Abstract
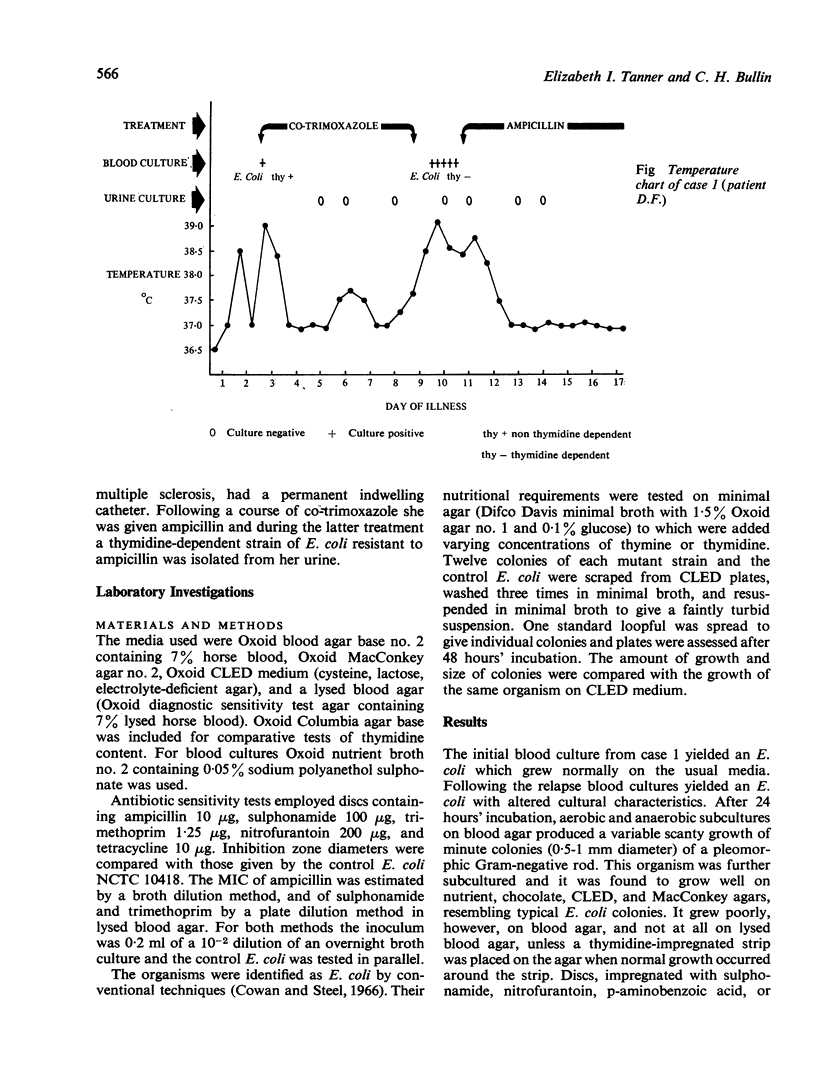
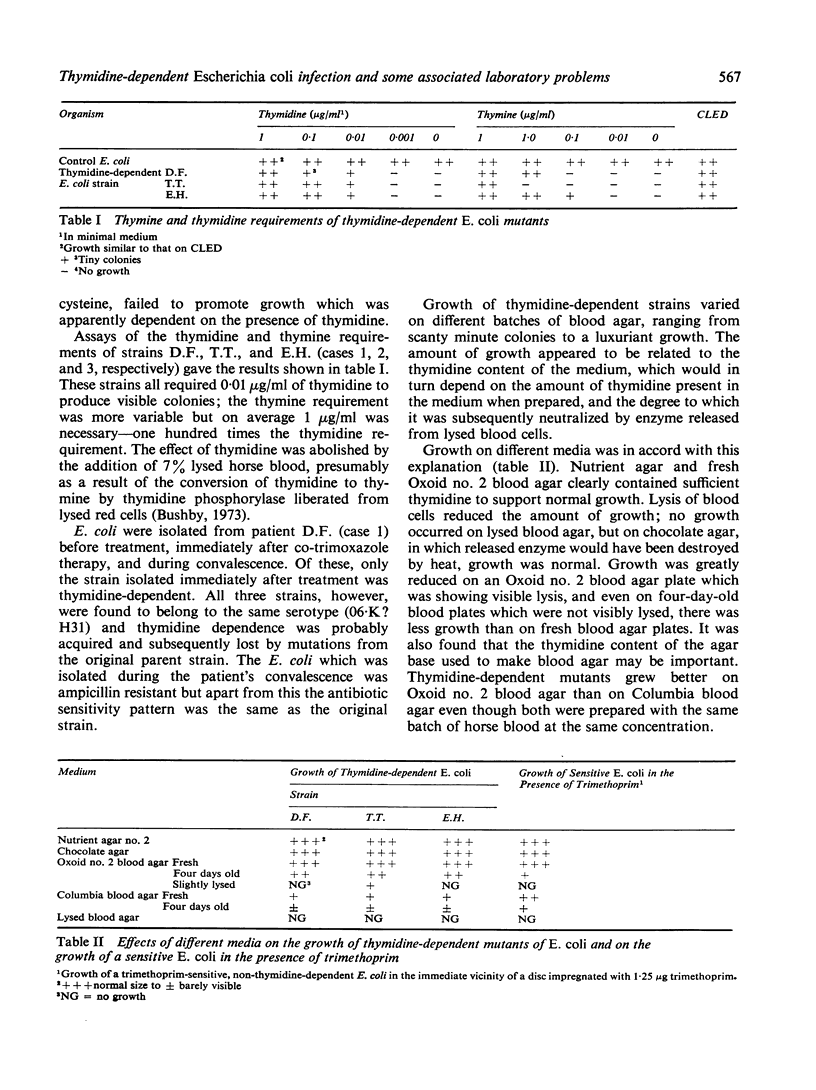
The rapid emergence of a thymidine-dependent strain of Escherichia coli in a patient treated with co-trimoxazole is described. The organism was recovered from blood cultures during a septicaemia which developed after only a few days of co-trimoxazole treatment. The cultural characteristics of three thymidine-dependent strains were studied and a remarkable variation was found in their ability to grow on different batches of blood agar, depending upon the age of the plates and the type of agar base used.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker J., Healing D., Hutchison J. G. Characteristics of some co-trimoxazole-resistant Enterobacteriaceae from infected patients. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Dec;25(12):1086–1088. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.12.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushby S. R. Sensitivity testing with trimethorpim-sulphamethoxazole. Med J Aust. 1973 Jun 30;1(2 Suppl):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Burchall J. J. Reversal of the antimicrobial activity of trimethoprim by thymidine in commercially prepared media. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):812–817. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.812-817.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubadejo O. A., Maskell R. M. Thymine-requiring mutants of Proteus mirabilis selected by co-trimoxazole in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Aug;77(2):533–535. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-2-533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney R. J., Smith J. T. Joint trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole resistance in bacteria infected with R factors. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):13–19. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


