Abstract
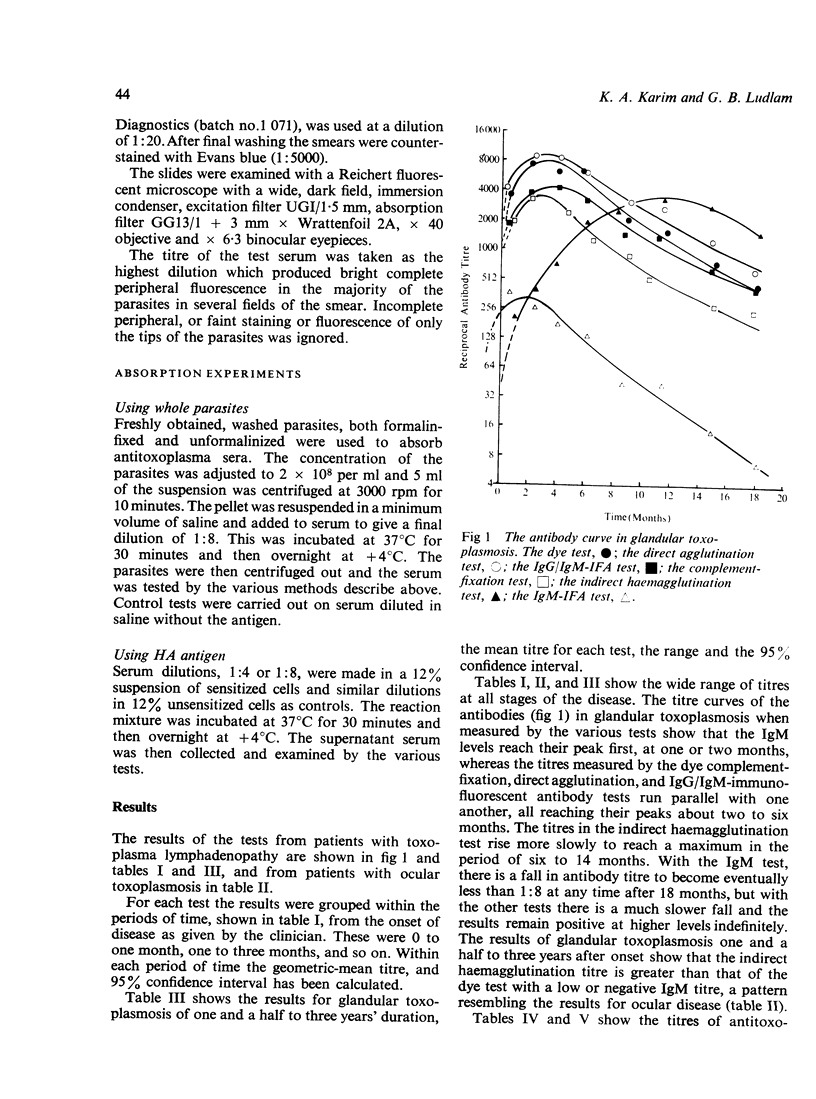
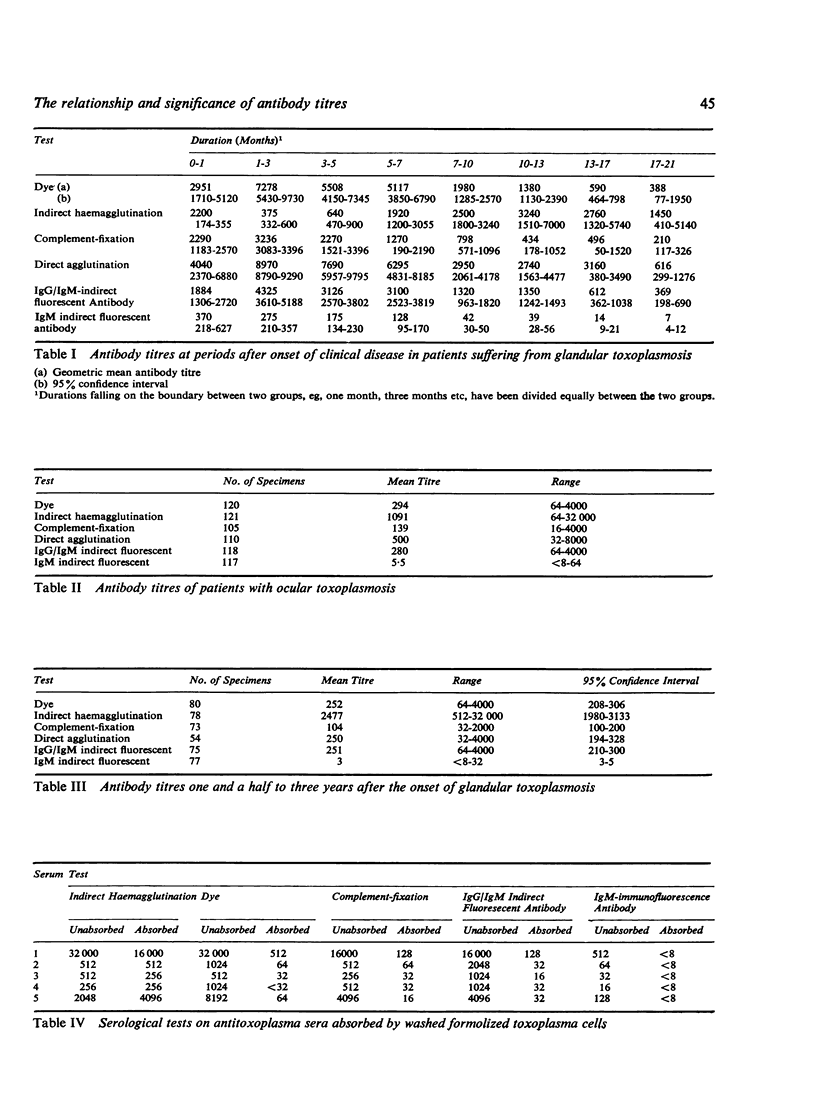
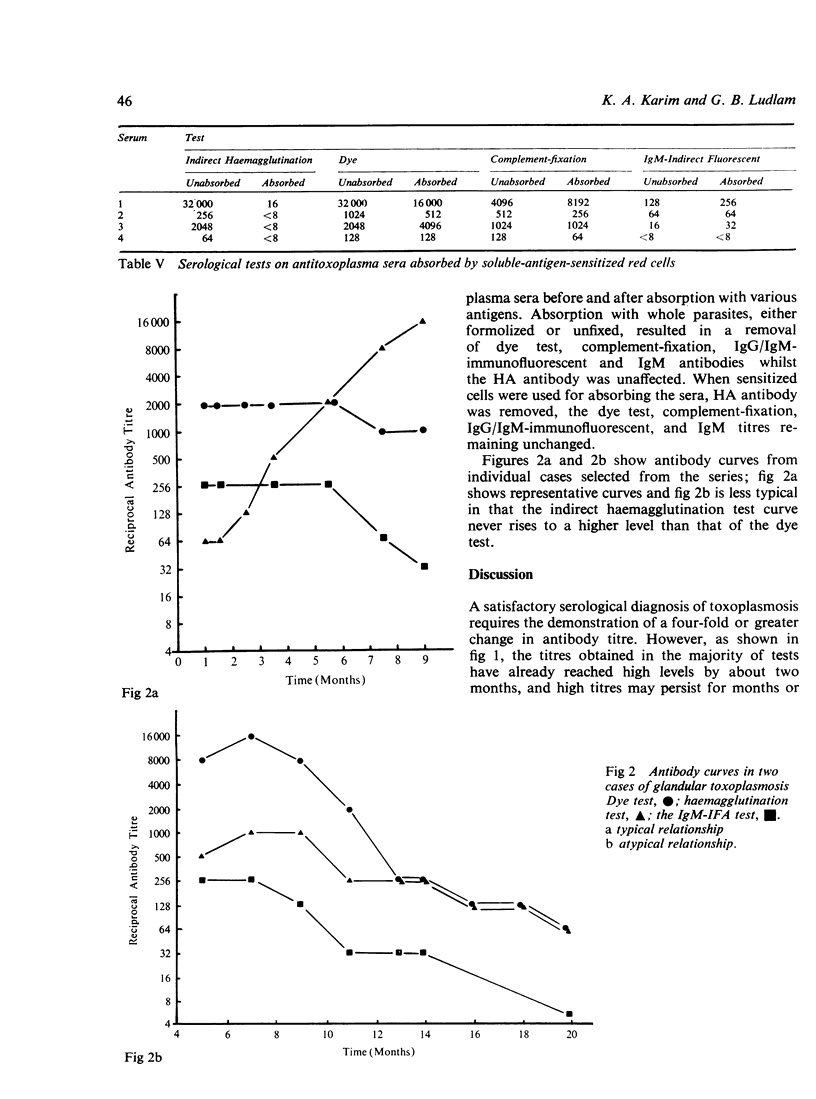
Three types of antibody curve have been demonstrated by testing sera during the course of acquired toxoplasmosis by six different techniques. These three types are due to cell-wall antibody, (demonstrated by four of the techniques), to antibody to soluble antigen, and to IgM antibody to the cell wall. These findings have been supported by absorption experiments. A scheme is presented for testing single sera by two or three different tests to indicate the stage and duration of the infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEATTIE C. P. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of toxoplasmosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1957 Mar;51(2):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(57)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEVERLEY J. K. A., BEATTIE C. P. Standardization of the dye test for toxoplasmosis. J Clin Pathol. 1952 Nov;5(4):350–353. doi: 10.1136/jcp.5.4.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADSTREET C. M., TAYLOR C. E. Technique of complementfixation test applicable to the diagnosis of virus diseases. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1962 May;21:96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHORDI A., WALLS K. W., KAGAN I. G. STUDIES ON THE SPECIFICITY OF THE INDIRECT HEMAGGLUTINATION TEST FOR TOXOPLASMOSIS. J Immunol. 1964 Dec;93:1024–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessum B. S. Examination of sera for toxoplasmosis antibody using immunofluorescence. J Med Lab Technol. 1970 Jan;27(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couzineau P., Baufine-Ducrocq H. Agglutination directe des toxoplasmes. Préparation de l'antigène et examen de 400 sérums. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1970;28(5):411–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dropsy G., Carquin J., Croix J. C. Techniques de mise en évidence des anticorps de type IgM dans les infections congénitales. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1971;29(1):67–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDMAN H. A., MILLER L. T. Serological study of toxoplasmosis prevalence. Am J Hyg. 1956 Nov;64(3):320–335. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLECK D. G. Serological tests for toxoplasmosis. Nature. 1961 Jun 10;190:1018–1019. doi: 10.1038/1901018b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER S. INDIRECT FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE IN THE SEROLOGY OF TOXOPLASMA GONDII. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Mar;18:193–199. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENKEL J. K., JACOBS L. Ocular toxoplasmosis; pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1958 Feb;59(2):260–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENKEL J. K., WEBER R. W., LUNDE M. N. Acute toxoplasmosis. Effective treatment with pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, leucovorin calcium, and yeast. JAMA. 1960 Jul 30;173:1471–1476. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03020310059017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON J. D., TURK J. L. Direct agglutination test for Toxoplasma gondii. Lancet. 1959 Dec 12;2(7111):1068–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91535-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild G. A., Greenwald P., Decker H. A. An evaluation of the indirect hemagglutination test as a serologic test for toxoplasmosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 May;16(3):278–283. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN M. Staining toxoplasma gondii with fluorescein-labelled antibody. II. A new serologic test for antibodies to Toxoplasma based upon inhibition of specific staining. J Exp Med. 1957 Jun 1;105(6):557–573. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.6.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS L., LUNDE M. N. A hemagglutination test for toxoplasmosis. J Parasitol. 1957 Jun;43(3):308–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennis F. A simplified haemagglutination test for toxoplasmosis using pyruvic aldehyde treated cells. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):317–322. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAYHOE D. E., JACOBS L., BEYE H. K., McCULLOUGH N. B. Acquired toxoplasmosis; observations on two parasitologically proved cases treated with pyrimethamine and triple sulfonamides. N Engl J Med. 1957 Dec 26;257(26):1247–1254. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195712262572601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim K. A., Ludlam G. B. Haemagglutination test for toxoplasmosis. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Feb;26(2):162–162. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.2.162-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS W. P., KESSEL J. F. Hemagglutination in the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis and amebiasis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1961 Oct;66:471–476. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1961.00960010473006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunde M. N., Jacobs L. Differences in Toxoplasma dye test and hemagglutination antibodies shown by antigen fractionation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 Jan;16(1):26–30. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL R. G., GREEN C. A. The haemagglutination test for toxoplasma antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Jul;13:331–335. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.4.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Brown H. W. The serologic diagnosis of parasitic infections in medical practice. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Nov;71(5):983–992. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-71-5-983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. II. Prevalence and significance in acquired cases. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):855–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEEN E., KASS E. A new toxoplasma antigen for complement fixation test. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1951;28(1):36–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1951.tb04999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THALHAMMER O. Uber ein neues haltbares Antigen für KBR und Hauttest auf Toxoplasmose. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1956 Mar;104(3):110–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann E., Stagno S. Demonstración de anticuerpos IgM en casos de toxoplasmosis aguda y crónica. Bol Chil Parasitol. 1971 Jan-Jun;26(1):55–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn H., Williams H. A stable haemagglutinating antigen for detecting toxoplasma antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Sep;25(9):762–767. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.9.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tönder O., Closs O., Digranes A. Comparison of the indirect haemagglutination and dye test for detection of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(1):63–68. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODS A. C., JACOBS L., WOOD R. M., COOK M. K. A study of the role of toxoplasmosis in adult chorioretinitis. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1954 Mar-Apr;58(2):172–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


