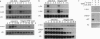Abstract
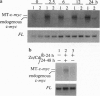
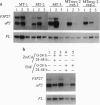
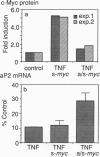
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibits and reverses differentiation of mouse adipogenic TA1 cells. We have found that TNF induces c-myc in a sustained manner in both preadipocytes and adipocytes; in contrast, serum induces c-myc transiently and only in preadipocytes. This TNF-mediated c-myc induction is not coupled with cell proliferation but is correlated with TNF-mediated inhibition of adipocyte differentiation. We prepared an inducible c-myc transformant of TA1 cells by transfection of the mouse c-myc gene under the control of the metallothionein-I promoter. These cells are unable to differentiate to adipocytes in the presence of Zn2+/Cd2+, and in differentiated TA1 cells, Zn2+/Cd2+ causes reduction of adipocyte-specific gene expression as does TNF. Lastly, exposure of TA1 cells to antisense c-myc oligonucleotide partially blocked the TNF-mediated reduction of adipocyte-specific gene expression. Thus, TNF-mediated c-myc expression is distinct in character from that involved in mitogenic responses but appears to play an important role in inhibition and reversal of adipocyte differentiation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard O., Cory S., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Adams J. M. Sequence of the murine and human cellular myc oncogenes and two modes of myc transcription resulting from chromosome translocation in B lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Kretzner L., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max function as a nucleoprotein complex. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. B., Knight D. M., Dieckmann B. S., Ringold G. M. Analysis of gene expression during differentiation of adipogenic cells in culture and hormonal control of the developmental program. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15548–15555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Kaestner K. H., Geiman D. E., Lane M. D. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein gene promoter: binding of nuclear factors during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danesch U., Hoeck W., Ringold G. M. Cloning and transcriptional regulation of a novel adipocyte-specific gene, FSP27. CAAT-enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) and C/EBP-like proteins interact with sequences required for differentiation-dependent expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7185–7193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O. Enforced expression of the c-myc oncogene inhibits cell differentiation by precluding entry into a distinct predifferentiation state in G0/G1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1614–1624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Geddes T. J. Reciprocal regulation of adipogenesis by Myc and C/EBP alpha. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haliday E. M., Ramesha C. S., Ringold G. TNF induces c-fos via a novel pathway requiring conversion of arachidonic acid to a lipoxygenase metabolite. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):109–115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel P. A., Gill R. M., Phillips R. A., Gallie B. L. Transcriptional repression of the E2-containing promoters EIIaE, c-myc, and RB1 by the product of the RB1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3431–3438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Redner R. L., Nienhuis A. W. An oligomer complementary to c-myc mRNA inhibits proliferation of HL-60 promyelocytic cells and induces differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):963–973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 cause a rapid and transient stimulation of c-fos and c-myc mRNA levels in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11908–11911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., McGehee R. E., Jr, Habener J. F. Tumor necrosis factor-induced reversal of adipocytic phenotype of 3T3-L1 cells is preceded by a loss of nuclear CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP). J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):223–233. doi: 10.1172/JCI115566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Cleveland J. L., Shurtleff S. A., Sherr C. J. Myc rescue of a mutant CSF-1 receptor impaired in mitogenic signalling. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):361–363. doi: 10.1038/353361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson L., Strömberg K., Vikman K., Bjursell G., Enerbäck S. The CCAAT/enhancer binding protein and its role in adipocyte differentiation: evidence for direct involvement in terminal adipocyte development. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3787–3793. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Berkovic D., Tomsing O., Unger C., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor induces rapid production of 1'2'diacylglycerol by a phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):975–988. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya H., Yoneyama M., Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Matsumoto K., Taniguchi T. IL-2 and EGF receptors stimulate the hematopoietic cell cycle via different signaling pathways: demonstration of a novel role for c-myc. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90533-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. M., Pekala P. H. Transcriptional repression of the C/EBP-alpha and GLUT4 genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Regulations is coordinate and independent of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13580–13584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. M., Pekala P. H. Transcriptional repression of the GLUT4 and C/EBP genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21839–21845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Torti S. V., Larrick J. W., Ringold G. M. Modulation of adipocyte differentiation by tumor necrosis factor and transforming growth factor beta. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):1105–1113. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji Y., Miller L. L., Miller S. C., Torti S. V., Torti F. M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1-alpha regulate transferrin receptor in human diploid fibroblasts. Relationship to the induction of ferritin heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7257–7261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji Y., Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Torti S. V., Torti F. M. Augmentation by IL-1 alpha of tumor necrosis factor-alpha cytotoxicity in cells transfected with adenovirus E1A. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):1897–1907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein: a component of a differentiation switch. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):288–292. doi: 10.1126/science.1987644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. M., Chang D. J., Danesch U., Ringold G. M., Heller R. A. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein expression is rapidly extinguished in TA1 adipocyte cells treated with tumor necrosis factor. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jul;6(7):1135–1141. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.7.1508226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]