Abstract
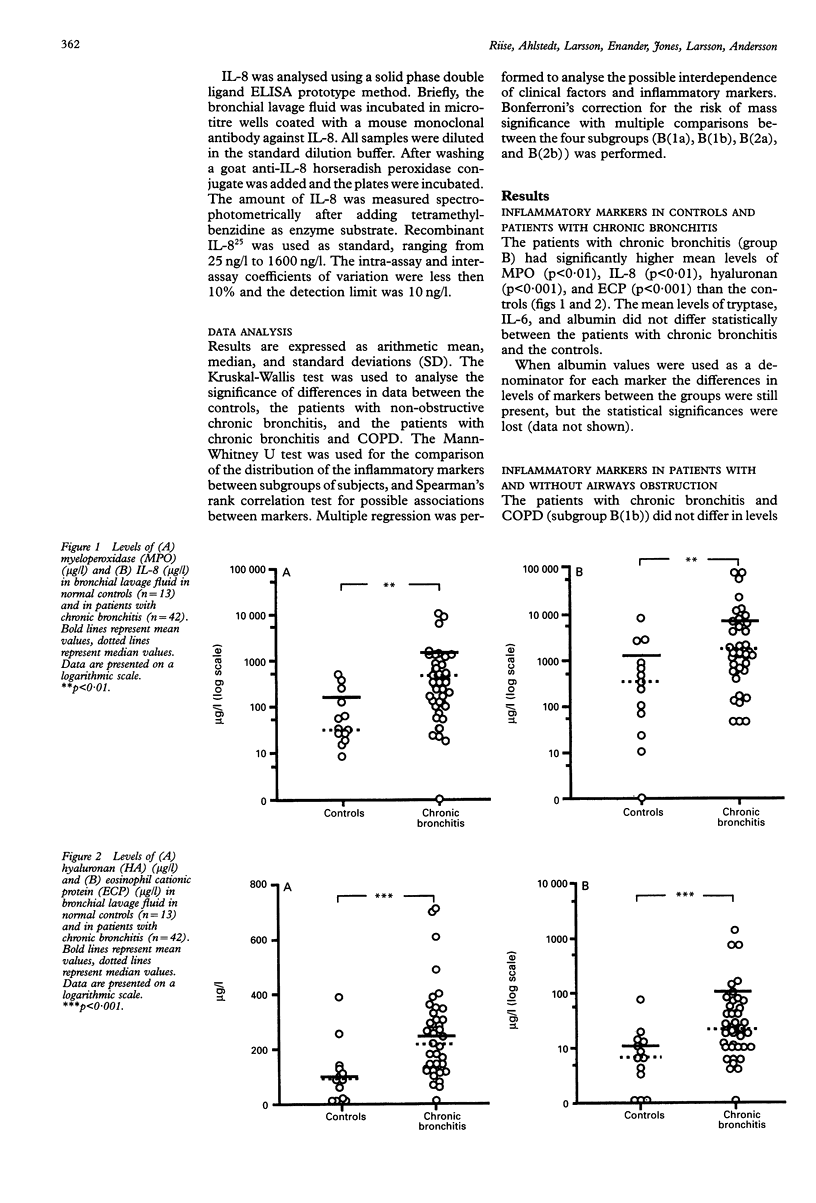
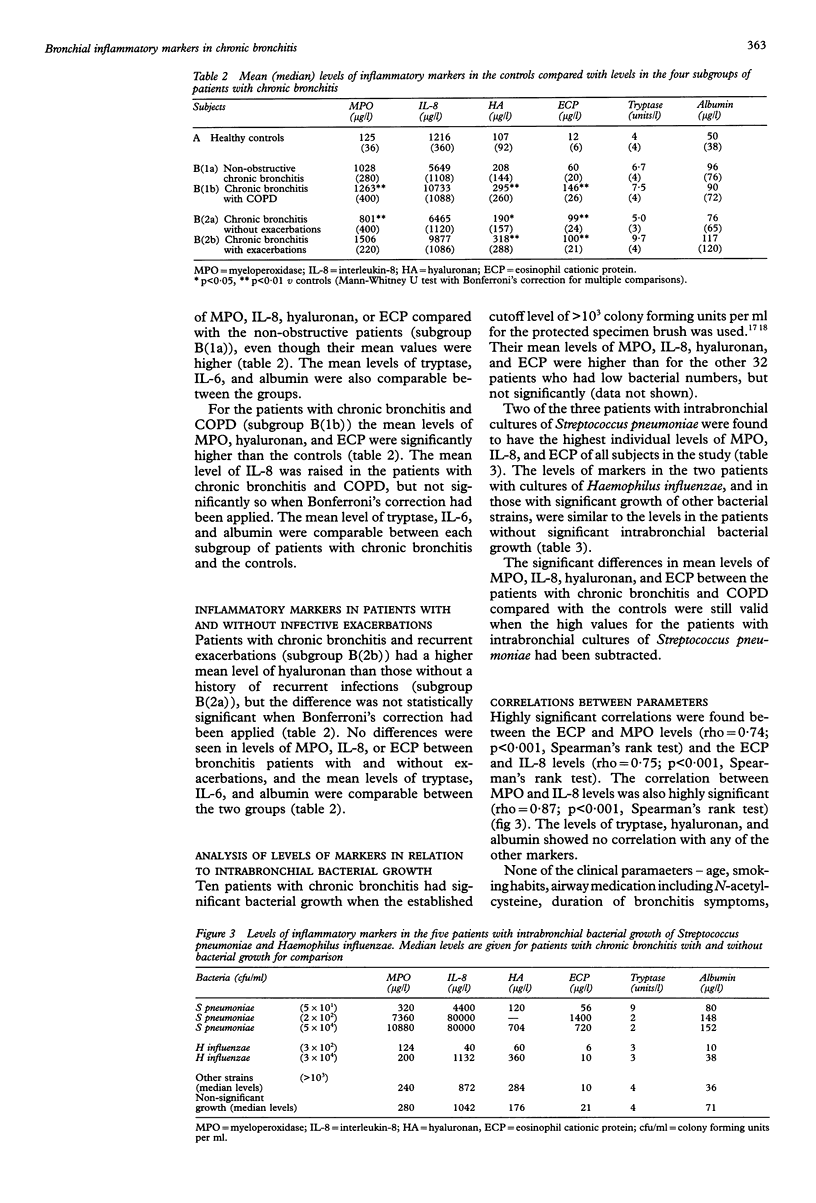
BACKGROUND--Bronchial inflammation in chronic bronchitis has not been characterised as well as in asthma. The present study was undertaken to assess whether a characteristic pattern of bronchial inflammatory markers could be found in patients with chronic bronchitis. METHODS--Bronchoscopy with bronchial lavage was performed in 42 patients with chronic bronchitis and in 13 healthy controls. Twenty three of the patients had non-obstructive chronic bronchitis and 19 had chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Eighteen of the patients with bronchitis had recurrent infective exacerbations and 24 did not. Intrabronchial bacterial cultures were taken with a protected specimen brush. RESULTS--Increased activity of neutrophils, fibroblasts, and eosinophils was found in the patients with chronic bronchitis as assessed by the levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO) and interleukin-8 (IL-8), hyaluronan, and eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), respectively. The levels of tryptase did not differ from the controls. High correlations were found between the levels of MPO and IL-8, as well as ECP and IL-8. No differences were found between the patients with COPD and those with non-obstructive chronic bronchitis. CONCLUSIONS--Recruitment and activation of both neutrophils and eosinophils seem to be a characteristic of chronic bronchitis. This activation is associated with IL-8. The patients with intrabronchial cultures of Streptococcus pneumoniae had the highest individual levels of MPO, ECP, and IL-8 of all subjects in the study, indicating that colonisation with S pneumoniae could promote bronchial inflammation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman G., Bäcker U., Larsson S., Melander B., Wåhlander L. Oral acetylcysteine reduces exacerbation rate in chronic bronchitis: report of a trial organized by the Swedish Society for Pulmonary Diseases. Eur J Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;64(6):405–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet J., Chanez P., Lacoste J. Y., Barnéon G., Ghavanian N., Enander I., Venge P., Ahlstedt S., Simony-Lafontaine J., Godard P. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 11;323(15):1033–1039. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010113231505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet J., Chanez P., Lacoste J. Y., Enander I., Venge P., Peterson C., Ahlstedt S., Michel F. B., Godard P. Indirect evidence of bronchial inflammation assessed by titration of inflammatory mediators in BAL fluid of patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Oct;88(4):649–660. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90159-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt R., Hedlöf E., Asman I., Bucht A., Tengblad A. A convenient radiometric assay for hyaluronan. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1987;442:31–35. doi: 10.3109/00016488709102835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinical guidelines and indications for bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL): Report of the European Society of Pneumology Task Group on BAL. Eur Respir J. 1990 Sep;3(8):937–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djukanović R., Lai C. K., Wilson J. W., Britten K. M., Wilson S. J., Roche W. R., Howarth P. H., Holgate S. T. Bronchial mucosal manifestations of atopy: a comparison of markers of inflammation between atopic asthmatics, atopic nonasthmatics and healthy controls. Eur Respir J. 1992 May;5(5):538–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enander I., Matsson P., Nystrand J., Andersson A. S., Eklund E., Bradford T. R., Schwartz L. B. A new radioimmunoassay for human mast cell tryptase using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Apr 8;138(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90062-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C. M., Pride N. B. Definitions of emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma, and airflow obstruction: 25 years on from the Ciba symposium. Thorax. 1984 Feb;39(2):81–85. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.2.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges S., Anderson P., Lidin-Janson G., de Man P., Svanborg C. Interleukin-6 response to deliberate colonization of the human urinary tract with gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):421–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.421-427.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges S., Stenqvist K., Lidin-Janson G., Martinell J., Sandberg T., Svanborg C. Comparison of urine and serum concentrations of interleukin-6 in women with acute pyelonephritis or asymptomatic bacteriuria. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):653–656. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Brakenhoff J. P., De Groot E. R., Aarden L. A. Interleukin 6 is involved in interleukin 1-induced activities. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):957–959. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgate S. Mediator and cytokine mechanisms in asthma. Thorax. 1993 Feb;48(2):103–109. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen L. A., Laitinen A., Haahtela T. Airway mucosal inflammation even in patients with newly diagnosed asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Mar;147(3):697–704. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.3.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam S., Leriche J. C., Kijek K., Phillips D. Effect of bronchial lavage volume on cellular and protein recovery. Chest. 1985 Dec;88(6):856–859. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.6.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden M., Rasmussen J. B., Piitulainen E., Tunek A., Larson M., Tegner H., Venge P., Laitinen L. A., Brattsand R. Airway inflammation in smokers with nonobstructive and obstructive chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Nov;148(5):1226–1232. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.5.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindley I., Aschauer H., Seifert J. M., Lam C., Brunowsky W., Kownatzki E., Thelen M., Peveri P., Dewald B., von Tscharner V. Synthesis and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene encoding monocyte-derived neutrophil-activating factor: biological equivalence between natural and recombinant neutrophil-activating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9199–9203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Raghu G., Maunder R. J., Springmeyer S. C. The effects of chronic bronchitis and chronic air-flow obstruction on lung cell populations recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):254–260. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen J. B., Wright J. L., Wiggs B. R., Pare P. D., Hogg J. C. Reassessment of inflammation of airways in chronic bronchitis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Nov 2;291(6504):1235–1239. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6504.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollerenshaw S. L., Woolcock A. J. Characteristics of the inflammation in biopsies from large airways of subjects with asthma and subjects with chronic airflow limitation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Apr;145(4 Pt 1):922–927. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.4_Pt_1.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. G., Jörnvall H., Venge P. Purification and characterization of eosinophil cationic protein from normal human eosinophils. Eur J Haematol. 1988 May;40(5):415–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1988.tb00850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Ghafouri M., Thompson A. B., Linder J., Vaughan W., Jones K., Ertl R. F., Christensen K., Prince A., Stahl M. G. Fractional processing of sequential bronchoalveolar lavage to separate bronchial and alveolar samples. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Jan;141(1):208–217. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.1.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y. Bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):250–263. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman-Eisenstat J. B., Jorens P. G., Hébert C. A., Ueki I., Nadel J. A. Interleukin-8: an important chemoattractant in sputum of patients with chronic inflammatory airway diseases. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):L413–L418. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.264.4.L413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riise G. C., Larsson S., Larsson P., Jeansson S., Andersson B. A. The intrabronchial microbial flora in chronic bronchitis patients: a target for N-acetylcysteine therapy? Eur Respir J. 1994 Jan;7(1):94–101. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07010094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saetta M., Di Stefano A., Maestrelli P., Ferraresso A., Drigo R., Potena A., Ciaccia A., Fabbri L. M. Activated T-lymphocytes and macrophages in bronchial mucosa of subjects with chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Feb;147(2):301–306. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saetta M., Di Stefano A., Maestrelli P., Ferraresso A., Drigo R., Potena A., Ciaccia A., Fabbri L. M. Activated T-lymphocytes and macrophages in bronchial mucosa of subjects with chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Feb;147(2):301–306. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmekel B., Karlsson S. E., Linden M., Sundström C., Tegner H., Venge P. Myeloperoxidase in human lung lavage. I. A marker of local neutrophil activity. Inflammation. 1990 Aug;14(4):447–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00914095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmekel B., Venge P. The distribution of myeloperoxidase, eosinophil cationic protein, albumin and urea in sequential bronchoalveolar lavage. Eur Respir J. 1991 May;4(5):517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shute J. Interleukin-8 is a potent eosinophil chemo-attractant. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994 Mar;24(3):203–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1994.tb00220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurzem J. R., Thompson A. B., Daughton D. M., Mueller M., Linder J., Rennard S. I. Chronic inflammation is associated with an increased proportion of goblet cells recovered by bronchial lavage. Chest. 1991 Aug;100(2):389–393. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. B., Daughton D., Robbins R. A., Ghafouri M. A., Oehlerking M., Rennard S. I. Intraluminal airway inflammation in chronic bronchitis. Characterization and correlation with clinical parameters. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1527–1537. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venge P., Strömberg A., Braconier J. H., Roxin L. E., Olsson I. Neutrophil and eosinophil granulocytes in bacterial infection: sequential studies of cellular and serum levels of granule proteins. Br J Haematol. 1978 Apr;38(4):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel S. E., Fowler A. A., 3rd, Schwartz L. B. Activation of pulmonary mast cells by bronchoalveolar allergen challenge. In vivo release of histamine and tryptase in atopic subjects with and without asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 May;137(5):1002–1008. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.5.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimberley N., Faling L. J., Bartlett J. G. A fiberoptic bronchoscopy technique to obtain uncontaminated lower airway secretions for bacterial culture. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):337–343. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. L., Lawson L. M., Pare P. D., Wiggs B. J., Kennedy S., Hogg J. C. Morphology of peripheral airways in current smokers and ex-smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Apr;127(4):474–477. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuoka S., Nakayama T., Kawano T., Ogushi F., Doi H., Hayashi H., Tsubura E. Comparison of cell profiles of bronchial and bronchoalveolar lavage fluids between normal subjects and patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1985 May;146(1):33–45. doi: 10.1620/tjem.146.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


