Abstract
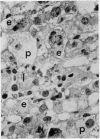
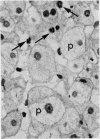
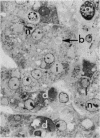
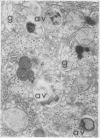
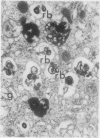
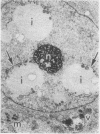
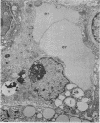
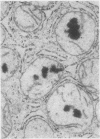
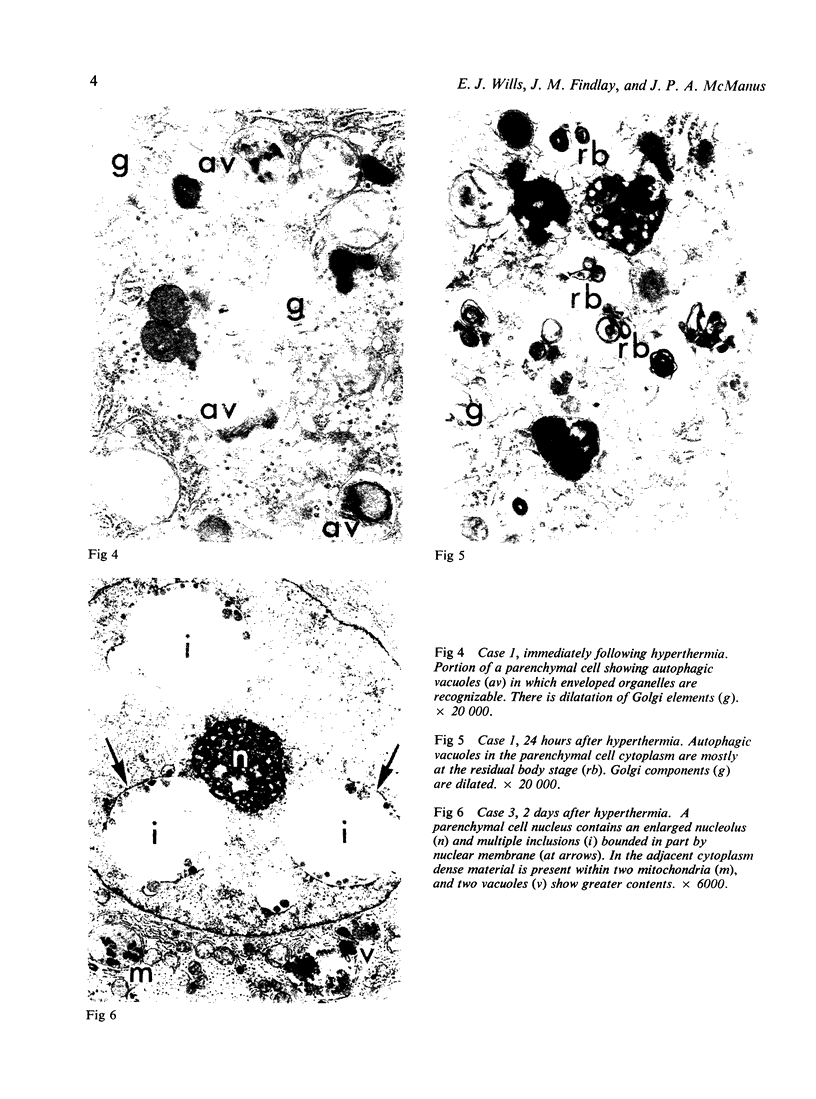
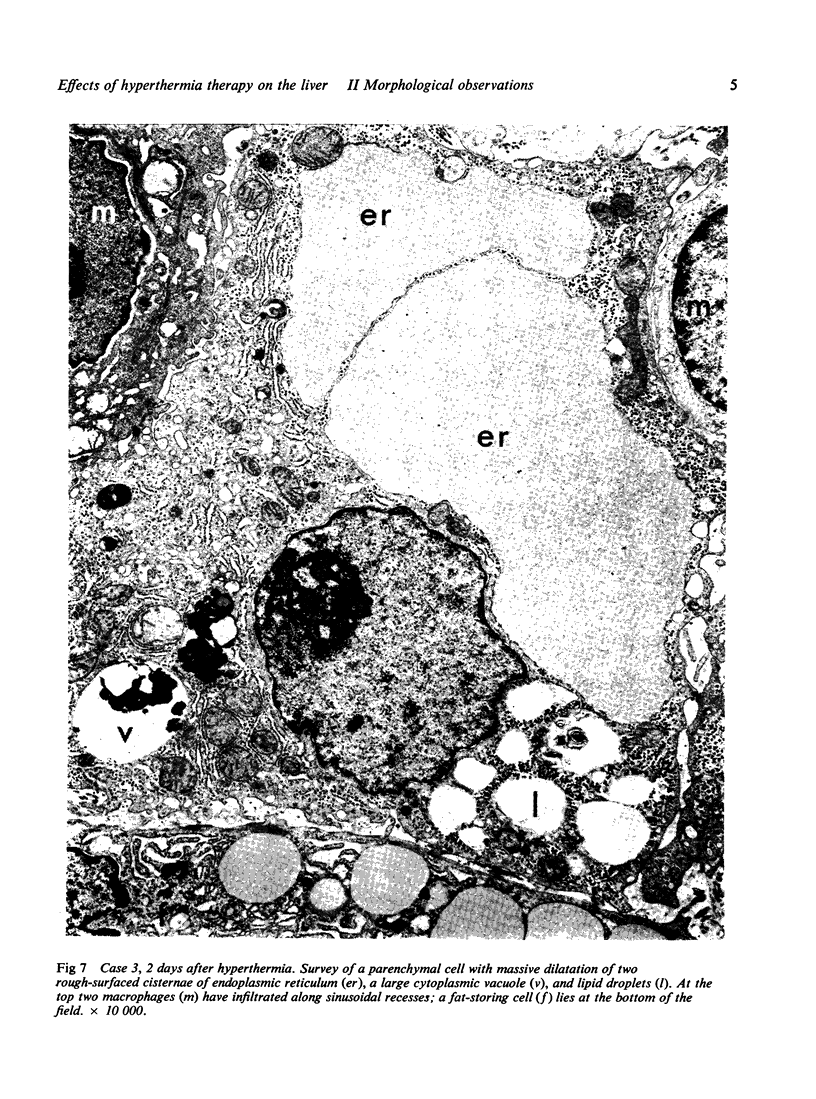
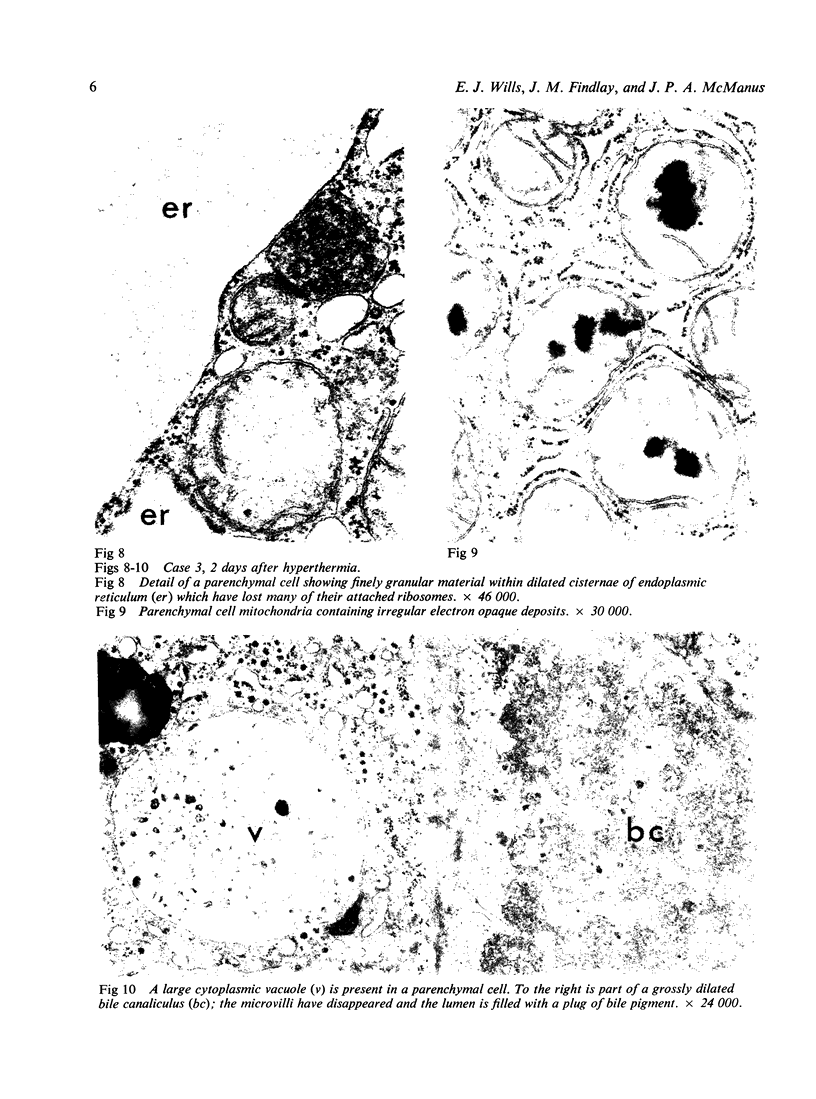
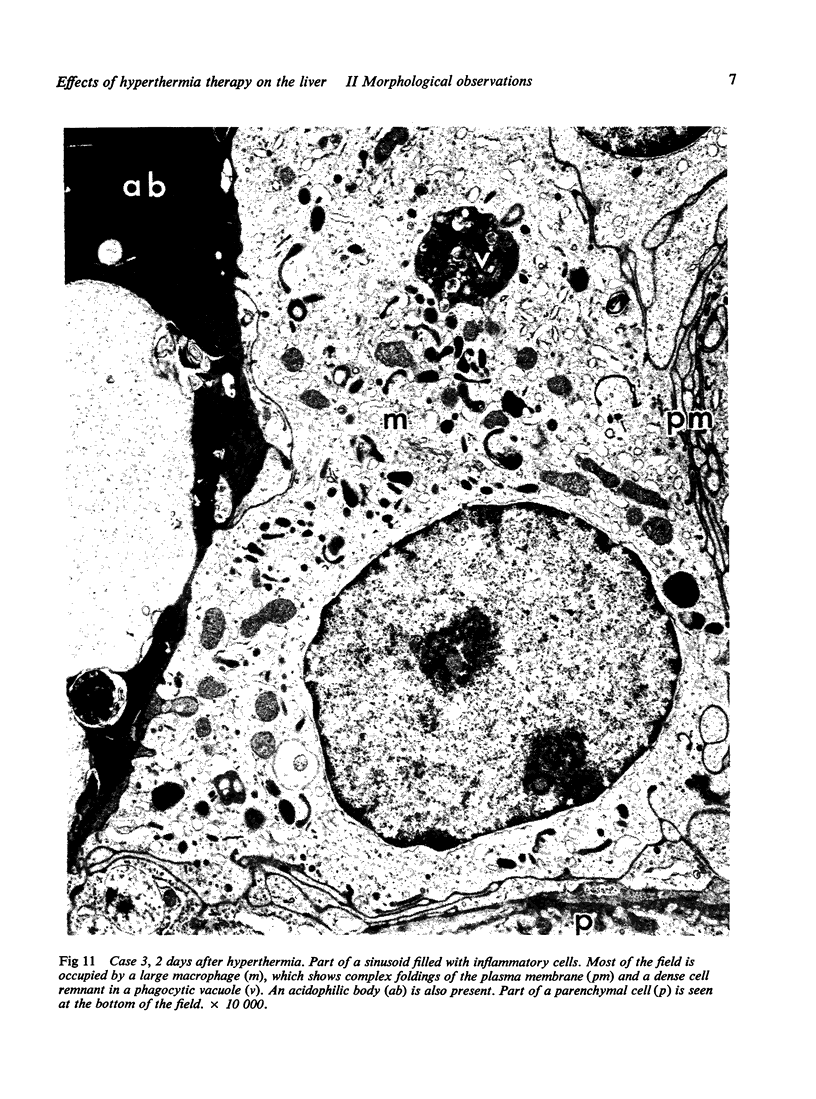
Liver biopsy specimens obtained from three patients during treatment of advanced malignant disease by exogenous hyperthermia were studied by light and electron microscopy. In two patients the parenchymal cells showed either slight swelling or nuclear alterations by light microscopy and, at the fine structural level, large numbers of autophagic vacuoles, dilatation of Golgi elements and endoplasmic reticulum, and large cytoplasmic vacuoles. Similar changes, but in much more severe form together with parenchymal cell necrosis and cholestasis, were seen in the liver of case 3, who developed jaundice 24 hours after hyperthermia. The findings are discussed in relation to earlier accounts of liver changes following hyperthermia, and the functional implications are considered.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIAVA C. STUDIES ON CHOLESTASIS. THE FINE STRUCTURE AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HEPATOCELLULAR AND CANALICULAR BILE PIGMENT. Lab Invest. 1964 Sep;13:1099–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi L., Ohnacker H., Beck K., Zimmerli-Ning M. Liver damage in heatstroke and its regression. A biopsy study. Hum Pathol. 1972 Jun;3(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(72)80077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David H., Uerlings I., Grupe M. Strukturveränderungen von Leberzellen bei supranormalen Temperaturen. Exp Pathol (Jena) 1971;5(1):2–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enat R., Buschmann R. J., Chomet B. Ultrastructure of cytoplasmic hyaline inclusions in a case of human hepatocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1973 Nov;65(5):802–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORE I., ISAACSON N. H. The pathology of hyperpyrexia; observations at autopsy in 17 cases of fever therapy. Am J Pathol. 1949 Sep;25(5):1029–1059. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinsmann W. H., Ericsson J. L. Observations on the subcellular organization of hepatic parenchymal cells. II. Evolution of reversible alterations induced by hypoxia. Lab Invest. 1966 Apr;15(4):762–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew M., Bersohn I., Seftel H., Kent G. Liver damage in heatstroke. Am J Med. 1970 Aug;49(2):192–202. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. M. Toxic Hepatitis in Fever Therapy. Can Med Assoc J. 1944 Nov;51(5):445–449. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibolet S., Coll R., Gilat T., Sohar E. Heatstroke: its clinical picture and mechanism in 36 cases. Q J Med. 1967 Oct;36(144):525–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner J. W., Phillips M. J., Miyai K. Ultrastructural and subcellular pathology of the liver. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1964;3:65–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills E. J. Acute infective hepatitis. Fine structural and cytochemical alterations in human liver. Arch Pathol. 1968 Aug;86(2):184–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]