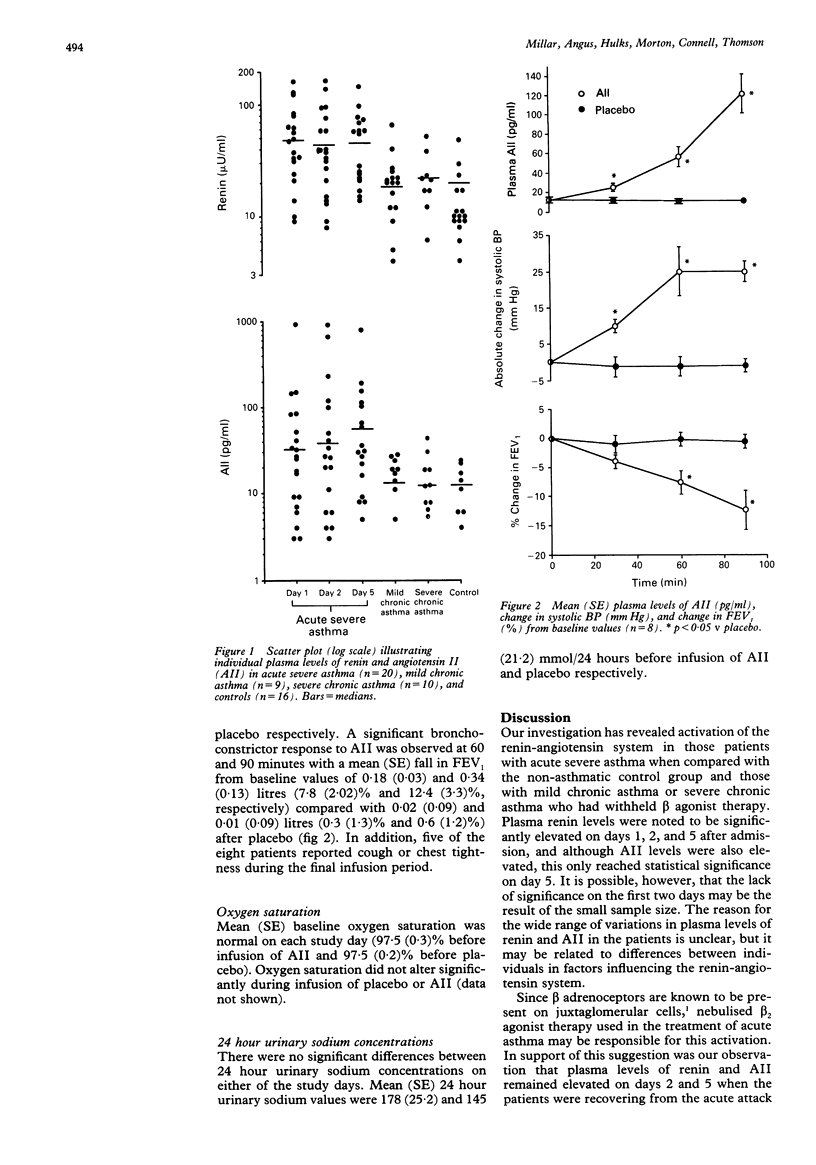
Abstract
BACKGROUND--The activity of the renin-angiotensin system in asthma has not been studied previously and the effect of angiotensin II (AII) on bronchomotor tone in vivo is unknown. METHODS--Plasma levels of renin and AII levels were measured in 20 patients with acute severe asthma, nine with mild asthma, 10 with severe chronic asthma, and 16 normal volunteers. The effect of AII, given as an intravenous infusion, on bronchomotor tone was also investigated in eight mild asthmatic patients. RESULTS--In acute severe asthma plasma levels of renin [median (interquartile range)] were elevated on days 1, 2, and 5 after admission [48.7 (24-79), 44.2 (15-75), and 45.5 (21-70) microU/ml, respectively]. Plasma AII levels were significantly elevated at day 5 [56 (12-109) pg/ml]. In the second study a bronchoconstrictor response to intravenous AII was seen with a mean (SE) maximal fall in FEV1 of 0.34 (0.13) litres or 12.4 (3.3)% from baseline following the high dose infusion of AII (8 ng/kg/min) with a corresponding plasma AII concentration of 121.3 pg/ml. CONCLUSIONS--The renin-angiotensin system is activated in acute asthma and AII causes bronchoconstriction in vivo in man. These observations suggest that in some patients AII may contribute to bronchoconstriction during acute severe asthma.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell-Boswell M., Robertson A. L., Jr Effects of angiotensin II and vasopressin on human smooth muscle cells in vitro. Exp Mol Pathol. 1981 Oct;35(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(81)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould A. B., Goodman S. A. The effect of hypoxia on the renin-angiotensinogen system. Lab Invest. 1970 May;22(5):443–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ind P. W., Causon R. C., Brown M. J., Barnes P. J. Circulating catecholamines in acute asthma. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jan 26;290(6464):267–269. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6464.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno M., Horio T., Yokokawa K., Kurihara N., Takeda T. C-type natriuretic peptide inhibits thrombin- and angiotensin II-stimulated endothelin release via cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Hypertension. 1992 Apr;19(4):320–325. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.19.4.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. A., Leckie B. J., Morton J. J., Jordan J., Tree M. A microassay for active and total renin concentration in human plasma based on antibody trapping. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Feb 14;101(1):5–15. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. J., Webb D. J. Measurement of plasma angiotensin II. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Apr;68(4):483–484. doi: 10.1042/cs0680483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilly J. B., Clark C. J., Tweddel A., Rae A. P., Hughes D. M., Hutton I., Morton J. J., Stevenson R. D. Transpulmonary angiotensin II formation in patients with chronic stable cor pulmonale. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Apr;135(4):891–895. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.4.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. J., Matthews A. Transpulmonary angiotensin II formation and pulmonary haemodynamics in stable hypoxic lung disease: the effect of captopril. Respir Med. 1992 Jan;86(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(06)80143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P. J., Vedig A. E., Jones P. L., Chapman M. G., Collins M., Edwards J. B., Smeaton T. C., Duncan B. M. Metabolic and cardiovascular side effects of the beta 2-adrenoceptor agonists salbutamol and rimiterol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 May;9(5):483–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb05844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H., Maselli J., Reid I. A. Correlation of plasma angiotensin II concentration and plasma renin activity during acute hypoxia in dogs. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1985 Jan-Feb;12(1):91–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1985.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. A., Morris B. J., Ganong W. F. The renin-angiotensin system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:377–410. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. F., Tewksbury D. A., Schechter N. M., Travis J. Rapid conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II by neutrophil and mast cell proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8619–8622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinin M., Koulu M., Laurikainen E., Allonen H. Hypokalaemia and other non-bronchial effects of inhaled fenoterol and salbutamol: a placebo-controlled dose-response study in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;24(5):645–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szidon P., Bairey N., Oparil S. Effect of acute hypoxia on the pulmonary conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II in dogs. Circ Res. 1980 Feb;46(2):221–226. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


