Abstract
FHY3 and FAR1 are positively acting transcription factors that directly regulate expression of a number of target genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Here, we looked at the regulation of one specific target gene, ELF4. We demonstrate that the action of FHY3 and FAR1 in upregulation of ELF4 is light dependent. Furthermore, although FHY3 and FAR1 have been exclusively characterized as components of the phytochrome A signaling pathway because of their importance in regulating expression of phyA nuclear importers, we show that, as transcription factors in their own right, FHY3 and FAR1 act downstream of light stable phytochromes, phyB, phyD, and phyE. We demonstrate that light stable phytochrome acts in a red/far-red reversible manner to regulate the level of FHY3 protein. We also observed that ELF4 shows specific FHY3 and FAR1-mediated light induction in the evening and we show that regulation by light stable phytochromes at this time is important as it allows the plant to maintain normal ELF4 expression beyond dusk when the day length shortens, something which would not be possible through light labile phytochrome action. Without FHY3 and FAR1, ELF4 expression falls rapidly at dusk and in short days this results in an early drop in ELF4 expression, accompanied by a de-repression of an ELF4 target gene later in the night. Our results, therefore, demonstrate an important role for FHY3 and FAR1 as mediators of light stable phytochrome signaling.
Keywords: light, phytochrome, Arabidopsis, signal transduction, transcription
Introduction
Responses to light are one of the most important aspects of a plant’s adaptation to its environment. Germination, establishment, and the growth patterns throughout the life history of a plant are optimized to ensure the best possible acquisition of light energy for photosynthesis. Plants possess a wide range of photoreceptors in order to gather information about the light environment but among the most important are the red light and far red light-absorbing phytochromes.
Phytochromes are dimeric proteins, each phytochrome monomer binding a linear tetrapyrrole chromophore (Rockwell et al., 2006). Phytochrome exists in two photo-interconvertible forms, a red light-absorbing Pr form and a far red light-absorbing Pfr form. Conversion to the Pfr form results in nuclear entry and activation of target gene expression (Klose et al., 2015). Five phytochromes exist in Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis), named phytochrome A to phytochrome E (phyA to phyE; Franklin and Quail, 2010). PhyB–phyE are responsible for classical red/far red-reversible phytochrome responses, activated by red and deactivated by far red irradiation. PhyB–phyE Pfr is relatively stable (Sharrock and Clack, 2002) and, indeed, phytochrome B Pfr has been shown to remain active in darkness for up to 12 h following illumination (Hennig et al., 1999). PhyA, in contrast, shows activity in both red and far red and even in blue as Pfr levels sufficient to trigger phyA responses can be formed in all of these wavelengths (Whitelam et al., 1993; Casal et al., 1998). However, phyA is light labile and is rapidly degraded in the Pfr form. Thus, on cessation of illumination, phyA action ceases (Casal et al., 1998). None-the-less, despite this light lability, a significant pool of phyA is maintained in established seedlings where it continues to function throughout the life of the plant (Franklin et al., 2007).
Far-red elongated hypocotyl 3 (FHY3) and far-red-impaired response (FAR1) were originally identified as components of the phytochrome A (phyA) signal transduction pathway. Mutants in FHY3 and FAR1 show impaired inhibition of hypocotyl elongation in far red light (Whitelam et al., 1993; Hudson et al., 1999). The FHY3 and FAR proteins are close homologs and are part of a wider family of proteins showing similarity to mutator-like transposases (Hudson et al., 2003; Lin and Wang, 2004). The two proteins dimerize and function as transcription factors by binding to the FHY3/FAR1 binding sequence (fbs) to positively regulate expression of a number of genes (Wang and Deng, 2002; Lin et al., 2007; Ouyang et al., 2011). Indeed, the role of FHY3 and FAR1 in phyA signaling has been revealed to be due to their positive regulation of expression of the phyA nuclear importers, FHY1 and FHL (Lin et al., 2007). FHY3 and FAR1 act permissively in this respect: loss of either FHY3 or FAR1 results in a loss of target gene expression (Hudson et al., 2003; Li et al., 2011).
Among the FHY3 and FAR1 targets is the central clock gene, ELF4. The fhy3, far1, and fhy3 far1 mutants show dramatically reduced, essentially arrhythmic expression of ELF4 in constant light (Li et al., 2011). FHY3 and FAR1 are, therefore, proposed to be part of the light input pathway to the circadian clock acting downstream of phytochrome. However, although the role of FHY3 and FAR1 in positively regulating ELF4 has been demonstrated, neither a light- nor phytochrome-specific role has yet been proven. This is particularly pertinent as FHY3 has been shown to be involved in a wide range of processes, not necessarily all light or phytochrome dependent (Huang et al., 2012; Wang and Wang, 2015; Wang et al., 2016).
We sought to examine the light dependency of FHY3 and FAR1 in the regulation of ELF4 expression, originally aiming to confirm their importance in light input to the circadian clock. We demonstrated that FHY3 and FAR1, indeed, show a light dependent regulation of ELF4 expression. Significantly, in this respect, we observed a previously unknown mode of FHY3 and FAR1 action downstream of light stable phytochromes, specifically, phyB, phyD, and phyE. Light stable phytochrome acts in a red/far-red reversible manner to regulate FHY3 protein level. We showed that ELF4 expression is light responsive in the evening and demonstrated an important role for light stable phytochrome at this time in maintaining ELF4 expression beyond dusk when day length is shortened. Without FHY3 and FAR1 action downstream of light stable phytochromes at this time, ELF4 expression drops sharply at dusk. Consistent with this, we observed reduced repression of the ELF4 target gene, PIF4, later in the night in short days in fhy3 far1 mutants. We, therefore, demonstrate that FHY3 and FAR1 are components of light stable phytochrome signaling and propose an argument that this may even be their primary mechanism of action in phytochrome signaling.
Materials and Methods
Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
The fhy3-4 far1-2 double mutant of Arabidopsis is in the No-0 ecotype (Wang and Deng, 2002). Luciferase reporter lines containing ELF4::LUC, mFBS ELF4::LUC, and FHY3::FHY3-LUC/fhy3-4 have been described previously (Li et al., 2011). Phytochrome mutant lines study were phyB-1 (Koornneef et al., 1980), phyB-1 phyD-1 (Devlin et al., 1999), phyB-1 phyE-1 (Devlin et al., 1998).
In all experiments, seeds were sterilized in 30% bleach, 0.02% Triton X-100, sown on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 2% sucrose, then stratified for 3 days in darkness at 4°C before germination. All experiments were carried out at 21°C.
For RT-qPCR analysis of ELF4 response to monochromatic red light, following stratification, seeds were germinated and grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 7 days (equally mixed red and blue light, 100 μmol m–2 s–1). The plates were then transferred to red light at the fluence rates indicated for 4 days. All light used in this assay was provided by red (λ-max 660 nm) and blue (λ-max 450 nm) LEDs within Fytoscope FS 80-RGBIR Mini cabinets (Photon Systems International, Brno, Czech Republic).
For analysis of luciferase bioluminescence and for RT-qPCR analysis of PIF4 expression, plants were germinated and grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 7 days prior to treatment conditions. White light for this and for the treatment during RT-qPCR analysis of PIF4 expression consisted of equally mixed red and blue light, 100 μmol m–2 s–1, provided by LEDs within Fytoscope FS 80-RGBIR Mini cabinets as above.
Light conditions during luciferase bioluminescence imaging experiments were provided within the imaging chamber by a custom-made LED rig providing red light (λ-max 660 nm, 40 μmol m–2 s–1), blue light (λ-max 450 nm, 40 μmol m–2 s–1) or white light consisting of equally mixed red and blue light. Timing of LED illumination within the chamber was controlled by a MLU2 digital timer (RS components, UK). However, EODFR treatment during imaging was carried out manually as described in Wang et al. (2011) using the same light sources. Far red irradiance was 15 μmol m–2 s–1. Seedlings were transferred to and from EODFR treatment under green safelight.
All light measurements were made using a StellarNet EPP2000-HR spectroradiometer.
Luciferase Imaging
Luciferase imaging was carried out using a NightOwl ultra-cooled CCD (charge-coupled device) camera (Berthold Technologies, UK) as described by Wang et al. (2011) except that 1 day prior to commencement of imaging, seedlings were sprayed with a slightly higher concentration (5 mM) of d-luciferin dissolved in 0.01% Triton (1 ml per plate). Data were analyzed by using Winlight image analysis software version 2.17 (Berthold Technologies, UK). All data represent the findings of at least two independent experiments.
RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis
RNA extraction and qRT-PCR were carried out exactly as described previously (Wang et al., 2011). All gene expression values are expressed relative to either an Arabidopsis UBQ10 or IPP2 housekeeping control. All data represent the findings of at least two independent experiments. The following primers were used for qRT-PCR: ELF4, AGTTTCTCGTCGGGCTTTCACG and TAAGCTCTAGTTCCGGCAGCAC; PIF4, TCAGATGCAGCCGATGGAGATG and CGACGGTTGTTGACTTTGCTGTC; UBQ10, AAAGAGATAACAGGAACGGAAACATAGT and GGCCTTGTATAATCCCTGATGAATAAG; IPP2, TCGTGTTCCACGAGGACTCTAC and TCAACTGCACCTTCGATCTTAGC.
Results
The Action of FHY3 and FAR1 in Regulation of ELF4 is Light Dependent and Specific to the Early Part of the Night
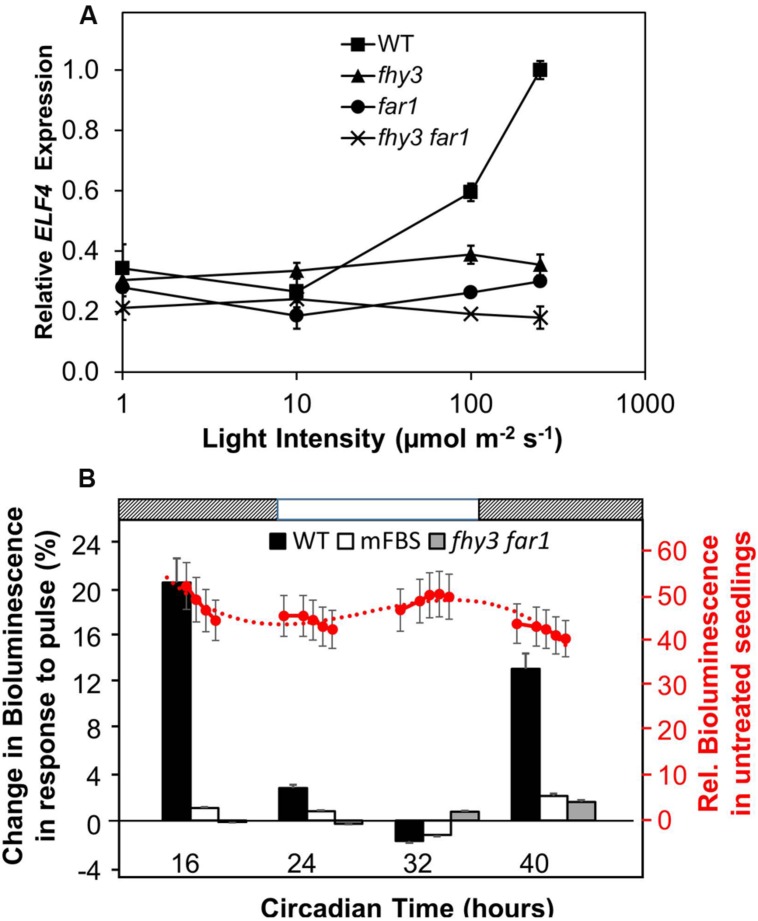
In order to carry out an initial investigation into the light dependency of FHY3 and FAR1 action in the positive regulation of ELF4 expression in established seedlings, fhy3, far1, and fhy3 far1 mutant seedlings were grown in 12 h white light:12 h dark cycles for 1 week before transfer to constant red for a further 4 days at of a range of different intensities. Wild-type (WT) seedlings showed an increase in ELF4 transcript levels with increasing light intensity above 10 μmol m–2 s–1 (Figure 1A). In contrast, ELF4 expression in fhy3, far1, and fhy3 far1 mutant seedlings remained relatively unchanged across the range of light intensities. It is notable, though, that both the fhy3 and far1 monogenic mutants display a slightly greater ELF4 expression than the fhy3 far1 double mutant at light intensities above 10 μmol m–2 s–1 suggesting that some light responsiveness is retained in each of the single mutants. However, ELF4 expression in fhy3 or far1 is still dramatically lower than that in WT at these intensities (Figure 1A), suggesting a synergistic action of both FHY3 and FAR1 is required for full responsiveness in WT. Most significantly, this confirms the light dependence of the action of FHY3 or FAR1 in regulating ELF4 expression.
FIGURE 1.
(A) The action of FHY3 and FAR1 in regulation of ELF4 expression is light dependent. Wild-type (WT), fhy3, far1, and fhy3 far1 mutant seedlings were grown in 12 h white light:12 h dark cycles for 1 week before transfer to constant red light for a 4 days at of a range of different intensities. Mean ELF4 expression relative to IPP2 measured by RT-qPCR for two independent replicates + standard error. (B) FHY3 and FAR1 directly regulate acute light responsive ELF4 expression in the early part of the subjective night. WT and fhy3 far1 seedlings, both expressing ELF4::LUC, as well as WT seedlings expressing an ELF4::LUC construct in which the FHY3/FAR1 binding site was mutated (mFBS), were grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 1 week prior to transfer to constant darkness at dawn (Circadian Time 0). Seedlings were then given a 30 min pulse of 100 μmol m–2 s–1 red light at one of four time points over a circadian cycle. Left hand axis (black labels): percentage increase in bioluminescence recorded 30 min after the pulse at the four time points indicated. Right hand axis (red labels): mean relative bioluminescence of untreated WT seedlings, shown by red circles, and measured at a number of points over the time course to show the background pattern of ELF4 expression. Dotted line represents trend line based on third order polynomial. Light and dark bars above the figure indicate the times of subjective day and night. N = at least 19 seedlings + standard error.
We then examined the response of WT and fhy3 far1 mutant seedlings to red light pulses. As ELF4 is an evening phased clock gene, we examined the effect of red pulses at various times over a 24 period in constant darkness. WT and fhy3 far1 double mutant seedlings expressing the ELF4::LUC transgene were grown in 12 h light:12 h dark cycles for 1 week prior to transfer to constant darkness at dawn (Circadian Time 0, CT 0). Seedlings were then given a 30 min pulse of 100 μmol m–2 s–1 red light at one of four time points over a circadian cycle and induction of ELF4::LUC bioluminescence was recorded 30 min after the pulse. WT seedlings showed a strong induction of bioluminescence at CT 16 and 40, just after the subjective evening peaks of ELF4 expression in constant darkness (Figure 1B). However, WT seedlings showed only minimal response at CT 24, corresponding to the minimum of ELF4 expression at subjective dawn; and no response at CT 32, corresponding to the time at which ELF4 expression is rising in the constant dark control. fhy3 far1 seedlings by contrast showed little or no induction of ELF4 expression at any of the time points tested (Figure 1B), demonstrating that FHY3 and FAR1 act downstream of red light photoreceptors in a time-of-day specific manner to promote expression of ELF4. In order to confirm the fact that FHY3 and FAR1 act in this way as a result of direct transcriptional regulation of ELF4 expression via the fbs, we also examined responses in an ELF4::LUC construct in which the fbs sequences were mutated (mFBS; Li et al., 2011). The mFBS line also showed little or no induction of ELF4 expression at any of the time points tested (Figure 1B). Thus, FHY3 and FAR1 act downstream of red light photoreceptors just after subjective dusk to upregulate ELF4 expression via the fbs.
FHY3 and FAR1 Buffer the Pattern of ELF4 Expression Against Variation in Day Length
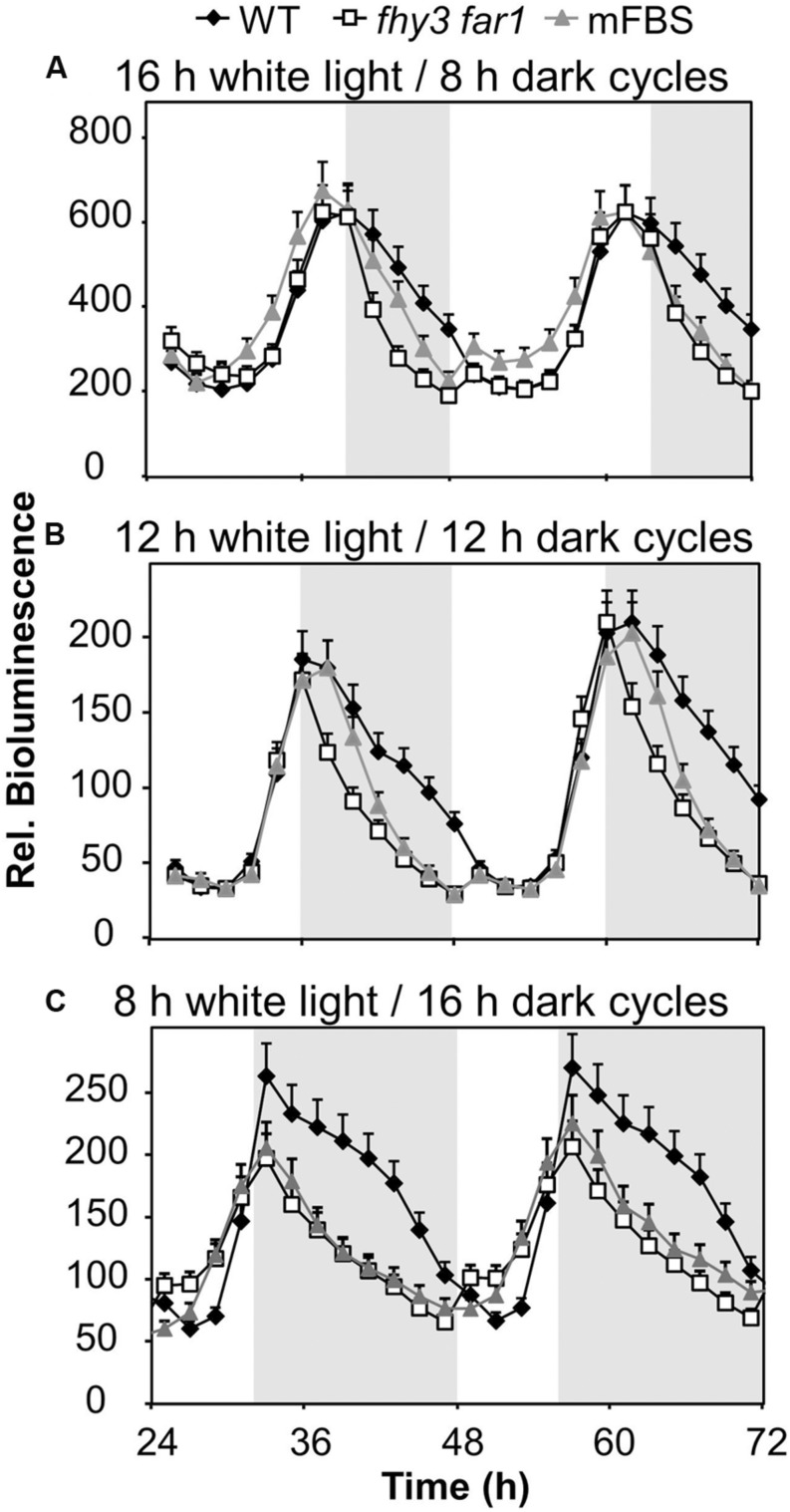
We proposed that a strong positive regulation of the evening-phased gene, ELF4, by light dependent transcription factors, FHY3 and FAR1, around dusk would afford a mechanism by which the pattern of ELF4 expression could adapt to day length as the time of dusk shifts with the seasons. As such, later dusk could be tracked courtesy of continued light input to the system which would maintain the ELF4 peak for a longer duration and, therefore, allow the circadian clock to adapt to different day lengths. We therefore examined the pattern of expression from an ELF4::LUC construct in a range of day lengths in WT and in double mutant seedlings lacking FHY3 and FAR1. As expected, the peak of ELF4 expression in WT seedlings closely followed the time of dusk (Figure 2). However, contrary to our predictions, the ELF4 peak also faithfully tracked dusk in the fhy3 far1 mutants (Figure 2) demonstrating that FHY3 and FAR1 were not involved in this aspect of light input to the clock. Significantly, though, while the WT peak remained roughly sinusoidal in all day lengths, we observed that the peak of ELF4 expression in the double mutant showed a shark’s tooth expression pattern with a sharp drop immediately at dusk which becomes increasingly evident in shorter day lengths (Figure 2). Thus, rather than allowing the tracking of dusk, FHY3 and FAR1 appear to buffer the pattern of ELF4 expression just following dusk against variation in day length.
FIGURE 2.
ELF4 expression in fhy3 far1 mutant seedlings is not buffered against changes in day length. WT and fhy3 far1 seedlings, both expressing ELF4::LUC, as well as WT seedlings expressing an ELF4::LUC construct in which the FHY3/FAR1 binding site was mutated (mFBS), were grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 1 week before either (A) transfer to long days (16 h white light/8 h dark cycles); (B) maintenance in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles; or (C) transfer to short days (8 h white light/16 h dark cycles). Values shown represent mean bioluminescence normalized to WT values at time zero of at least 17 seedlings + standard error.
As previously, in order to confirm that the effects of FHY3 and FAR1 here were mediated as a result of direct transcriptional regulation of ELF4 expression, we also examined the response pattern of the (mFBS line). The mFBS line behaved in the same way as the fhy3 far1 double mutants line in that ELF4 expression dropped sharply following dusk, confirming that FHY3 and FAR1 act directly on the ELF4 promoter in this buffering mechanism (Figure 2).
The Role of FHY3 and FAR1 in Buffering the Pattern of ELF4 Expression is Red Light Dependent and is Downstream of Light Stable Phytochrome Pfr
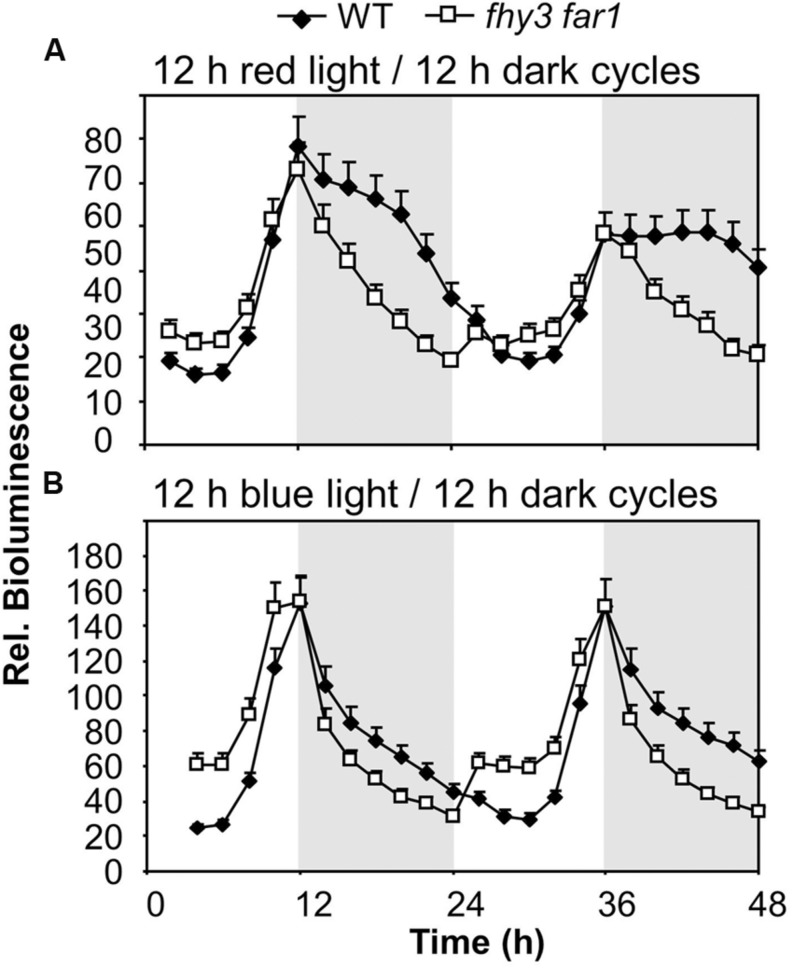
To determine whether the role of FHY3 and FAR1 in buffering the pattern of ELF4 expression was red light dependent we examined whether the phenomenon was observed in both red/dark cycles and blue/dark cycles. Under 12 h red/12 h dark cycles we observed the same sinusoidal shape to the ELF4 expression peak in WT seedlings as was observed in white light/dark cycles, with a peak of expression at dusk. The fhy3 far1 double mutant seedlings also displayed the same pattern of ELF4 expression as they had shown in white light/dark cycles, with a sharp drop in ELF4 expression immediately at dusk (Figure 3A). However, under 12 h blue/12 h dark cycles, both WT and fhy3 far1 double mutant seedlings showed a sharp drop in ELF4 expression immediately at dusk. In blue/dark cycles the WT exactly phenocopied the fhy3 far1 double mutant suggesting that the buffering of the ELF4 peak by FHY3 and FAR1 is dependent on red light (Figure 3B).
FIGURE 3.
Maintenance of the ELF4 expression peak beyond dusk in WT seedlings is observed following red light but not blue light. WT and fhy3 far1 seedlings, both expressing ELF4::LUC were grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 1 week before transfer to either (A) 12 h red light/12 h dark cycles; or (B) 12 h blue light/12 h dark cycles. Values shown represent mean bioluminescence normalized to WT values at time zero of at least 19 seedlings + standard error.
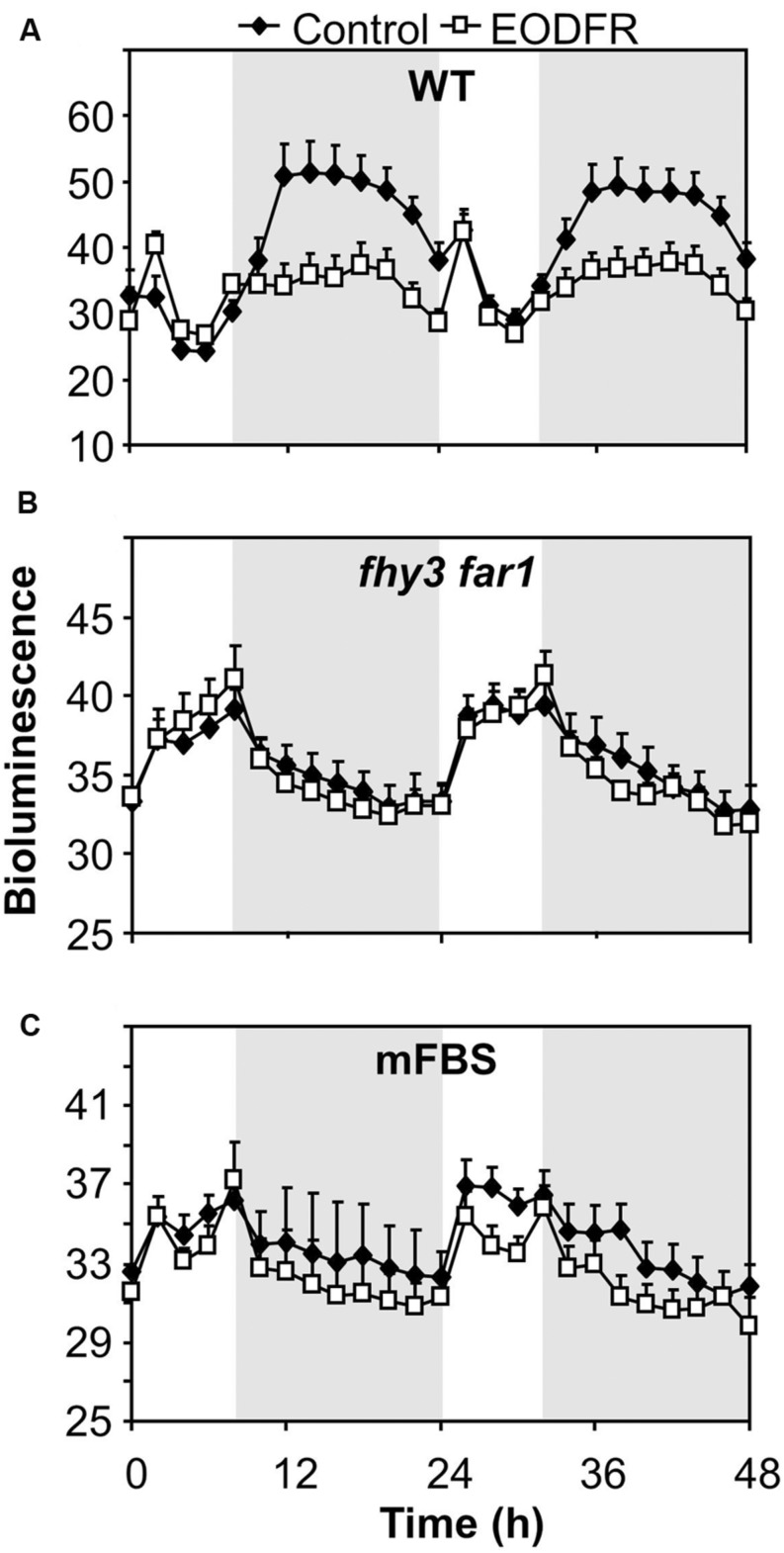
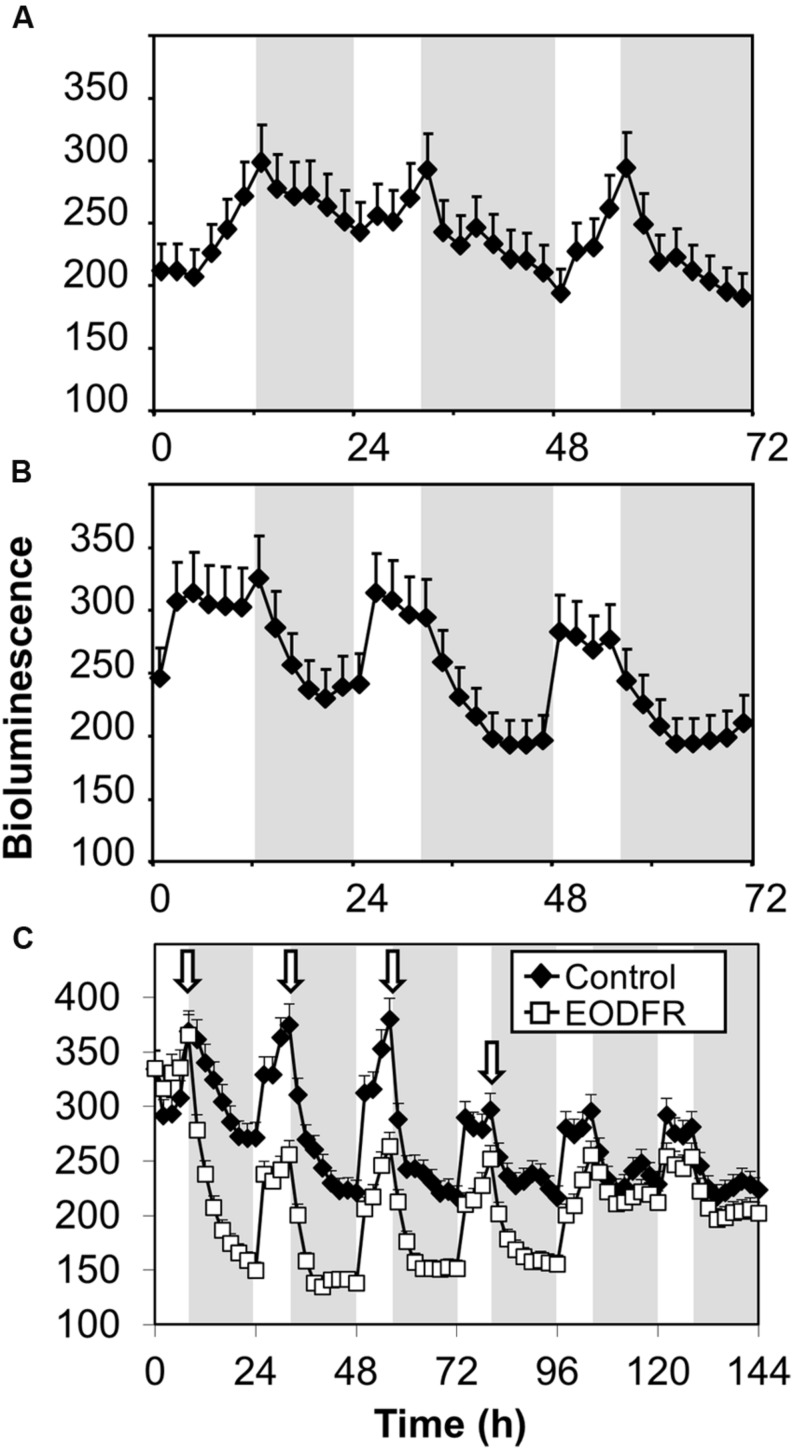
The fact that the action of FHY3 and FAR1 on ELF4 expression is dependent on red light suggests a role for phytochrome. However, FHY3 and FAR1 maintain the ELF4 peak beyond dusk in WT seedlings meaning that, during the key period when FHY3 and FAR1 are required, light is not incident on the seedlings. Instead, the action of FHY3 and FAR1 appears to follow a period of red light. Such a phenomenon more-specifically suggests the action of stable phytochrome Pfr, implicating phyB, C, D, or E. In order to test the possible role of FHY3 and FAR1 in light-stable phyB-E signaling, an End of Day Far red light (EODFR) experiment was performed. An EODFR pulse will have the effect of severely depleting the pool of stable Pfr at dusk. ELF4::LUC expression was monitored in WT and fhy3 far1 mutant plants grown in 8 h red light/16 h dark cycles with or without an EODFR pulse. WT seedlings treated with an EODFR pulse showed a loss of the sinusoidal pattern of the ELF4 expression peak (Figure 4A), such as was seen previously in fhy3 far1 double mutant seedlings (Figure 2C). Upon EODFR treatment, ELF4 expression in WT seedlings stopped rising and plateaued at a much lower level through the subsequent night. Conversely, EODFR treatment had no effect on fhy3 far1 double mutants or on ELF4 expressed from the mFBS line, confirming a constitutive lack of stable Pfr signaling in these lines (Figures 4B,C).
FIGURE 4.
Maintenance of the ELF4 expression peak beyond dusk in WT seedlings is red/far red reversible. (A) WT seedlings expressing ELF4::LUC, (B) fhy3 far1 seedlings expressing ELF4::LUC, and (C) WT seedlings expressing an ELF4::LUC construct in which the FHY3/FAR1 binding site was mutated (mFBS), were grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 1 week before transfer to short days (8 h white light/16 h dark cycles). Seedlings were either treated with a 15 min end of day far red pulse (EODFR) or maintained in short days without EODFR treatment (Control). Values shown represent mean relative bioluminescence of at least 15 seedlings + standard error.
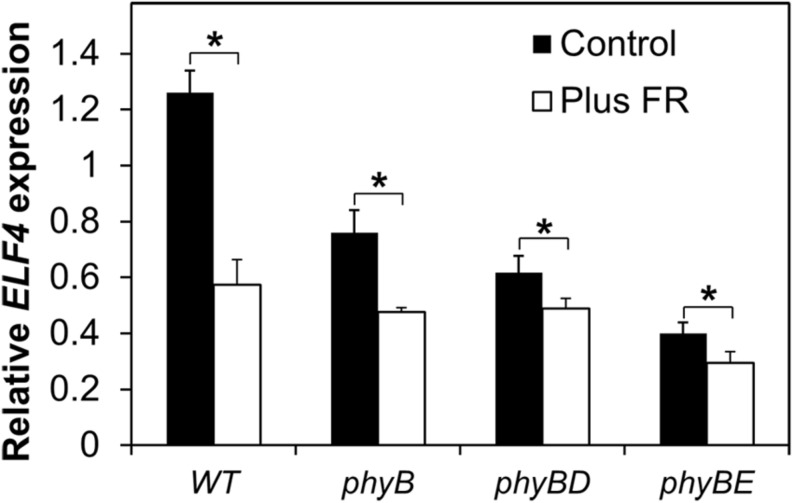
In order to examine which phytochrome is responsible for regulation of ELF4 expression following dusk, we examined a range of phytochrome deficient mutants. WT and phytochrome deficient mutants were grown in 8 h red light/16 h dark cycles with or without an EODFR treatment. Measurement of ELF4 expression by qPCR at a single time-point 4 h after dusk was used to examine effectiveness of an EODFR pulse. As previously (Figure 4), WT seedlings showed a strong reduction in ELF4 expression as a result of an EODFR pulse (Figure 5). Untreated phyB mutants showed lower ELF4 expression than WT at this point and, crucially, phyB mutants showed a greatly reduced response to EODFR indicating the involvement of phyB in this response (Figure 5). None-the-less, phyB mutants still showed a significant EODFR response indicating the additional action of other light stable phytochromes. The phyB phyD double mutant seedlings showed a further drop in ELF4 transcript compared to the phyB monogenic mutant and, significantly, showed a further reduced response to EODFR, implying some redundancy between phyB and phyD in the regulation of ELF4 expression. The phyB phyE double mutant showed a yet more dramatic reduction in ELF4 expression compared to phyB and also showed a reduced response to EODFR (Figure 5), together suggesting that phyB, phyD, and phyE all act following dusk to positively regulate ELF4 expression, allowing the maintenance of a sinusoidal expression pattern in short days.
FIGURE 5.
Maintenance of the ELF4 expression peak beyond dusk in WT seedlings involves phyB, phyD, and phyE. Seedlings were grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 1 week before transfer to short days (8 h white light/16 h dark cycles). Seedlings were either treated with a 15 min EODFR or maintained in short days without EODFR treatment (Control). Expression of ELF4 in WT phyB, phyB phyD, and phyB phyE mutant seedlings 4 h following dusk. Values shown represent mean expression of ELF4 relative to WT level at dusk, normalized to IPP2 for minimum two replicates + standard error. (∗p < 0.05 using a heteroscedastic t-test).
Stable Phytochrome Regulates FHY3 Protein Levels
It was previously observed that FHY3 protein levels are regulated by light (Li et al., 2011). No light regulation of FHY3 mRNA was observed by Li et al. (2011), demonstrating that this regulation occurs at the level of the protein itself. We, therefore, examined whether the action of phytochrome in triggering FHY3 activity in our assay could be mediated via a regulation of FHY3 protein levels. Seedlings containing an FHY3::FHY3-LUC construct, expressing an FHY3-LUC fusion protein under the control of the FHY3 promoter (Li et al., 2011) in the background of the fhy3 mutation were used in order to follow FHY3 protein levels.
FHY3::FHY3-LUC seedlings were grown in red/dark or blue/dark cycles. In red/dark cycles of 12 h red/12 h dark then 8 h red/16 h dark, bioluminescence from the FHY3-LUC fusion protein showed an evening-phased peak which gradually declined throughout the night (Figure 6A). In contrast, in blue/dark cycles of 12 h blue/12 h dark then 8 h blue/16 h dark, the evening peak of bioluminescence from the FHY3-LUC fusion protein dropped sharply at dusk reaching a basal level after just 6–8 h (Figure 6B). This pattern follows that of the FHY3 target gene ELF4 in such conditions (Figure 3) and, therefore, strongly supports the proposal that regulation of FHY3 protein levels by light stable phytochrome Pfr is at least partly responsible for the red/far-red reversible regulation of FHY3 activity in our ELF4 assay. It is notable, however, that a pronounced dawn acute induction of bioluminescence from the FHY3-LUC fusion protein was observed in blue/dark cycles, suggesting involvement of a blue light receptor during the day time, though, clearly not following dusk.
FIGURE 6.
Maintenance of FHY3 protein beyond dusk is red light-specific and shows red/far red reversibility. Seedlings of the fhy3 mutant expressing an FHY3::FHY3-LUC translational-fusion reporter construct were grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 1 week before transfer to either (A) red light/dark cycles; (B) blue light/dark cycles; or (C) 8 h white light/16 h dark cycles with a 15 min EODFR or without (Control). Arrows represent times of EODFR treatment. Values shown represent mean relative bioluminescence of at least 20 seedlings + standard error.
If FHY3::FHY3-LUC plants grown in white/dark cycles were treated with an EODFR pulse an immediate sharp drop in bioluminescence from the FHY3-LUC fusion protein followed (Figure 6C). After the first treatment with EODFR, levels fell and were not able to recover fully during the following day. Each subsequent EODFR treatment given over 4 days caused a similar immediate drop in bioluminescence from the FHY3-LUC fusion protein to a basal level. Following two further cycles of white/dark without EODFR treatment, bioluminescence from the FHY3-LUC fusion protein recovered to follow a WT pattern again (Figure 6C). Again, this pattern follows that of the FHY3 target gene ELF4 in these conditions and suggests that light stable phytochrome regulation of FHY3 protein levels is at least partly responsible for the red/far-red reversible regulation of FHY3 activity.
Growth of fhy3 far1 Mutant Seedlings in Short Days Reveals Early Derepression of an ELF4 Target
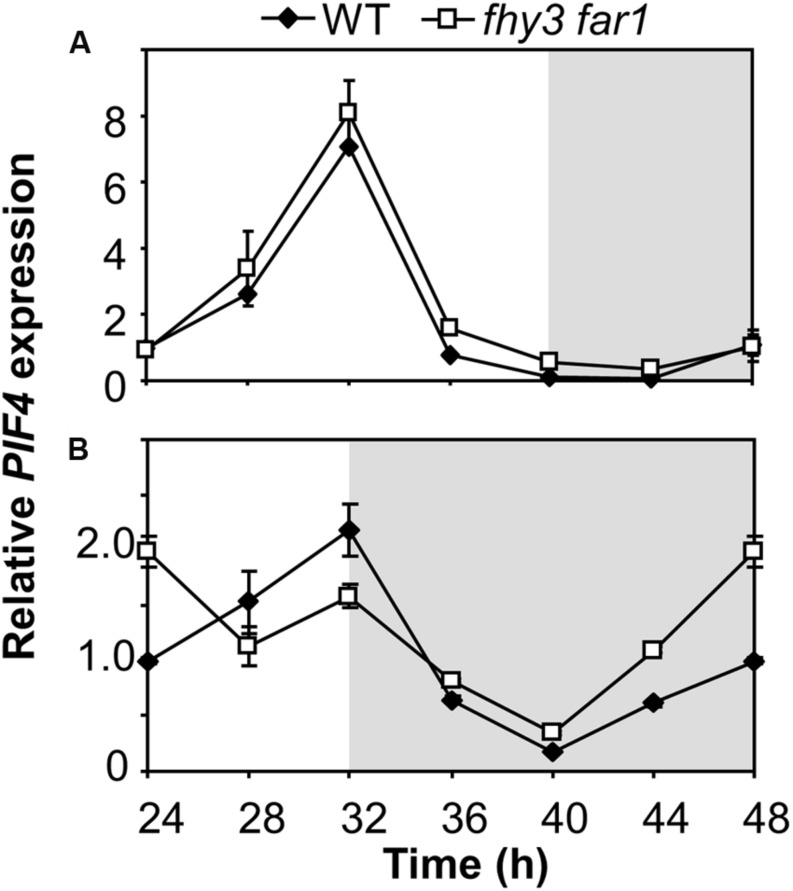
The mechanism of FHY3 and FAR1 action downstream of light stable phytochrome Pfr in buffering ELF4 expression following dusk in short days would be expected to have a knock-on effect on any ELF4 target genes. ELF4 mediates direct night-time repression of expression of PIF4 (Nusinow et al., 2011) and so we examined PIF4 expression patterns in WT and fhy3 far1 mutants in both longs and short days. We observed the expected cyclic pattern of PIF4 expression in both long and short days, with a PIF4 showing a peak of expression 8 h after dawn (Figure 7). PIF4 levels were almost identical in both WT and fhy3 far1 seedlings in long days (Figure 7A). However, we noted a significantly earlier rise in PIF4 expression prior to dawn specifically in fhy3 far1 seedlings grown in short days (Figure 7B) consistent with the observed early drop in ELF4 expression seen at dusk in these conditions (Figure 2C).
FIGURE 7.
Growth of fhy3 far1 mutant seedlings in short days reveals an early release of PIF4 repression. Expression of PIF4 relative to UBQ10 as measured by RT-qPCR in WT and fhy3 far1 seedlings grown in 12 h white light/12 h dark cycles for 1 week before transfer to either long days (16 h white light/8 h dark cycles; A); or short days (8 h white light/16 h dark cycles; B). Values shown represent mean expression normalized to UBQ10 for three replicates ± standard error.
Discussion
The transcription factors, FHY3 and FAR1, have been shown to play an important role in the clock in positively regulating transcription of the evening-phased ELF4 gene, an action that is required to maintain rhythmicity in constant light (Li et al., 2011). FHY3 and FAR1 have been shown to be key components of the phyA signaling pathway; hence, the assumption has been that they play a role in light input to the clock; however, this role had not yet been empirically proven. We set out to demonstrate the light dependency of FHY3 and FAR1 action in the upregulation of ELF4 expression. Our findings demonstrate clear light-dependent action of FHY3 and FAR1 in the regulation of ELF4, with FHY3 and FAR1 acting permissively. We show that FHY3 and FAR1 act directly via the fbs in red light to upregulate ELF4, specifically in the early part of the subjective night. Loss of ELF4 expression at this time has a knock on effect on downstream ELF4 target gene, PIF4. We demonstrate that this action of FHY3 and FAR1 is regulated in a red/far-red reversible manner by phyB, phyD and phyE. This can be at least in-part explained by our demonstration that FHY3 protein levels are also controlled in a red/far-red reversible manner. Most significantly, however, this represents the first demonstration of FHY3 and FAR1 as components of light stable phytochrome signaling pathways.
The permissive action of FHY3 and FAR1 in regulation of ELF4 expression (Figure 1A) is consistent with previous observations of permissive action of these two transcription factors (Hudson et al., 2003; Li et al., 2011). However, fhy3 or far1 monogenic mutants did show slightly greater ELF4 expression than the double mutant at light intensities above 10 μmol m–2 s–1. This is still dramatically lower than ELF4 expression in WT seedlings at higher light intensities suggesting that any action of FHY3 alone or FAR1 alone is minimal in this response and that a synergistic or cooperative action between the two transcription factors is required for correct function.
As part of our investigation, we hypothesized that this light responsive action of FHY3 and FAR1 upregulating ELF4 around dusk might form a means by which plants could track a later dusk in lengthening days during spring by delaying the peak of ELF4 expression under these conditions. We had speculated that this might allow the circadian clock to adapt to different day lengths. Conversely, we found that plants lacking FHY3 and FAR1 responded normally in terms of tracking dusk meaning that FHY3 and FAR1 are not involved in this aspect of light regulation of ELF4. However, we observed that, whereas WT seedlings displayed a sinusoidal decline in ELF4 expression following the dusk peak, the fhy3 far1 double mutant showed a sharp drop in ELF4 expression at dusk and this was particularly apparent under short day conditions. FHY3 and FAR1, therefore, act to buffer the ELF4 peak following dusk to maintain ELF4 expression into the early part of the night and this seems especially important in short days. In long days at dusk the expression of ELF4 will be beginning to be suppressed by the accumulating circadian clock components, CCA1 and LHY (Li et al., 2011), meaning that levels will fall rapidly even in WT seedlings in spite of any positive effect of FHY3 and FAR1 action. Thus, little effect of FHY3 and FAR1 deficiency would be expected in long days. However, in short days, dusk is reached prior to the commencement of accumulation of CCA1 and LHY meaning that, in WT, the positive effects of FHY3 and FAR1 would be expected to be much more apparent just after dusk.
End of day far red light treatment given to WT seedlings grown in short days was able to replicate the effect of FHY3 and FAR1 deficiency, in that WT seedlings treated with EODFR showed a loss of the sinusoidal pattern of the ELF4 expression peak. It is notable, though, that ELF4 expression in WT seedlings stopped rising and plateaued rather than dropping as it did in the fhy3 far1 mutant. This is consistent with the fact that EODFR treatment does not remove all light stable phytochrome Pfr. A small amount of Pfr is known to remain in broadband far red since Pr and Pfr have overlapping absorption spectra below 730 nm (Smith and Holmes, 1977). It is likely that this a small amount of Pfr signaling contributes to the maintenance of some promotion of ELF4 expression which would not be seen if the signaling pathway were knocked out completely due to mutation.
The action of FHY3 and FAR1 downstream of light stable phytochromes, phyB, phyD, and phyE raises the question of how light regulates the activity of these transcription factors. We have shown that FHY3 protein levels are regulated in a red/far-red reversible manner by the action of light stable phytochromes. There is no light or temporal regulation of FHY3 transcript (Li et al., 2011); thus, our observation of light stable phytochrome regulation of bioluminescence from an FHY3-LUC fusion protein means that there is a level of regulation of the FHY3 protein itself. It is important to note that the reaction of luciferase fusion reporter with its substrate, luciferin, inactivates the luciferase enzyme. The measured bioluminescence is, therefore, recording previously unreacted luciferase only. However, this does not necessarily mean that we are simply measuring light regulation of translation. It is quite possible that this could reflect different rates of turnover too. Significantly, the luciferase-luciferin reaction is not instantaneous. This is evidenced by the “pre-spray effect” observed when plants are sprayed 24 h prior to commencement of an imaging experiment as is standard practice to inactivate the previously accumulated luciferase. If imaged immediately after this pre-spray, plants give off extremely high levels of bioluminescence. It commonly takes over 12 h for the pre-spray to inactivate all of the previously produced luciferase in 5-day-old seedlings (Somers et al., 1998). The delay in reaction of newly synthesized luciferase means that there would be sufficient time for degradation effects to also have an impact on bioluminescence. It is likely that a rapid turnover of a luciferase-linked protein would lead a much lower level of luciferase bioluminescence being recorded during a 25 min imaging window, just as reduced production would. One possibility is, therefore, that the FHY3 protein is stabilized by light stable phytochrome action. This could only be definitively concluded by future generation and analysis of a 35S::FHY3-LUC line but this is a very common mechanism for the transmission of light signals, with a number of phytochrome signaling components being controlled in this way (Franklin and Quail, 2010). It has been demonstrated that there is a direct interaction between the FHY3 and FAR1 proteins and the phyA protein (Saijo et al., 2008) and so it would be important in the future to investigate whether other phytochromes also show such an interaction which might mediate this effect. Furthermore, it would be interesting to examine whether this might involve the COP1 protein which acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and directly targets a number of other light signaling transcription factors for degradation in darkness (Osterlund et al., 2000; Bauer et al., 2004; Yang et al., 2005). Indeed, both phyA and phyB have been shown to mediate the light-induced reduction of COP1 in Arabidopsis nuclei (Osterlund and Deng, 1998).
We also show that the sharp drop in ELF4 expression at dusk in short days in fhy3 far1 mutants precedes a subsequent aberrant repression of PIF4 in the later part of the night. PIF4, a direct negative target of ELF4, shows an earlier rise prior to dawn in fhy3 far1 mutants in short days. Higher PIF4 expression levels in the later part of the night following the lower ELF4 levels at the beginning of the night in fhy3 far1 mutants in short days is consistent with the proven role of ELF4 as a repressor of PIF4 expression during the subjective night (Nusinow et al., 2011).
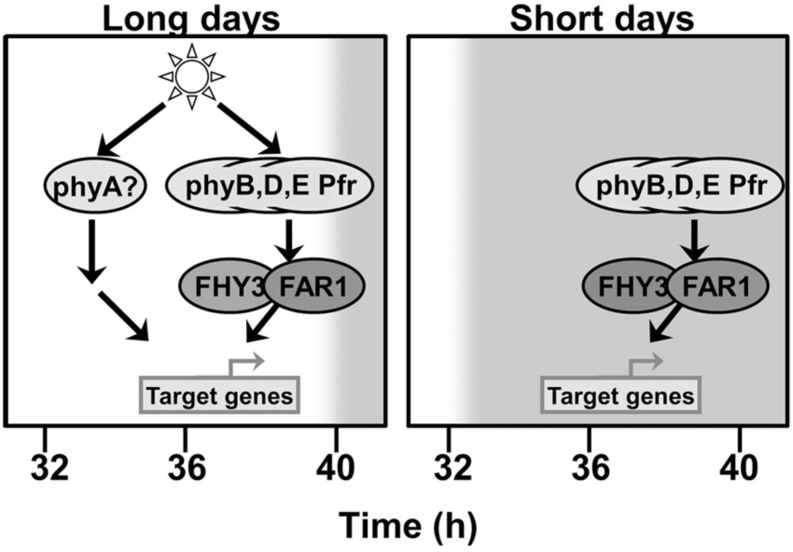
The fact that the deficiency in FHY3 and FAR1 is only observed to affect the pattern of expression of ELF4 following dusk suggests that another photoreceptor signaling pathway which does not require FHY3 and FAR1 is able to maintain ELF4 expression prior to this as long as light is incident on the plant. This maintenance of ELF4 expression until dusk is also observed under both red light/dark cycles and blue light/dark cycles. The action of continuous red light is strongly suggestive of phyA signaling as phyA Pfr is rapidly degraded and so ceases to function when illumination stops (Casal et al., 1998). PhyA also shows strong activity under blue wavelengths (Whitelam et al., 1993), suggesting that it may be the photoreceptor responsible for upregulation of ELF4 expression during illumination in both red and blue. Consistent with this, ELF4 expression has been previously shown to be phyA regulated (Tepperman et al., 2001). Figure 8 attempts to combine these proposals to a comprehensive scheme to explain the mechanisms of regulation of ELF4 expression by phytochromes and the role of FHY3 and FAR1 in both long and short days. The proposed continued action of phyA in an fhy3 far1 mutant does, of course, raise one additional issue, though. FHY3 and FAR1 are components of phyA signal transduction and, as a consequence, a number of phyA responses are severely impaired in the fhy3 or far1 monogenic mutants (Whitelam et al., 1993; Hudson et al., 1999). However, it has been shown that a number of phyA mediated physiological responses do not require FHY3 (Yanovsky et al., 2000). Similarly, the action of FHY3 and FAR1 in phyA signal transduction has been shown to be due to their action in promoting expression of FHY1 and FHL which facilitate nuclear entry of phyA Pfr (Lin et al., 2007) but other factors have also been shown to be capable of facilitating nuclear entry of phyA Pfr. PIF1 and PIF3 have been shown to mediate nuclear entry of a phyA N-terminal fragment in a cell-free system (Pfeiffer et al., 2012) and, consistent with this, several other phyA dependent nuclear responses have been observed in an fhy1 fhl mutant (Kami et al., 2012; Klose et al., 2015).
FIGURE 8.
FHY3 and FAR1 act downstream of phyB, phyD, and phyE Pfr to maintain ELF4 expression into the early part of the night following a short day. An additional pathway acts to compensate for the loss of FHY3 and FAR1 at this same time in long days. This additional pathway can be activated by either red or blue light but is triggered only in the continued presence of light, suggesting the involvement of phyA as a photoreceptor.
Our demonstration here that FHY3 and FAR1 act as signaling components downstream of light stable phytochromes also raises some interesting points for the field of photomorphogenesis research. Our findings reveal that, by acquiring phytochrome responsivity, the evolution of FHY3 and FAR1 from transposases has involved two steps in a relatively short space of time. They have not simply acquired roles as constitutive activators of transcription needed for phyA function, but they have also acquired active roles as part of the signal transduction pathway itself downstream of light stable phytochromes. In addition, the findings raise a question as to whether this activity may mean that FHY3 and FAR1 have an important role in de-etiolation responses downstream of light stable phytochromes. We demonstrated a link between FHY3/FAR1 and PIF4, an important player in de-etiolation, while the potential role of COP1 in regulation of FHY3 protein stability also warrants further investigation, not least because of the important role of COP1 in de-etiolation. Such a role for COP1 would make its role even more complex and nuanced in the control of de-etiolation. Some effect of FHY3 and FAR1 on gene expression in darkness has actually been observed previously too. Hudson et al. (2003) showed altered gene expression in fhy3 and far1 mutants germinated in darkness. This raises the question as to whether this may be explained as light stable phytochrome Pfr in the seed activating FHY3 and FAR1 to trigger the activation of these gene targets. Light stable phytochrome Pfr is known to be contained even within dry seed and can have significant effects on germination. Furthermore, it is common to use a pulse of white light to synchronize germination 24 h prior to assays of phytochrome responses. It has been observed that such pre-treatment of seeds has a significant effect on subsequent gene expression responses (Leivar et al., 2008). It may be that this action involves activation of FHY3 and FAR1 as well as PIFs as demonstrated by those authors. Not least, such activation of FHY3 and FAR1 would be expected to trigger FHY1 and FHL production so as to allow phyA signaling. Consistent with this, treatment of seeds with a white light pulse 24 h prior to transfer to far red light, greatly enhances subsequent phyA signaling effects in promoting germination (Devlin et al., 1995).
Conclusion
We show here that FHY3 and FAR1, originally identified as phyA signaling components, additionally act downstream of light stable phytochromes to promote ELF4 expression in a light dependent manner. FHY3 and FAR1 are essential for phyB, phyD, and phyE Pfr action in maintenance of a normal expression pattern of ELF4 following dusk in short days. However, one final whimsical thought occurs to the authors. Given the fact that the action of FHY3 and FAR1 in phyA signaling is due to their action as transcription factors to upregulate FHY1 and FHL, it could be said that this does not represent a direct role for FHY3 and FAR1 in phyA signaling itself, but, rather, an indirect role. In contrast, what we show here could be considered as the first evidence of their direct action as part of a light signaling pathway, in which case it might even be valid to reassign FHY3 and FAR1 as exclusively light stable phytochrome signaling components.
Author Contributions
PD and HS contributed to project design. HS and SK carried out the bioluminescence analyses of the LUC reporter lines. HS, SK, and BR carried out the qRT-PCR assays. HS and PD wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Haiyang Wang (Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) for the reporter lines used and Karen Halliday (University of Edinburgh) for the phytochrome mutant lines. We also thank the reviewers for insightful comments in production of the final manuscript.
Footnotes
Funding. This work was supported by a grant from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBF02116X1) to PD.
References
- Bauer D., Viczian A., Kircher S., Nobis T., Nitschke R., Kunkel T., et al. (2004). Constitutive photomorphogenesis 1 and multiple photoreceptors control degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3, a transcription factor required for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16 1433–1445. 10.1105/tpc.021568 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal J. J., Sánchez R. A., Botto J. F. (1998). Modes of action of phytochromes. J. Exp. Bot. 49 127–138. 10.1093/jxb/49.319.127 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin P. F., Halliday K. J., Whitelam G. C. (1995). “The phytochrome family and their role in the regulation of seed germination,” in Basic and Applied Aspects of Seed Biology, eds Ellis R. H., Black M., Murdoch A. J., Hong T. D. (Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; ), 159–171. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin P. F., Patel S. R., Whitelam G. C. (1998). Phytochrome E influences internode elongation and flowering time in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10 1479–1487. 10.1105/tpc.10.9.1479 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin P. F., Robson P. R., Patel S. R., Goosey L., Sharrock R. A., Whitelam G. C. (1999). Phytochrome D acts in the shade-avoidance syndrome in Arabidopsis by controlling elongation growth and flowering time. Plant Physiol. 119 909–915. 10.1104/pp.119.3.909 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin K. A., Allen T., Whitelam G. C. (2007). Phytochrome A is an irradiance-dependent red light sensor. Plant J. 50 108–117. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03036.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin K. A., Quail P. H. (2010). Phytochrome functions in Arabidopsis development. J. Exp. Bot. 61 11–24. 10.1093/jxb/erp304 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig L., Poppe C., Unger S., Schafer E. (1999). Control of hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana by photoreceptor interaction. Planta 208 257–263. 10.1007/s004250050557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X., Ouyang X., Yang P., Lau O. S., Li G., Li J., et al. (2012). Arabidopsis FHY3 and HY5 positively mediate induction of COP1 transcription in response to photomorphogenic UV-B light. Plant Cell 24 4590–4606. 10.1105/tpc.112.103994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson M., Ringli C., Boylan M. T., Quail P. H. (1999). The FAR1 locus encodes a novel nuclear protein specific to phytochrome A signaling. Genes Dev. 13 2017–2027. 10.1101/gad.13.15.2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson M. E., Lisch D. R., Quail P. H. (2003). The FHY3 and FAR1 genes encode transposase-related proteins involved in regulation of gene expression by the phytochrome A-signaling pathway. Plant J. 34 453–471. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01741.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kami C., Hersch M., Trevisan M., Genoud T., Hiltbrunner A., Bergmann S., et al. (2012). Nuclear phytochrome A signaling promotes phototropism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24 566–576. 10.1105/tpc.111.095083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klose C., Viczian A., Kircher S., Schafer E., Nagy F. (2015). Molecular mechanisms for mediating light-dependent nucleo/cytoplasmic partitioning of phytochrome photoreceptors. New Phytol. 206 965–971. 10.1111/nph.13207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koornneef M., Rolff E., Spruit C. J. P. (1980). Genetic control of light-inhibited hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana L. Heynh. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 100 147–160. 10.1016/S0044-328X(80)80208-X [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Leivar P., Monte E., Oka Y., Liu T., Carle C., Castillon A., et al. (2008). Multiple phytochrome-interacting bHLH transcription factors repress premature seedling photomorphogenesis in darkness. Curr. Biol. 18 1815–1823. 10.1016/j.cub.2008.10.058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Siddiqui H., Teng Y., Lin R., Wan X. Y., Li J., et al. (2011). Coordinated transcriptional regulation underlying the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Nat. Cell Biol. 13 616–622. 10.1038/ncb2219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R., Ding L., Casola C., Ripoll D. R., Feschotte C., Wang H. (2007). Transposase-derived transcription factors regulate light signaling in Arabidopsis. Science 318 1302–1305. 10.1126/science.1146281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R., Wang H. (2004). Arabidopsis FHY3/FAR1 gene family and distinct roles of its members in light control of Arabidopsis development. Plant Physiol. 136 4010–4022. 10.1104/pp.104.052191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusinow D. A., Helfer A., Hamilton E. E., King J. J., Imaizumi T., Schultz T. F., et al. (2011). The ELF4-ELF3-LUX complex links the circadian clock to diurnal control of hypocotyl growth. Nature 475 398–402. 10.1038/nature10182 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterlund M. T., Deng X. W. (1998). Multiple photoreceptors mediate the light-induced reduction of GUS-COP1 from Arabidopsis hypocotyl nuclei. Plant J. 16 201–208. 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00290.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterlund M. T., Hardtke C. S., Wei N., Deng X. W. (2000). Targeted destabilization of HY5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature 405 462–466. 10.1038/35013076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang X., Li J., Li G., Li B., Chen B., Shen H., et al. (2011). Genome-wide binding site analysis of FAR-RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL3 reveals its novel function in Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 23 2514–2535. 10.1105/tpc.111.085126 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer A., Nagel M. K., Popp C., Wust F., Bindics J., Viczian A., et al. (2012). Interaction with plant transcription factors can mediate nuclear import of phytochrome B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 5892–5897. 10.1073/pnas.1120764109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockwell N. C., Su Y. S., Lagarias J. C. (2006). Phytochrome structure and signaling mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 57 837–858. 10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saijo Y., Zhu D., Li J., Rubio V., Zhou Z., Shen Y., et al. (2008). Arabidopsis COP1/SPA1 complex and FHY1/FHY3 associate with distinct phosphorylated forms of phytochrome A in balancing light signaling. Mol. Cell 31 607–613. 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock R. A., Clack T. (2002). Patterns of expression and normalized levels of the five Arabidopsis phytochromes. Plant Physiol. 130 442–456. 10.1104/pp.005389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., Holmes M. G. (1977). The function of phytochrome in the natural environment III. Measurement and calculation of phytochrome photoequilibria. Photochem. Photobiol. 25 547–550. 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb09126.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Somers D. E., Devlin P. F., Kay S. A. (1998). Phytochromes and cryptochromes in the entrainment of the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science 282 1488–1490. 10.1126/science.282.5393.1488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepperman J. M., Zhu T., Chang H. S., Wang X., Quail P. H. (2001). Multiple transcription-factor genes are early targets of phytochrome A signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 9437–9442. 10.1073/pnas.161300998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Deng X. W. (2002). Arabidopsis FHY3 defines a key phytochrome A signaling component directly interacting with its homologous partner FAR1. EMBO J. 21 1339–1349. 10.1093/emboj/21.6.1339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Roig-Villanova I., Khan S., Shanahan H., Quail P. H., Martinez-Garcia J. F., et al. (2011). A novel high-throughput in vivo molecular screen for shade avoidance mutants identifies a novel phyA mutation. J. Exp. Bot. 62 2973–2987. 10.1093/jxb/err062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Wang H. (2015). Multifaceted roles of FHY3 and FAR1 in light signaling and beyond. Trends Plant Sci. 20 453–461. 10.1016/j.tplants.2015.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Tang W., Ma T., Niu D., Jin J. B., Wang H., et al. (2016). A pair of light signaling factors FHY3 and FAR1 regulates plant immunity by modulating chlorophyll biosynthesis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 58 91–103. 10.1111/jipb.12369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelam G. C., Johnson E., Peng J., Carol P., Anderson M. L., Cowl J. S., et al. (1993). Phytochrome A null mutants of Arabidopsis display a wild– type phenotype in white light. Plant Cell 5 757–768. 10.2307/3869613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Lin R., Sullivan J., Hoecker U., Liu B., Xu L., et al. (2005). Light regulates COP1-mediated degradation of HFR1, a transcription factor essential for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17 804–821. 10.1105/tpc.104.030205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanovsky M. J., Whitelam G. C., Casal J. J. (2000). fhy3-1 retains inductive responses of phytochrome A. Plant Physiol. 123 235–242. 10.1104/pp.123.1.235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]