Abstract
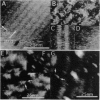
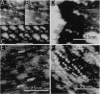
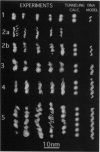
We have used the scanning tunneling microscope (STM) to image several synthetic oligonucleotides adsorbed onto a positively charged Au(111) electrode. The molecules were deposited and imaged in aqueous electrolyte under potential control, a procedure that eliminated the problem of the substrate artifacts that had limited some previous STM studies. Experiments were carried out with two types of single-stranded molecules (11 and 20 bases long) and three types of double-stranded molecules (20 and 61 base pairs and 31 bases with 25 bases paired and 6-base "sticky" ends). The molecules lie along symmetry directions on the reconstructed (23 x square root of 3) gold surface, and length measurements indicate that they adopt simple base-stacked structures. The base stacking distances are, within experimental uncertainty, equal to the 0.33 nm measured for polymeric aggregates of stacked purines by direct imaging in identical conditions. The images show features consistent with helical structures. Double helices have a major-groove periodicity that is consistent with a 36 degrees twist. The single helices appear to be more tightly twisted. A simple tunneling model of STM contrast generates good agreement between measured and calculated images.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. P., Bottomley L. A., Thundat T., Brown G. M., Woychik R. P., Schrick J. J., Jacobson K. B., Warmack R. J. Immobilization of DNA for scanning probe microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10129–10133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth JV, Brune H, Ertl G, Behm RJ. Scanning tunneling microscopy observations on the reconstructed Au(111) surface: Atomic structure, long-range superstructure, rotational domains, and surface defects. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1990 Nov 15;42(15):9307–9318. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.42.9307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe T. P., Jr, Wilson T. E., Ogletree D. F., Katz J. E., Balhorn R., Salmeron M. B., Siekhaus W. J. Direct observation of native DNA structures with the scanning tunneling microscope. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):370–372. doi: 10.1126/science.2911747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büttiker M, Imry Y, Landauer R, Pinhas S. Generalized many-channel conductance formula with application to small rings. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1985 May 15;31(10):6207–6215. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.31.6207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmer C. R., Beebe T. P., Jr Graphite: a mimic for DNA and other biomolecules in scanning tunneling microscope studies. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):640–642. doi: 10.1126/science.1992517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll R. J., Youngquist M. G., Baldeschwieler J. D. Atomic-scale imaging of DNA using scanning tunnelling microscopy. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):294–296. doi: 10.1038/346294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap D. D., García R., Schabtach E., Bustamante C. Masking generates contiguous segments of metal-coated and bare DNA for scanning tunneling microscope imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7652–7655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigler DM, Weiss PS, Schweizer EK, Lang ND. Imaging Xe with a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1991 Mar 4;66(9):1189–1192. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.66.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher AJ, Blöchl PE. Adsorption and scanning-tunneling-microscope imaging of benzene on graphite and MoS2. Phys Rev Lett. 1993 May 24;70(21):3263–3266. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.3263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulik A., Inoue H., Luzzati V. Conformation of single-stranded polynucleotides: small-angle x-ray scattering and spectroscopic study of polyribocytidylic acid in water and in water-alcohol solutions. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 28;53(2):221–238. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta G., García A. E., Hiriyanna K. T. Sampling of the conformations of the d(CGCTGCGGC) hairpin in solution by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance and theoretical methods. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 26;32(3):948–960. doi: 10.1021/bi00054a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckl W. M., Binnig G. Domain walls on graphite mimic DNA. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1073–1078. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang ND. Resistance of a one-atom contact in the scanning tunneling microscope. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1987 Nov 15;36(15):8173–8176. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.36.8173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S. M., Tao N. J., DeRose J. A., Oden P. I., Lyubchenko YuL, Harrington R. E., Shlyakhtenko L. Potentiostatic deposition of DNA for scanning probe microscopy. Biophys J. 1992 Jun;61(6):1570–1584. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81961-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S. M., Thundat T., Nagahara L., Knipping U., Rill R. L. Images of the DNA double helix in water. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1063–1064. doi: 10.1126/science.2727694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Helical periodicity of DNA determined by enzyme digestion. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):573–578. doi: 10.1038/286573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld R., Hansma P. K. Atomic-resolution microscopy in water. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):211–213. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4747.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang SL, McGhie AJ, Suna A. Molecular-resolution imaging of insulating macromolecules with the scanning tunneling microscope via a nontunneling, electric-field-induced mechanism. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1993 Feb 15;47(7):3850–3856. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.47.3850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan JY, Shao Z, Gao C. Alternative method of imaging surface topologies of nonconducting bulk specimens by scanning tunneling microscopy. Phys Rev Lett. 1991 Aug 12;67(7):863–866. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]