi: 10.1378/chest.103.6.1854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. L., Churg A. Severe diffuse small airways abnormalities in long term chrysotile asbestos miners. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Aug;42(8):556–559. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.8.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano E., Tanaka K., Funaki M., Maeda K., Matsunaga C., Yamaoka K. Effect of smoking on pleural thickening in asbestos workers. Br J Ind Med. 1993 Oct;50(10):898–901. doi: 10.1136/oem.50.10.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
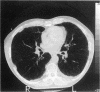
- Yoshimura H., Hatakeyama M., Otsuji H., Maeda M., Ohishi H., Uchida H., Kasuga H., Katada H., Narita N., Mikami R. Pulmonary asbestosis: CT study of subpleural curvilinear shadow. Work in progress. Radiology. 1986 Mar;158(3):653–658. doi: 10.1148/radiology.158.3.3945733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
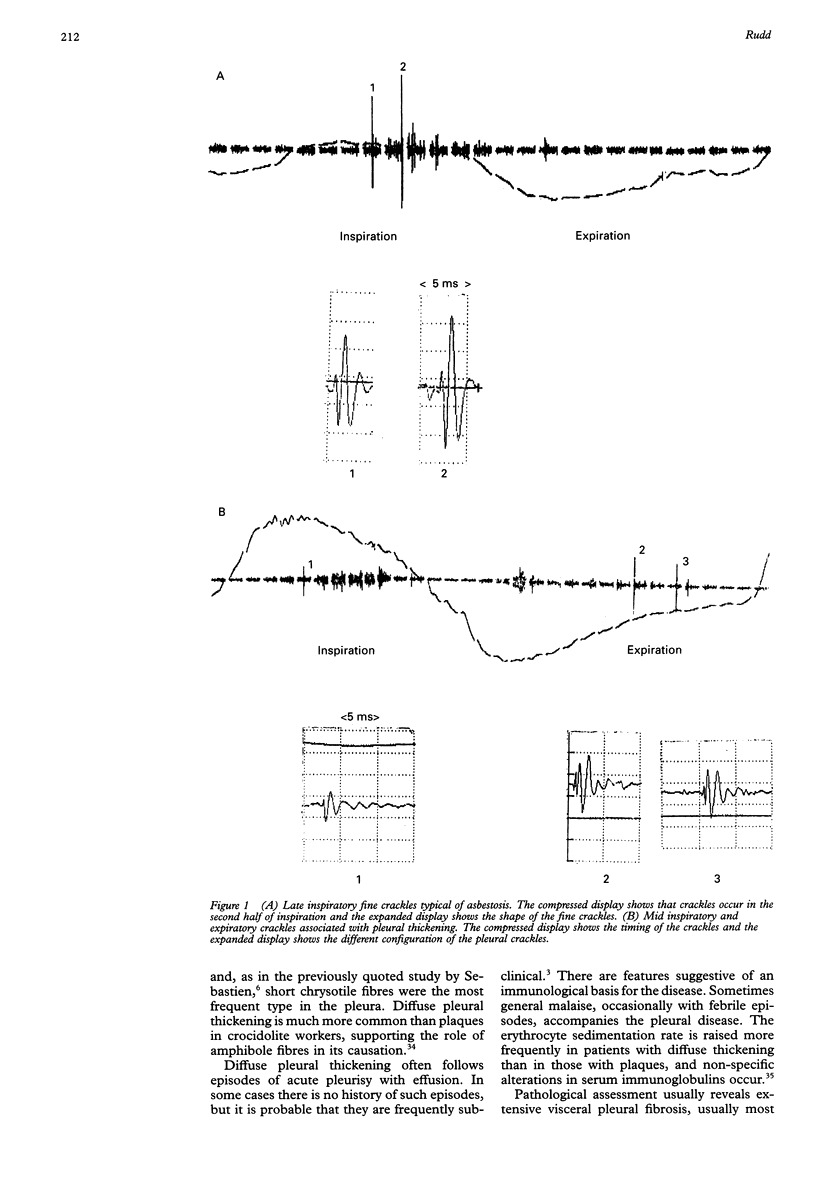
- al Jarad N., Davies S. W., Logan-Sinclair R., Rudd R. M. Lung crackle characteristics in patients with asbestosis, asbestos-related pleural disease and left ventricular failure using a time-expanded waveform analysis--a comparative study. Respir Med. 1994 Jan;88(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0954-6111(94)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klerk N. H., Cookson W. O., Musk A. W., Armstrong B. K., Glancy J. J. Natural history of pleural thickening after exposure to crocidolite. Br J Ind Med. 1989 Jul;46(7):461–467. doi: 10.1136/oem.46.7.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klerk N. H., Musk A. W., Cookson W. O., Glancy J. J., Hobbs M. S. Radiographic abnormalities and mortality in subjects with exposure to crocidolite. Br J Ind Med. 1993 Oct;50(10):902–906. doi: 10.1136/oem.50.10.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]