Abstract
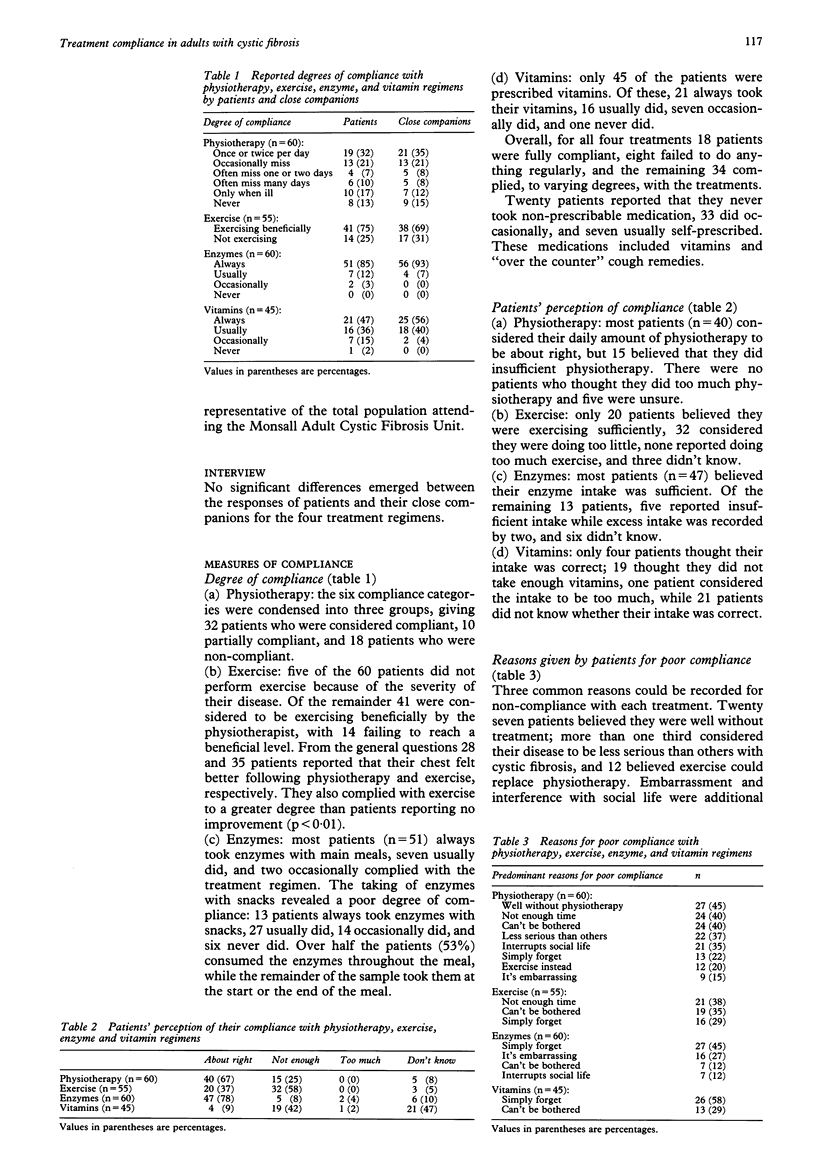
BACKGROUND--The study comprised three interrelated aims: (1) to ascertain (a) patient compliance with physiotherapy, exercise, enzyme and vitamin regimens, (b) how compliance was perceived by patients, and (c) the reasons for poor compliance (2) to identify demographic and clinical variables associated with compliance; and (3) to determine how accurately patient compliance can be predicted by carers. METHODS--Demographic and medical history data were obtained from medical records and a patient questionnaire. The data obtained included age, sex, employment status, inpatient or outpatient status, frequency of contact with the clinic, age at diagnosis, and the number of years practising physiotherapy. Measures of clinical status, including FEV1 and FVC percentage predicted, Shwachman score, and 24 hour sputum weight were recorded before completion of the questionnaire. The questionnaire, administered by a psychologist, assessed the reported degree of patient compliance, their perception of compliance, and their reasons for poor compliance. RESULTS--Sixty patients participated in the study and 51/60 and 41/55 patients were considered compliant with enzyme and exercise therapies, respectively. Compliance was lower with physiotherapy (32/60) and vitamin treatment (21/45). Patients reporting immediate benefits following exercise and physiotherapy were more compliant than those reporting no improvement. The perception by patients that compliance was sufficient ("about right") was physiotherapy 67%, exercise 37%, enzymes 78%, and vitamins 9%. Compliance was not influenced by demographic details nor by severity of disease, although patients producing large amounts of sputum and receiving help with physiotherapy were more compliant with physiotherapy. The physiotherapist and physician judged correctly the degree of compliance with physiotherapy in 83% and 75% of cases, respectively, and with exercise in 68% and 67% of cases, respectively. CONCLUSIONS--The reported degree of compliance and reasons for poor compliance were treatment specific. Demographic and disease severity variables were not associated with compliance. Those involved in the care of patients with cystic fibrosis were able to predict patient compliance.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilton D., Dodd M. E., Abbot J. V., Webb A. K. The benefits of exercise combined with physiotherapy in the treatment of adults with cystic fibrosis. Respir Med. 1992 Nov;86(6):507–511. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(96)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chintu C., McClure P. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in two children with Graves disease. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jan;129(1):101–102. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120380073016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski D. R., Koocher G. P. Medical compliance and coping with cystic fibrosis. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1987 Mar;28(2):311–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1987.tb00213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushlin A. I., Appel F. A. Diagnosing potential noncompliance. Physicians' ability in a behavioral dimension of medical care. Arch Intern Med. 1977 Mar;137(3):318–321. doi: 10.1001/archinte.137.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passero M. A., Remor B., Salomon J. Patient-reported compliance with cystic fibrosis therapy. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1981 Apr;20(4):264–268. doi: 10.1177/000992288102000406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd S. L., Hovell M. F., Harwood I. R., Granger L. E., Hofstetter C. R., Molgaard C., Kaplan R. M. A comparative study of the psychosocial assets of adults with cystic fibrosis and their healthy peers. Chest. 1990 Jun;97(6):1310–1316. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.6.1310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss G. D., Wellisch D. K. Psychosocial adaptation in older cystic fibrosis patients. J Chronic Dis. 1981;34(4):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(81)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardman A. G., Knox A. J., Muers M. F., Page R. L. Profiles of non-compliance with antituberculous therapy. Br J Dis Chest. 1988 Jul;82(3):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(88)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


