Abstract
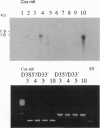
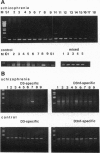
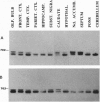
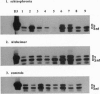
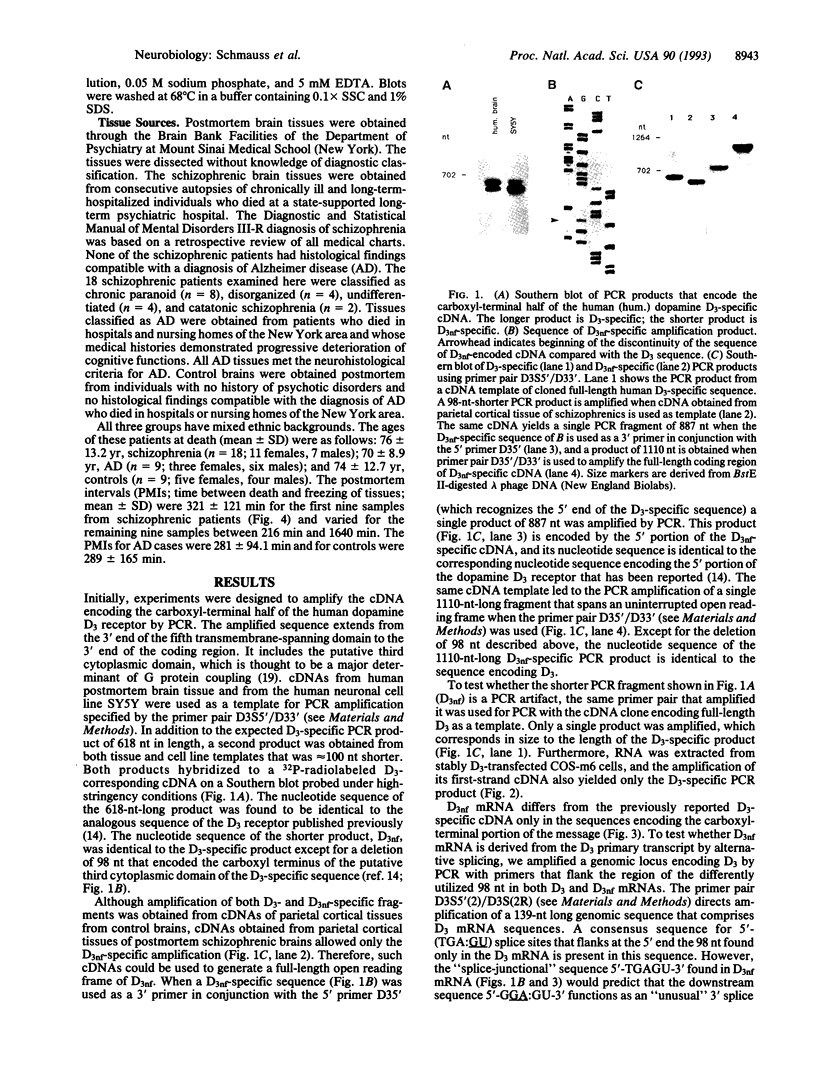
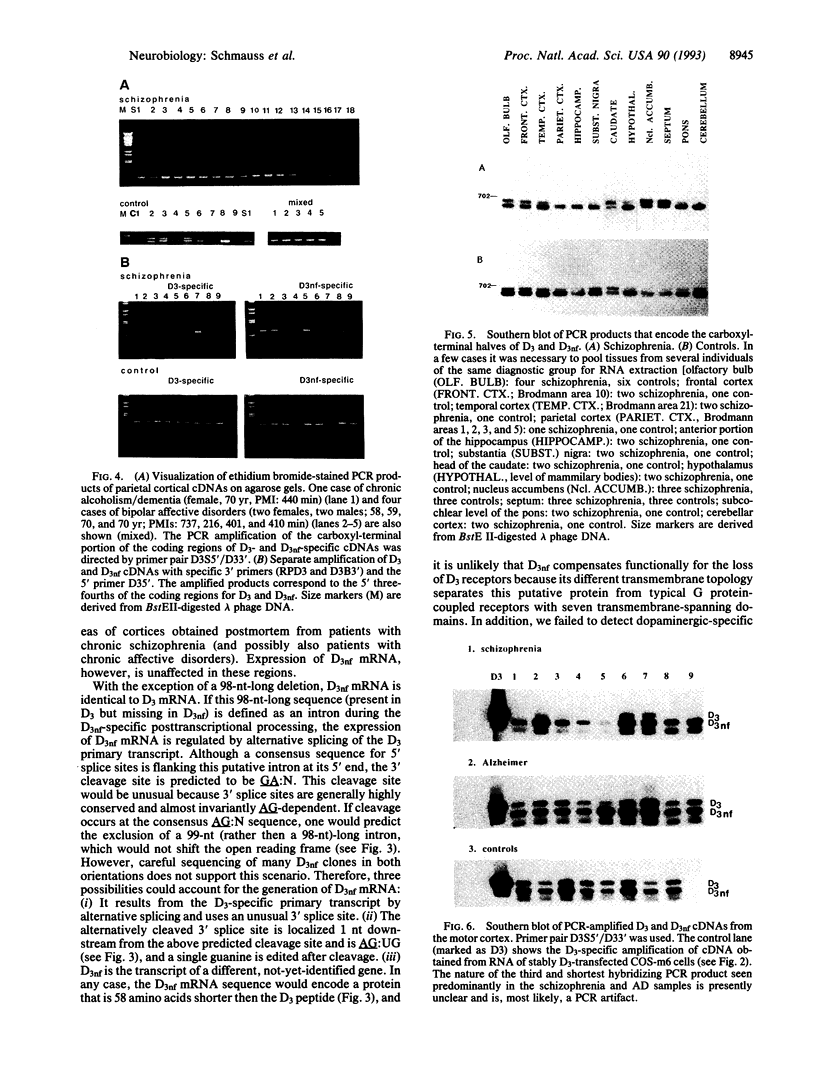
The expression of dopamine D3-subtype-receptor mRNA was analyzed in defined anatomic regions of brain obtained postmortem from patients with chronic schizophrenia and from controls. The specific amplification of D3-encoding cDNA by PCR allowed the identification of D3 mRNA expression in a wide variety of anatomic regions in both control brains and brains obtained from schizophrenic patients. However, in the parietal cortex (Brodmann areas 1, 2, 3, and 5) and motor cortex (Brodmann area 4), a selective loss of D3 mRNA expression was found in schizophrenia. A different D3 mRNA species was identified that appears to be widely expressed and that is still found in those regions of schizophrenic brains where D3 mRNA could not be detected. Compared with D3 mRNA this RNA is significantly less abundant, and at present its function (if any) is unclear. Many variables associated with either the course and/or the therapeutic management of the disease may account for the selective loss of D3 mRNA in the motor, somatosensory, and somatosensory association areas of schizophrenic brains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L. G proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Toso R., Sommer B., Ewert M., Herb A., Pritchett D. B., Bach A., Shivers B. D., Seeburg P. H. The dopamine D2 receptor: two molecular forms generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4025–4034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearry A., Gingrich J. A., Falardeau P., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Bates M. D., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):72–76. doi: 10.1038/347072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giros B., Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Schwartz J. C. Clonage du gène du récepteur dopaminergique D3 humain et identification de son chromosome. C R Acad Sci III. 1990;311(13):501–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giros B., Sokoloff P., Martres M. P., Riou J. F., Emorine L. J., Schwartz J. C. Alternative splicing directs the expression of two D2 dopamine receptor isoforms. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):923–926. doi: 10.1038/342923a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsma F. J., Jr, McVittie L. D., Gerfen C. R., Mahan L. C., Sibley D. R. Multiple D2 dopamine receptors produced by alternative RNA splicing. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):926–929. doi: 10.1038/342926a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L. A., Roberts J. L., Sealfon S. C. Alternative transcripts of the rat and human dopamine D3 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):1031–1035. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Andrieux M., Besançon R., Pilon C., Martres M. P., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacology of human dopamine D3 receptor expressed in a mammalian cell line: comparison with D2 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 10;225(4):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Guan H. C., O'Dowd B. F., Seeman P., Laurier L. G., Ng G., George S. R., Torchia J., Van Tol H. H., Niznik H. B. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):614–619. doi: 10.1038/350614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Niznik H. B., Weiner D. M., Stormann T. M., Brann M. R., Kennedy J. L., Gelernter J. E., Rozmahel R., Yang Y. L., Israel Y. Human dopamine D1 receptor encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):80–83. doi: 10.1038/347080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiberi M., Jarvie K. R., Silvia C., Falardeau P., Gingrich J. A., Godinot N., Bertrand L., Yang-Feng T. L., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Caron M. G. Cloning, molecular characterization, and chromosomal assignment of a gene encoding a second D1 dopamine receptor subtype: differential expression pattern in rat brain compared with the D1A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Guan H. C., Sunahara R. K., Seeman P., Niznik H. B., Civelli O. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):610–614. doi: 10.1038/350610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshank R. L., Adham N., Macchi M., Olsen M. A., Branchek T. A., Hartig P. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a high affinity dopamine receptor (D1 beta) and its pseudogene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22427–22435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Grandy D. K., Thambi L., Kushner J. A., Van Tol H. H., Cone R., Pribnow D., Salon J., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of human and rat D1 dopamine receptors. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):76–80. doi: 10.1038/347076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]