Abstract
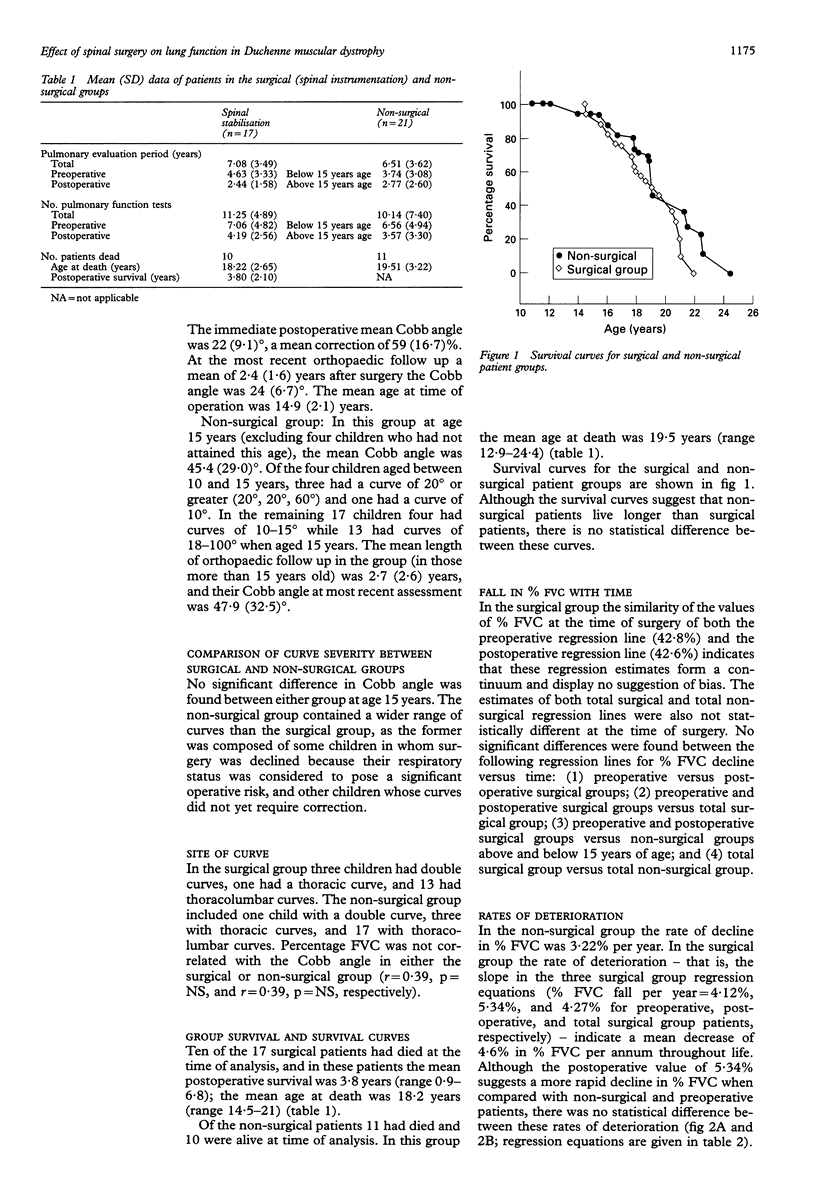
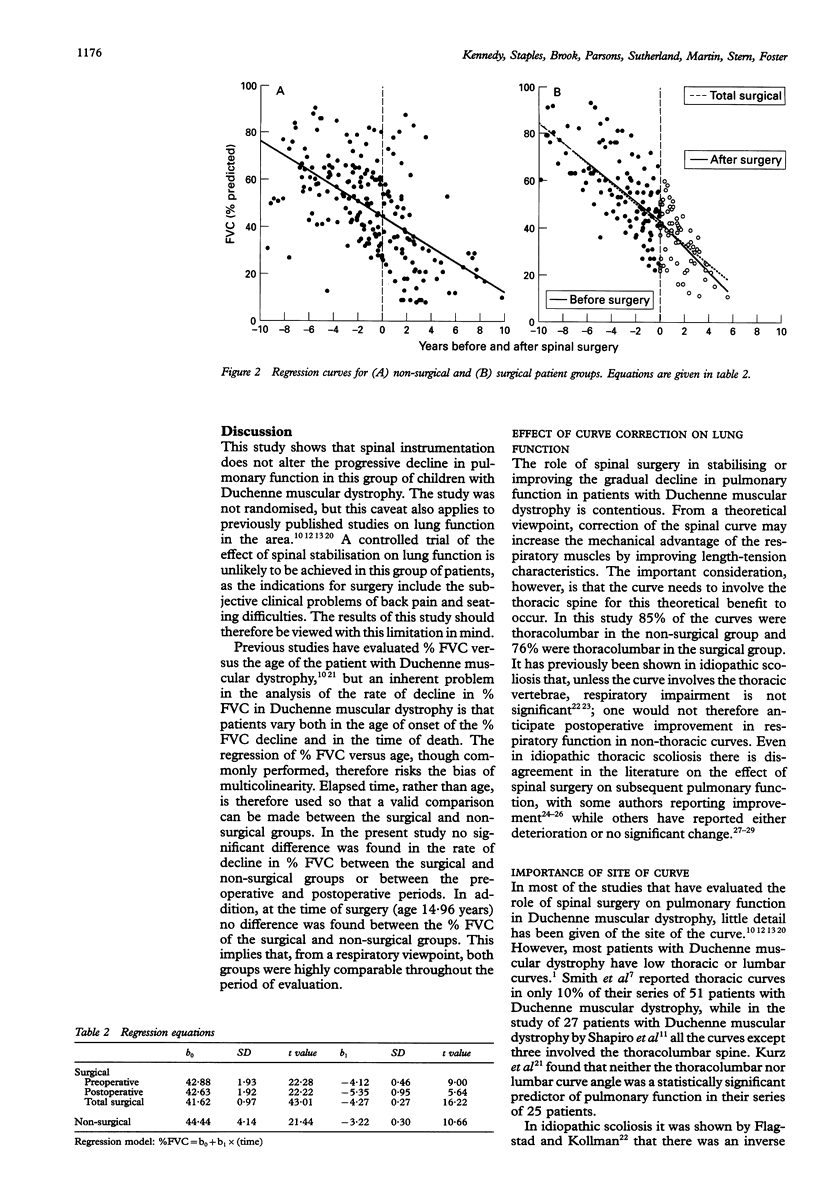
BACKGROUND--The effect on subsequent respiratory function of spinal stabilisation for scoliosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy is unclear. In order to clarify this clinical problem, changes in the forced vital capacity of a group of children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy who had undergone spinal surgery were measured and compared with a group of children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy who had not had surgery. METHODS--In this retrospective study 17 boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy who underwent spinal stabilisation at a mean age of 14.9 years (surgical group) were compared with 21 boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy who had not had surgery (non-surgical group). The mean (SD) Cobb angle of the surgical group at 14.9 years was 57 (16.4) degrees, and of the non-surgical group at 15 years was 45 (29.9) degrees. Forced vital capacity expressed as percentage predicted (% FVC) was measured in total over a seven year period in the surgical group and over 6.5 years in the non-surgical group, and regression equations were calculated. Survival curves for both groups were also constructed. RESULTS--No difference was found between spinal stabilisation (surgical group) and the non-surgical group in the rate of deterioration of % FVC which was 3-5% per year. There was no difference in survival in either group. CONCLUSIONS--Spinal stabilisation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy does not alter the decline in pulmonary function, nor does it improve survival.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cambridge W., Drennan J. C. Scoliosis associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):436–440. doi: 10.1097/01241398-198707000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo R. O., Morris A. H., Gardner R. M. Reference spirometric values using techniques and equipment that meet ATS recommendations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jun;123(6):659–664. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.6.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnon S., Jodoin A., Martin R. Pulmonary function test study and after spinal fusion in young idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1989 May;14(5):486–490. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198905000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galasko C. S., Delaney C., Morris P. Spinal stabilisation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992 Mar;74(2):210–214. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.74B2.1544954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. J., Pride N. B., Davis J. N., Loh L. C. Pulmonary mechanics in patients with respiratory muscle weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Mar;115(3):389–395. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey S. Respiratory and cardiovascular consequences of scoliosis. Respiration. 1970;27(Suppl):67–70. doi: 10.1159/000192722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPER N. G., BLACK L. F., FOWLER W. S. RELATIONSHIPS OF LUNG VOLUME TO HEIGHT AND ARM SPAN IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH SPINAL DEFORMITY. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Mar;91:356–362. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.3.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin abnormalities in Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90226-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. G., Bohn D., Edmonds J. F., Levison H., Barker G. A. Evaluation of pulmonary function in muscular dystrophy patients requiring spinal surgery. Crit Care Med. 1982 Oct;10(10):645–649. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198210000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafer E. R. Idiopathic scoliosis. Mechanical properties of the respiratory system and the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1153–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI108032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan Y., Heckmatt J. Z. Obstructive apnoeas in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Thorax. 1994 Feb;49(2):157–161. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz L. T., Mubarak S. J., Schultz P., Park S. M., Leach J. Correlation of scoliosis and pulmonary function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop. 1983 Jul;3(3):347–353. doi: 10.1097/01241398-198307000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindh M., Bjure J. Lung volumes in scoliosis before and after correction by the Harrington instrumentation method. Acta Orthop Scand. 1975 Dec;46(6):934–948. doi: 10.3109/17453677508989282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F., Moseley C. F., Koreska J., Levison H. Pulmonary function and scoliosis in Duchenne dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop. 1988 Mar-Apr;8(2):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Chalmers A. C., Dao H., Filler-Katz A., Holman D., Bost F. The effect of spine fusion on respiratory function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology. 1991 Jan;41(1):38–40. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rideau Y., Gatin G., Bach J., Gines G. Prolongation of life in Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 1983 Apr;5(2):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rideau Y., Glorion B., Delaubier A., Tarlé O., Bach J. The treatment of scoliosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1984 May;7(4):281–286. doi: 10.1002/mus.880070405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro F., Sethna N., Colan S., Wohl M. E., Specht L. Spinal fusion in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a multidisciplinary approach. Muscle Nerve. 1992 May;15(5):604–614. doi: 10.1002/mus.880150512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro F., Specht L. The diagnosis and orthopaedic treatment of inherited muscular diseases of childhood. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993 Mar;75(3):439–454. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199303000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Koreska J., Moseley C. F. Progression of scoliosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989 Aug;71(7):1066–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. E., Calverley P. M., Edwards R. H., Evans G. A., Campbell E. J. Practical problems in the respiratory care of patients with muscular dystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1987 May 7;316(19):1197–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198705073161906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank S. M., Brown J. C., Perry R. E. Spinal fusion in Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1982 Sep-Oct;7(5):484–491. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198209000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig L. M., Chernick V., Wood R., Farrell P., Mellins R. B. Standardization of lung function testing in children. Proceedings and Recommendations of the GAP Conference Committee, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. J Pediatr. 1980 Oct;97(4):668–676. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay S. S., Ho E. K., Gunawardene W. M., Leong J. C., Hsu L. C. Changes in residual volume relative to vital capacity and total lung capacity after arthrodesis of the spine in patients who have adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993 Jan;75(1):46–52. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199301000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vianello A., Bevilacqua M., Salvador V., Cardaioli C., Vincenti E. Long-term nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation in advanced Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. Chest. 1994 Feb;105(2):445–448. doi: 10.1378/chest.105.2.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber B., Smith J. P., Briscoe W. A., Friedman S. A., King T. K. Pulmonary function in asymptomatic adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Apr;111(4):389–397. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.4.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S. L., Zavala D. C., Ponseti I. V. Idiopathic scoliosis: long-term follow-up and prognosis in untreated patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981 Jun;63(5):702–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westate H. D., Moe J. H. Pulmonary function in kyphoscoliosis before and after correction by the Harrington instrumentation method. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969 Jul;51(5):935–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapletal A., Motoyama E. K., Van De Woestijne K. P., Hunt V. R., Bouhuys A. Maximum expiratory flow-volume curves and airway conductance in children and adolescents. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Mar;26(3):308–316. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.3.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapletal A., Motoyama E. K., Van De Woestijne K. P., Hunt V. R., Bouhuys A. Maximum expiratory flow-volume curves and airway conductance in children and adolescents. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Mar;26(3):308–316. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.3.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


