Abstract
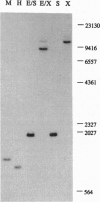
Allatostatins (ASTs) are insect neuropeptides that inhibit juvenile hormone biosynthesis by the corpora allata. We have isolated a cDNA from the cockroach Diploptera punctata that encodes a 41.5-kDa precursor polypeptide containing the AST family of peptides. Translation of the cDNA revealed a 370-amino acid pre-pro-peptide consisting of 13 AST-type peptides and appropriate processing sites for endoproteolytic cleavage and amidation. The 13 potential AST sequences are characterized by the C-terminal AST corestructure Phe-Gly-Leu-NH2, with only one exception. Separating the clustered ASTs in the precursor, three acidic spacer regions are found. Contained within the largest of these are two potentially related peptides that may also be processed. Southern blot analysis revealed the presence of a single copy of the AST gene per haploid genome, as well as the probability that the gene may be present in at least two allelic forms. In situ hybridization indicated the AST-encoding gene is expressed in neurosecretory cells of D. punctata brain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayme-Southgate A., Lasko P., French C., Pardue M. L. Characterization of the gene for mp20: a Drosophila muscle protein that is not found in asynchronous oscillatory flight muscle. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):521–531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury A. F., Finnie M. D., Smyth D. G. Mechanism of C-terminal amide formation by pituitary enzymes. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):686–688. doi: 10.1038/298686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield J. Y., Keeley L. L. Adipokinetic hormone gene sequence from Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12791–12793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusson M., Prestwich G. D., Stay B., Tobe S. S. Photoaffinity labeling of allatostatin receptor proteins in the corpora allata of the cockroach, Diploptera punctata. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):736–742. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusson M., Yagi K. J., Guan X. C., Tobe S. S. Assessment of the role of cyclic nucleotides in allatostatin-induced inhibition of juvenile hormone biosynthesis in Diploptera punctata. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Nov;89(1-2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90218-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digan M. E., Roberts D. N., Enderlin F. E., Woodworth A. R., Kramer S. J. Characterization of the precursor for Manduca sexta diuretic hormone Mas-DH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11074–11078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodyski F. M., Riddiford L. M., Truman J. W. Isolation and expression of the eclosion hormone gene from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8123–8127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masler E. P., Kelly T. J., Menn J. J. Insect neuropeptides: discovery and application in insect management. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1993;22(1-2):87–111. doi: 10.1002/arch.940220109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt G. E., Farnsworth D. E., Fok K. F., Siegel N. R., McCormack A. L., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Feyereisen R. Identity of a second type of allatostatin from cockroach brains: an octadecapeptide amide with a tyrosine-rich address sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer M., Picciotto M. R., Kreiner T., Kaldany R. R., Taussig R., Scheller R. H. Aplysia neurons express a gene encoding multiple FMRFamide neuropeptides. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):457–467. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider L. E., Taghert P. H. Isolation and characterization of a Drosophila gene that encodes multiple neuropeptides related to Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 (FMRFamide). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1993–1997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stay B., Chan K. K., Woodhead A. P. Allatostatin-immunoreactive neurons projecting to the corpora allata of adult Diploptera punctata. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Oct;270(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00381875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead A. P., Stay B., Seidel S. L., Khan M. A., Tobe S. S. Primary structure of four allatostatins: neuropeptide inhibitors of juvenile hormone synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5997–6001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead A. P., Stoltzman C. A., Stay B. Allatostatins in the nerves of the antennal pulsatile organ muscle of the cockroach Diploptera punctata. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1992;20(4):253–263. doi: 10.1002/arch.940200403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]