Abstract
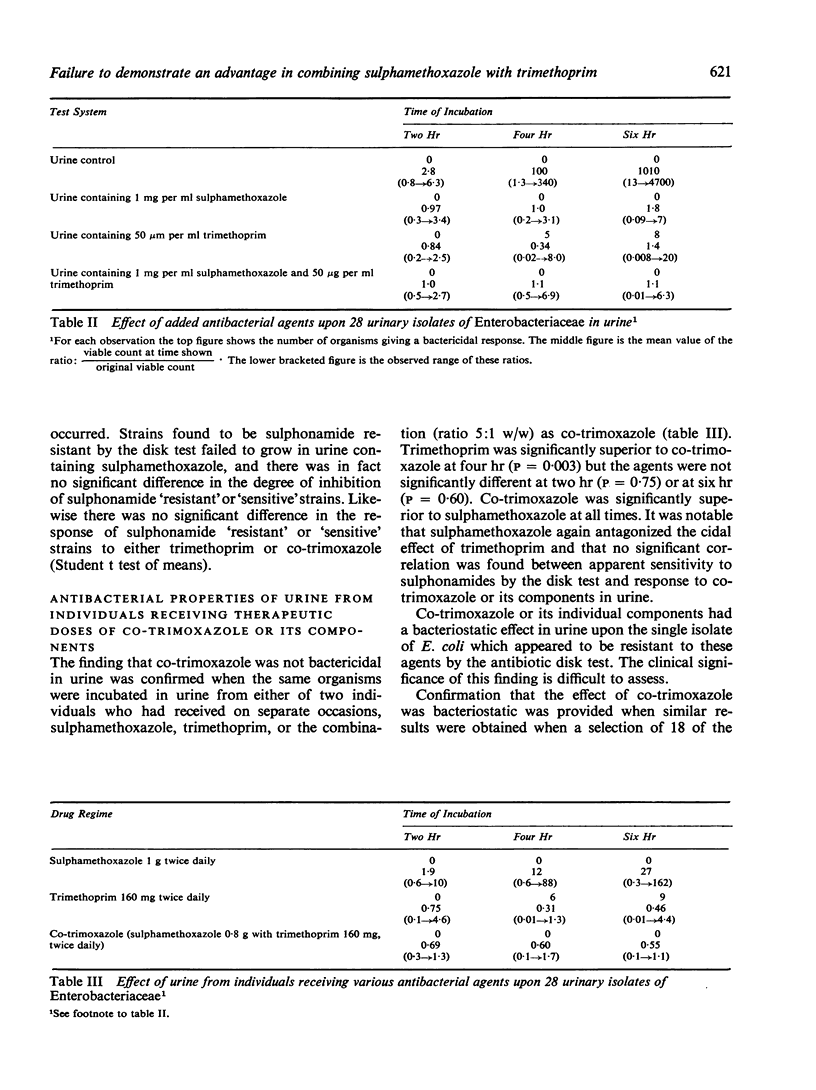
Co-trimoxazole was found to have a predominantly bacteriostatic effect upon 28 urinary isolates of Enterobacteriaceae in nutrient broth and was never bactericidal in artificially infected urine. The components of co-trimoxazole were tested individually and trimethoprim was found to be at least as effective as co-trimoxazole in nutrient broth and in urine. Trimethoprim alone produced some bactericidal effect in urine but this was antagonized by sulphamethoxazole.
Laboratory tests for evaluating these drugs may give a misleading impression of their activity in vivo. Further clinical comparisons should therefore be made between trimethoprim and cotrimoxazole to determine when trimethoprim should be used in preference to the combination.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brumfitt W., Pursell R. Double-blind trial to compare ampicillin, cephalexin, co-trimoxazole, and trimethoprim in treatment of urinary infection. Br Med J. 1972 Jun 17;2(5815):673–676. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5815.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoigné R., Müller U., Schneider H. R. Bactrim Roche, ein Kombinationspräparat von Sulfamethoxazol und Trimethoprim. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1969 Oct 18;99(42):1511–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küchler R., Koch U. J. The in vitro demonstration of the efficacy of trimethoprim as an antibacterial agent in a comparative bacteriological study of the effects of trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole and the combination trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Chemotherapy. 1973;18(4):242–252. doi: 10.1159/000221268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Anderson J. D., Lewis E. L., Gillespie W. A. Comparative efficacy of sulphonamide and co-trimoxazole. Lancet. 1973 Sep 1;2(7827):509–509. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. L., Anderson J. D., Lacey R. W. A reappraisal of the antibacterial action of cotrimoxazole in vitro. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Feb;27(2):87–91. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Faiers M. C., Pursell R. E., Brumfitt W. Trimethoprim--sulphamethoxazole: comparative study in urinary infection in hospital. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 1;1(5643):541–544. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5643.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


