Abstract
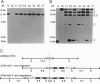
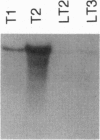
Tetrahymena thermophila has been transformed to paromomycin-resistant phenotypes by microinjection of an aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (neo) gene under the control of the T. thermophila histone H4-I promoter. This chimeric neo gene, by itself or on a vector containing a rRNA-encoding DNA (rDNA) origin of replication, transforms T. thermophila. In cells transformed with the rDNA origin vector, the neo gene is usually found integrated into the endogenous rDNA molecules and is present in high copy number. In transformants obtained by microinjecting only the linear chimeric gene, the neo gene is found to have replaced the histone H4-I gene or is found integrated into the 5' flanking region of the H4-I gene. The relative transcript levels of the neo gene in T. thermophila transformed by the linear chimeric gene are much higher than in cells transformed with the vector. The neo gene provides an effective selectable marker for transformation of T. thermophila.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannon G. A., Bowen J. K., Yao M. C., Gorovsky M. A. Tetrahymena H4 genes: structure, evolution and organization in macro- and micronuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1961–1975. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Ludwig G., Auerswald E. A., Reiss B., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Hanawalt P. C. Repair of damaged DNA in a eucaryotic cell: Tetrahymena pyriformis. Science. 1967 Nov 3;158(3801):663–664. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3801.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Navas P. Transformation of Tetrahymena thermophila by electroporation and parameters effecting cell survival. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Feb;174(2):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90322-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Sadler L. A. Characterization of the promoter region of Tetrahymena genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):323–329. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. Gene targeting. How efficient can you get? Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):109–109. doi: 10.1038/348109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover R. K., Brunk C. F. Macronuclear DNA molecules of Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):900–905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz A., Beverley S. M. Gene replacement in parasitic protozoa. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):171–173. doi: 10.1038/348171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaertig J., Gorovsky M. A. Efficient mass transformation of Tetrahymena thermophila by electroporation of conjugants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9196–9200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Cech T. R. DNA cleavage catalysed by the ribozyme from Tetrahymena. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):405–409. doi: 10.1038/344405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Gorovsky M. A. An unusual genetic code in nuclear genes of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2452–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. D., Blackburn E. H., Yaeger P. C., Orias E. Control of rDNA replication in Tetrahymena involves a cis-acting upstream repeat of a promoter element. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90445-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martindale D. W. Codon usage in Tetrahymena and other ciliates. J Protozool. 1989 Jan-Feb;36(1):29–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb02679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield S. P., Kindle K. L. Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a C. reinhardtii gene as the selectable marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2087–2091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. A., Orias E. Further evidence for lack of gene expression in the Tetrahymena micronucleus. Genetics. 1981 Aug;98(4):747–762. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.4.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orias E., Bruns P. J. Induction and isolation of mutants in Tetrahymena. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:247–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B., Rudman B. M., Barnett A. J. Deviation from the universal code shown by the gene for surface protein 51A in Paramecium. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):188–190. doi: 10.1038/314188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stargell L. A., Karrer K. M., Gorovsky M. A. Transcriptional regulation of gene expression in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6637–6639. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondravi M. M., Yao M. C. Transformation of Tetrahymena thermophila by microinjection of ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Yao C. H. Transformation of Tetrahymena to cycloheximide resistance with a ribosomal protein gene through sequence replacement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9493–9497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Zhu S. G., Yao C. H. Gene amplification in Tetrahymena thermophila: formation of extrachromosomal palindromic genes coding for rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Blackburn E. H. Transformation of Tetrahymena thermophila with a mutated circular ribosomal DNA plasmid vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8487–8491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Bradley J. D., Attardi L. D., Blackburn E. H. In vivo alteration of telomere sequences and senescence caused by mutated Tetrahymena telomerase RNAs. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):126–132. doi: 10.1038/344126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Hasson M., Blackburn E. H. Circular ribosomal DNA plasmids transform Tetrahymena thermophila by homologous recombination with endogenous macronuclear ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5151–5155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]